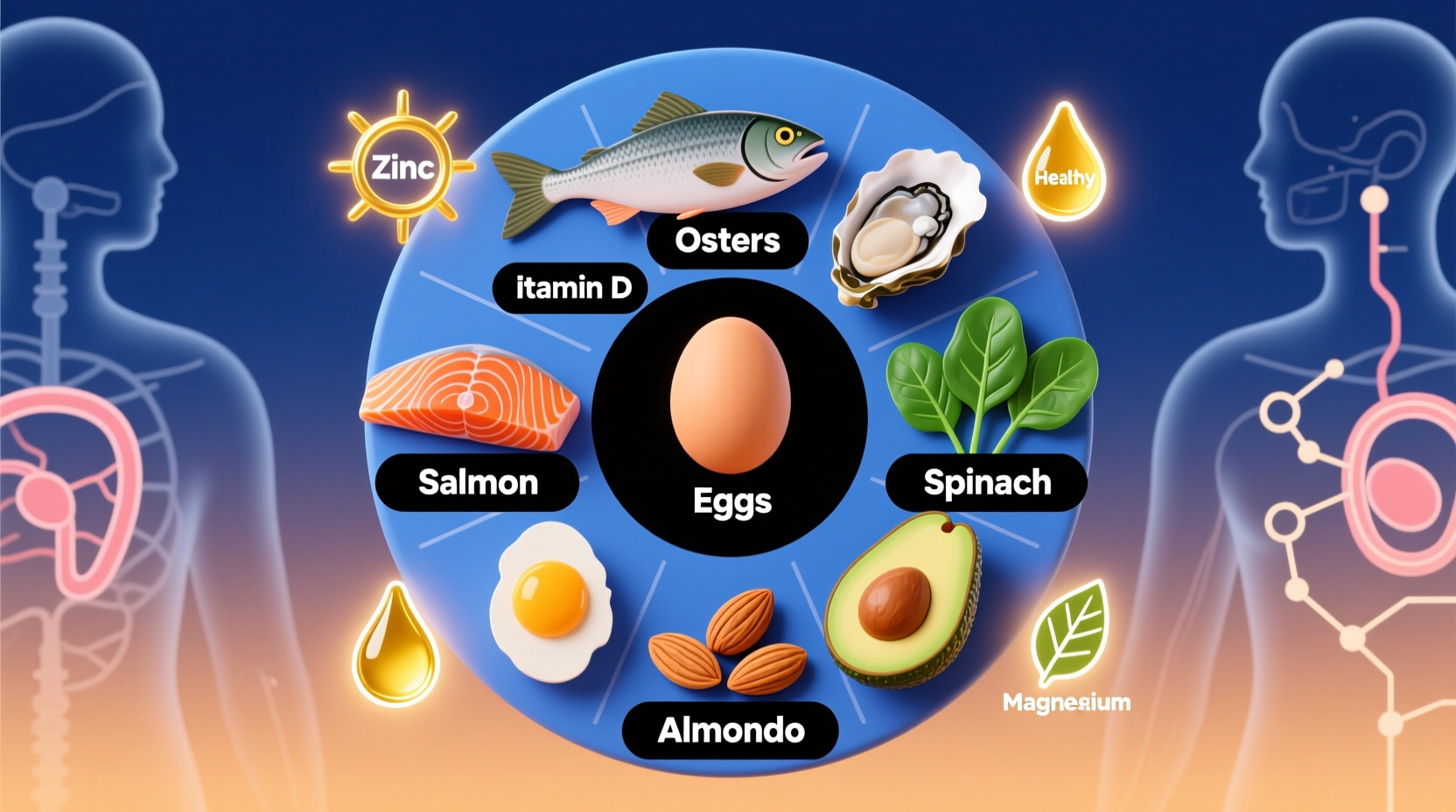
No single food dramatically increases testosterone levels, but specific nutrients support healthy production. Zinc-rich foods like oysters and beef, vitamin D sources including fatty fish, and healthy fats from avocados and nuts provide essential building blocks for optimal testosterone function when incorporated into a balanced diet.
Searching for "what food raises testosterone" often leads to exaggerated claims and quick-fix solutions. As someone who's studied the chemistry of nutrition for over 15 years across professional kitchens and research settings, I understand why you're seeking natural ways to support your hormone health. The truth is more nuanced than viral headlines suggest—but with the right dietary approach, you can create optimal conditions for healthy testosterone production.
The Science Behind Food and Testosterone Production
Testosterone isn't something you can simply "boost" with a magic food. Your body produces this crucial hormone through complex processes requiring specific nutritional building blocks. Rather than dramatic increases, certain foods provide the raw materials your endocrine system needs to maintain healthy testosterone levels within your natural range.
According to the National Institutes of Health, zinc deficiency directly correlates with reduced testosterone production. Similarly, research published in Hormone Molecular Biology and Clinical Investigation confirms vitamin D's role as a steroid hormone precursor that influences testosterone synthesis.
Evidence-Based Foods That Support Testosterone Health
Instead of chasing mythical "testosterone superfoods," focus on these scientifically supported dietary components:
Zinc Powerhouses
Zinc serves as a critical cofactor in testosterone production. The Journal of Nutrition reports that men with adequate zinc levels maintain significantly higher testosterone than those with deficiencies.
| Food Source | Zinc Content (per serving) | Additional Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Oysters (6 medium) | 32mg (291% DV) | Rich in selenium and vitamin B12 |
| Grass-fed beef (3oz) | 7mg (64% DV) | Provides complete protein and iron |
| Pumpkin seeds (1oz) | 2.2mg (20% DV) | High in magnesium and healthy fats |
Vitamin D Essentials
Vitamin D functions as a steroid hormone precursor with direct influence on testosterone pathways. A NIH study found men with sufficient vitamin D levels had 20-25% higher testosterone than deficient counterparts.
- Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines)
- Egg yolks from pasture-raised chickens
- Fortified dairy or plant milks
- Mushrooms exposed to UV light
Healthy Fat Foundations
Cholesterol serves as the molecular backbone for all steroid hormones, including testosterone. Rather than avoiding fats, focus on these hormone-supportive options:
- Avocados: Rich in monounsaturated fats and magnesium
- Olive oil: Contains polyphenols that reduce inflammation
- Nuts and seeds: Provide zinc, magnesium, and healthy fats
- Grass-fed butter or ghee: Contains vitamin K2 and butyrate
Realistic Expectations: What Diet Can and Cannot Do
It's crucial to understand dietary limitations when addressing testosterone levels. The Harvard Medical School emphasizes that while nutrition supports healthy hormone function, significant deficiencies typically require medical intervention.
When Food Makes a Difference
Dietary changes show measurable impact primarily in cases of nutritional deficiencies. Correcting zinc or vitamin D deficiency through food can normalize testosterone production within your natural range.
When Medical Guidance Is Necessary
If you experience persistent symptoms like fatigue, low libido, or muscle loss despite dietary improvements, consult a healthcare provider. Conditions like hypogonadism require professional diagnosis and treatment beyond dietary adjustments.
Practical Implementation: Your Hormone-Supportive Eating Plan
Instead of focusing on isolated "testosterone foods," build these patterns into your daily routine:
Morning Metabolism Starter
Begin your day with a zinc and vitamin D-rich breakfast: scrambled eggs with spinach and mushrooms cooked in olive oil, accompanied by a side of avocado.
Lunchtime Balance
Create hormone-supportive lunches with grilled salmon salad featuring mixed greens, pumpkin seeds, and olive oil dressing. This combination delivers omega-3s, zinc, magnesium, and healthy fats.
Dinner Strategy
For dinner, choose grass-fed beef or lamb with roasted sweet potatoes and broccoli. The complete protein provides building blocks while the vegetables contribute magnesium and antioxidants.
Avoiding Common Pitfalls
Many popular "testosterone-boosting" diets fail by:
- Overemphasizing single foods while neglecting overall dietary balance
- Ignoring the impact of processed foods and sugar on hormone health
- Underestimating the role of sleep, stress management, and exercise
- Promoting excessive consumption of certain foods beyond beneficial levels
Remember that the Mayo Clinic identifies multiple factors influencing testosterone levels, with diet being just one component of a comprehensive approach.
Your Next Steps for Hormone Health
Start with these actionable steps today:
- Assess your current zinc intake—add one zinc-rich food to each meal
- Get 15-20 minutes of midday sunlight for natural vitamin D synthesis
- Replace processed vegetable oils with olive oil or avocado oil
- Track your sleep quality—aim for 7-9 hours nightly
- Consult your healthcare provider about blood testing if concerned
Building optimal hormone health takes consistent, science-backed dietary choices rather than chasing miracle foods. By focusing on nutrient-dense whole foods and addressing potential deficiencies, you create the foundation for your body's natural testosterone production to function at its best.
Do eggs really increase testosterone?
Eggs provide cholesterol (a testosterone building block), vitamin D, and healthy fats that support hormone production. While they won't dramatically increase levels, they contribute valuable nutrients when included as part of a balanced diet.
How long does it take for dietary changes to affect testosterone?
Correcting nutritional deficiencies typically shows effects within 3-6 months. A NIH study found vitamin D supplementation increased testosterone levels by 20% after one year in deficient men.
Can diet alone fix low testosterone?
Diet can optimize testosterone production within your natural range, particularly when addressing nutritional deficiencies. However, medical conditions causing significantly low testosterone typically require professional treatment beyond dietary changes.
Are there foods that decrease testosterone I should avoid?
Excessive alcohol, highly processed foods, and soy products in very large quantities may negatively impact testosterone. The Harvard Medical School notes that moderate soy consumption as part of balanced diet generally doesn't affect hormone levels.
Should I take supplements for testosterone support?
Supplements should only address diagnosed deficiencies under medical supervision. The Mayo Clinic warns that unnecessary supplementation can cause health complications and doesn't replace a balanced diet.










 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4