Ever wonder if that leftover steak or roast in your fridge has reached its expiration date? You're not alone. According to the USDA Food Safety and Inspection Service, improper handling of cooked meats causes millions of foodborne illness cases annually. Getting storage times right isn't just about avoiding waste—it's critical for your health and safety.
Refrigeration Guidelines: The 3-4 Day Rule
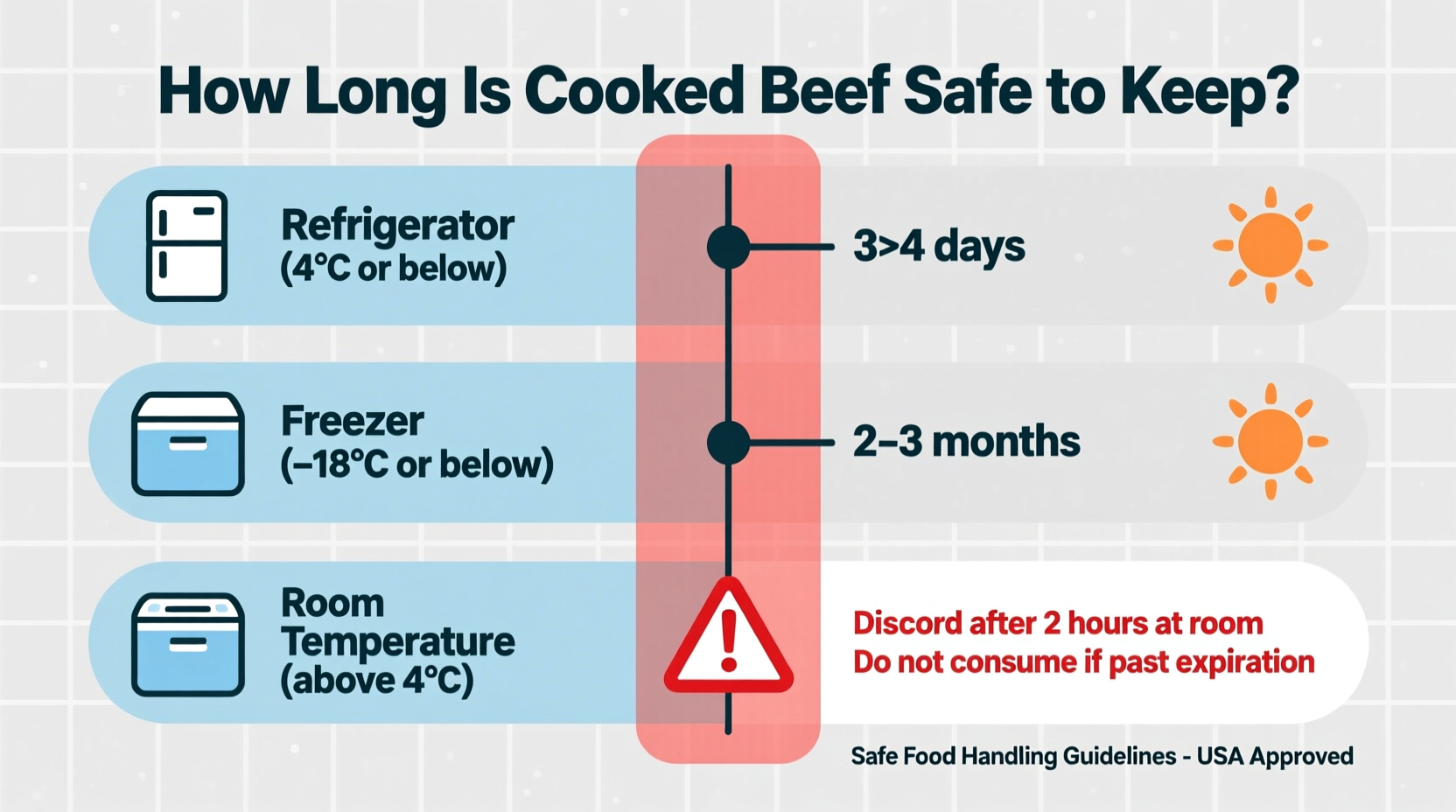
When stored in airtight containers at or below 40°F (4°C), cooked beef maintains both safety and quality for 3-4 days. This timeframe isn't arbitrary—it's based on bacterial growth rates at standard refrigerator temperatures.
The USDA Food Safety and Inspection Service emphasizes that the "danger zone" for bacterial growth spans 40°F to 140°F (4°C to 60°C). Within this range, pathogens like Staphylococcus aureus and Clostridium perfringens can double in number every 20 minutes.
| Storage Method | Maximum Safe Duration | Quality Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Refrigerator (40°F or below) | 3-4 days | Texture and flavor begin deteriorating after day 3 |
| Freezer (0°F or below) | 2-6 months | Fat content affects freezer burn resistance |
| Room Temperature | 2 hours (1 hour if above 90°F) | Enters food safety danger zone immediately |
Critical Factors That Affect Cooked Beef Shelf Life
Not all cooked beef lasts equally long. Several factors influence how quickly your leftovers become unsafe:
- Fat content: Higher-fat cuts like ribeye develop rancidity faster than leaner cuts like sirloin
- Cooking method: Slow-cooked beef has reduced moisture, potentially extending shelf life slightly
- Initial handling: Beef left at room temperature for more than 2 hours before refrigeration has already begun bacterial growth
- Storage container: Airtight containers prevent cross-contamination and moisture loss
Freezer Storage: Maximizing Long-Term Safety
When freezing cooked beef, proper packaging is essential for maintaining both safety and quality. The FDA recommends using freezer-safe containers or heavy-duty freezer bags to prevent freezer burn.
According to the FDA's freezing guidelines, properly packaged cooked beef remains safe indefinitely at 0°F (-18°C), though quality diminishes over time. For best results:
- Remove as much air as possible from packaging
- Label containers with cooking date
- Portion into single-serving sizes before freezing
- Use within 2-3 months for ground beef, 4-6 months for roasts and steaks
How to Spot Spoiled Cooked Beef: Beyond the Clock
While time-based guidelines are crucial, your senses provide the final safety check. Discard cooked beef showing any of these warning signs:
- Visual changes: Grayish or slimy appearance, especially if accompanied by discoloration
- Texture: Unusual sliminess or stickiness when touched
- Smell: Sour, ammonia-like, or otherwise unpleasant odors
- Taste: Never taste to check safety—if you suspect spoilage, discard immediately

Safe Reheating Practices for Leftover Beef
Proper reheating is as important as proper storage. The USDA requires that reheated cooked beef reach an internal temperature of 165°F (74°C) to ensure food safety. Use these methods for best results:
- Stovetop: Reheat in a covered skillet with a small amount of liquid to prevent drying
- Oven: Cover with foil and heat at 325°F (163°C) until properly heated through
- Microwave: Stir occasionally and check temperature in multiple spots
Never partially reheat and then refrigerate leftovers—this creates ideal conditions for bacterial growth.
Common Leftover Mistakes That Compromise Safety
Even when following time guidelines, these common errors can make your cooked beef unsafe:
- Overfilling the refrigerator: Crowded conditions prevent proper air circulation and cooling
- Using improper containers: Thin plastic containers may warp and create gaps allowing air exposure
- Ignoring temperature: Refrigerators should maintain 40°F (4°C) or below—use a thermometer to verify
- Reheating multiple times: Each cooling and reheating cycle increases bacterial growth opportunities
Special Considerations for Different Beef Preparations
Certain cooked beef preparations have unique storage considerations:
- Beef in sauce: Acidic sauces (tomato-based) may extend shelf life slightly
- Marinated beef: Acidic marinades can begin to break down proteins over time
- Ground beef: Has shorter shelf life (2-3 days) due to increased surface area
- Smoked beef: Properly smoked and stored beef may last longer but still follow standard guidelines
Food Safety Timeline: What Happens to Cooked Beef Over Time
Understanding the science behind spoilage helps make informed decisions:
- 0-2 hours: Safe at room temperature; bacteria begin multiplying slowly
- 2-4 hours: Enters danger zone; bacterial growth accelerates exponentially
- Day 1-2: Peak quality and safety; minimal bacterial growth if properly refrigerated
- Day 3-4: Quality begins declining; safety margin narrows significantly
- Day 5+: High risk of spoilage organisms and potential pathogens
This timeline, verified by CDC food safety research, explains why the 3-4 day guideline exists—it represents the point where safety margins become unacceptably narrow for most consumers.
When in Doubt, Throw It Out: The Golden Rule of Food Safety
No guideline can replace careful observation and judgment. If you're uncertain about the safety of your cooked beef, discard it. Foodborne illness can cause severe health complications, particularly for vulnerable populations including young children, older adults, pregnant women, and immunocompromised individuals.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I eat cooked beef after 5 days in the refrigerator?
No, cooked beef should not be consumed after 5 days in the refrigerator. The USDA recommends discarding cooked beef after 3-4 days even when properly refrigerated at 40°F (4°C) or below due to increased risk of foodborne illness.
How can I tell if cooked beef has gone bad?
Spoiled cooked beef typically shows visible changes like grayish discoloration, develops a slimy texture, emits sour or ammonia-like odors, and may have visible mold. When in doubt about cooked beef safety, follow the golden rule: when uncertain, throw it out.
Does freezing cooked beef kill bacteria?
Freezing does not kill bacteria but significantly slows their growth. When properly frozen at 0°F (-18°C) or below, bacteria become dormant but will reactivate upon thawing. This is why proper handling after thawing remains critical for food safety.
What's the best way to thaw frozen cooked beef?
The safest thawing methods are: 1) in the refrigerator (takes 24-48 hours), 2) in cold water (changing water every 30 minutes), or 3) using the microwave's defrost setting. Never thaw cooked beef at room temperature, as this allows the outer layers to enter the food safety danger zone while the center remains frozen.
Can I refreeze cooked beef after thawing?
Yes, you can refreeze cooked beef if it was thawed in the refrigerator and has not been left at room temperature for more than 2 hours. However, each freeze-thaw cycle affects texture and quality, so refreezing is best avoided when possible for optimal eating experience.










 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4