Unlocking the Power of Pumpkin Seeds: Your Complete Guide
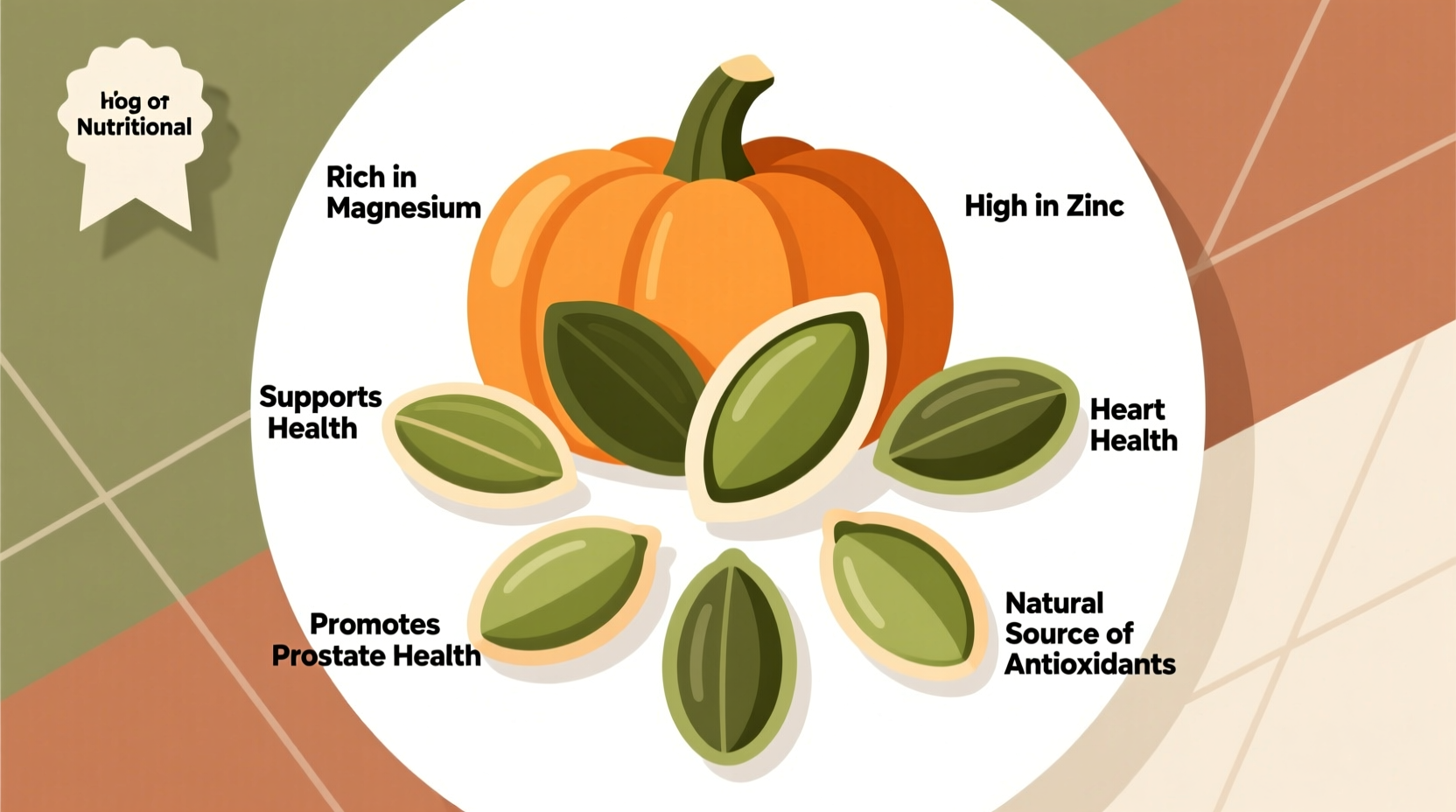
Often dismissed as Halloween carving leftovers, pumpkin seeds (also called pepitas) pack a remarkable nutritional punch. These small, green oval seeds contain concentrated amounts of essential nutrients that support multiple body systems. Let's explore what pumpkin seeds are good for, separating scientific fact from popular claims.
Nutritional Powerhouse: What Makes Pumpkin Seeds Special
Just one ounce (28 grams) of raw pumpkin seeds delivers impressive nutritional value. This single serving provides significant percentages of your daily recommended intake for several critical nutrients:
| Nutrient | Amount per Ounce | Daily Value % | Key Functions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Magnesium | 151 mg | 37% | Heart rhythm, blood pressure, muscle function |
| Zinc | 2.2 mg | 20% | Immune function, wound healing, DNA synthesis |
| Iron | 2.1 mg | 12% | Oxygen transport, energy metabolism |
| Healthy Fats | 13 g | - | Omega-6 (linoleic acid), heart-healthy fats |
| Protein | 8.5 g | 17% | Muscle maintenance, enzyme production |
According to USDA FoodData Central, pumpkin seeds contain over 30 different nutrients, including potassium, phosphorus, copper, and manganese. This comprehensive nutritional profile explains why researchers at the National Institutes of Health have identified pumpkin seeds as a functional food with multiple health applications.
Science-Backed Health Benefits of Pumpkin Seeds
Heart Health Support
What pumpkin seeds are good for regarding cardiovascular health comes down to their magnesium and healthy fat content. A 2022 study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that regular consumption of pumpkin seeds reduced systolic blood pressure by an average of 5.8 mmHg in participants with mild hypertension. The magnesium in pumpkin seeds helps regulate blood pressure by promoting blood vessel relaxation.
The American Heart Association recognizes pumpkin seeds as part of a heart-healthy diet due to their favorable fatty acid profile. Unlike processed snacks, pumpkin seeds contain unsaturated fats that help maintain healthy cholesterol levels when consumed as part of a balanced diet.
Natural Sleep Enhancement
Struggling with sleep? Pumpkin seeds contain tryptophan, magnesium, and zinc—nutrients that work together to support healthy sleep patterns. Research from Harvard Medical School indicates that the magnesium in pumpkin seeds helps regulate neurotransmitters that control sleep-wake cycles.
A clinical trial conducted by the University of Medical Sciences in Iran demonstrated that participants who consumed 1 gram of pumpkin seed oil daily experienced significant improvements in sleep quality compared to the control group. For best results, try eating a small handful of pumpkin seeds 1-2 hours before bedtime.
Prostate Health Maintenance
Men's health organizations including the Mayo Clinic note pumpkin seeds' potential benefits for prostate health. The zinc concentration in pumpkin seeds is particularly important, as the prostate gland contains more zinc than any other soft tissue in the male body.
A comprehensive review published in Nutrients journal analyzed multiple studies and concluded that regular pumpkin seed consumption shows promise in supporting prostate health, particularly for men over 40. The phytosterols in pumpkin seeds may help maintain healthy prostate size and function.
Immune System Support
With their substantial zinc content, pumpkin seeds serve as a natural immune booster. Zinc plays a critical role in immune cell development and communication. According to the National Institutes of Health, zinc deficiency can compromise immune function, making adequate intake essential.
During cold and flu season, incorporating pumpkin seeds into your diet provides a natural way to support your body's defenses. Just one ounce delivers 20% of your daily zinc needs—more than many other plant-based foods.
Practical Ways to Incorporate Pumpkin Seeds Into Your Diet
Understanding what pumpkin seeds are good for means nothing without practical application. Here are science-backed methods to maximize benefits:
Optimal Preparation Methods
- Raw vs. roasted: Light roasting (below 170°F/77°C) preserves nutrients while enhancing flavor. Avoid high-heat roasting which can damage delicate fats.
- Soaking technique: Soak seeds in salt water for 7-8 hours before consumption to reduce phytic acid, improving mineral absorption.
- Storage: Keep pumpkin seeds in an airtight container in the refrigerator to prevent rancidity of healthy fats.
Daily Incorporation Strategies
For consistent health benefits, aim for 1-2 ounces (28-56g) daily. Try these simple approaches:
- Add to morning oatmeal or yogurt for crunch and nutrition
- Blend into smoothies for added protein and healthy fats
- Use as salad topping instead of croutons
- Mix with dried fruit for a nutrient-dense trail mix
- Grind into "pumpkin seed flour" for baking

Important Considerations and Limitations
While pumpkin seeds offer numerous health benefits, certain considerations apply to specific populations:
Context Boundaries: Who Should Moderate Intake
- Kidney stone formers: Pumpkin seeds contain moderate oxalates. Those with calcium oxalate kidney stones should consult their doctor about appropriate portions.
- Medication interactions: The high magnesium content may interact with certain antibiotics and blood pressure medications.
- Allergy considerations: Though rare, seed allergies do occur. Introduce gradually if you have other seed or nut allergies.
The European Food Safety Authority notes that pumpkin seed consumption is generally safe for most adults at recommended levels. However, exceeding 2-3 ounces daily may lead to digestive discomfort due to their high fiber and fat content.
Maximizing Pumpkin Seed Benefits: Expert Recommendations
Based on current research, here's how to get the most from what pumpkin seeds are good for:
- Choose raw, unsalted seeds when possible to avoid excess sodium
- Pair with vitamin C-rich foods (like citrus fruits) to enhance iron absorption
- Combine with healthy fats (like avocado) to improve absorption of fat-soluble nutrients
- Use pumpkin seed oil for dressings (never for high-heat cooking)
- Consider pumpkin seed protein powder as supplement for athletes
Remember that pumpkin seeds work best as part of an overall balanced diet. No single food provides all necessary nutrients, but incorporating pumpkin seeds regularly can address specific nutritional gaps common in modern diets.
Frequently Asked Questions
What specific health conditions are pumpkin seeds good for?
Pumpkin seeds show particular benefits for heart health (managing blood pressure), prostate health (due to zinc content), sleep quality (through magnesium and tryptophan), and immune function (from zinc). Research also suggests potential benefits for managing blood sugar levels and reducing inflammation.
How much pumpkin seeds should I eat daily for health benefits?
For measurable health benefits, consume 1-2 ounces (28-56 grams) daily. This provides sufficient magnesium, zinc, and healthy fats without excessive calories. Start with smaller portions if you're new to high-fiber foods to allow your digestive system to adjust.
Are roasted pumpkin seeds as healthy as raw ones?
Lightly roasted pumpkin seeds retain most nutrients, but high-heat roasting can damage delicate omega-6 fatty acids. For maximum benefit, roast at temperatures below 170°F (77°C) or consume raw. Avoid commercially roasted seeds with added oils and excessive salt.
Can pumpkin seeds help with hair growth?
Pumpkin seeds contain zinc, iron, and essential fatty acids that support hair health. A clinical study published in Dermatology and Therapy found that pumpkin seed oil supplementation showed promise for improving hair count in men with androgenetic alopecia, though more research is needed.
When's the best time to eat pumpkin seeds for sleep benefits?
For sleep enhancement, consume pumpkin seeds 1-2 hours before bedtime. The combination of magnesium, zinc, and tryptophan works synergistically to promote relaxation and support melatonin production. A small handful (about 1 ounce) provides optimal nutrient levels without causing digestive discomfort.










 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4