Why Choline Matters More Than You Think
Choline often gets overlooked in nutrition discussions, yet it's as vital as B vitamins for cognitive function and cellular health. This water-soluble nutrient helps build cell membranes, produce neurotransmitters, and process fats. Without adequate choline, you risk fatty liver disease, muscle damage, and impaired brain development during pregnancy.
According to the National Institutes of Health, 90% of Americans don't meet daily choline requirements. The problem? Many top sources like organ meats aren't regular staples in modern diets. Let's explore practical ways to incorporate choline-rich foods that fit your lifestyle.
Your Complete Guide to Choline Food Sources
Understanding choline content requires precise measurements—not just "high in choline" claims. We've analyzed USDA FoodData Central data to give you exact values per standard serving. This helps you calculate your daily intake accurately.
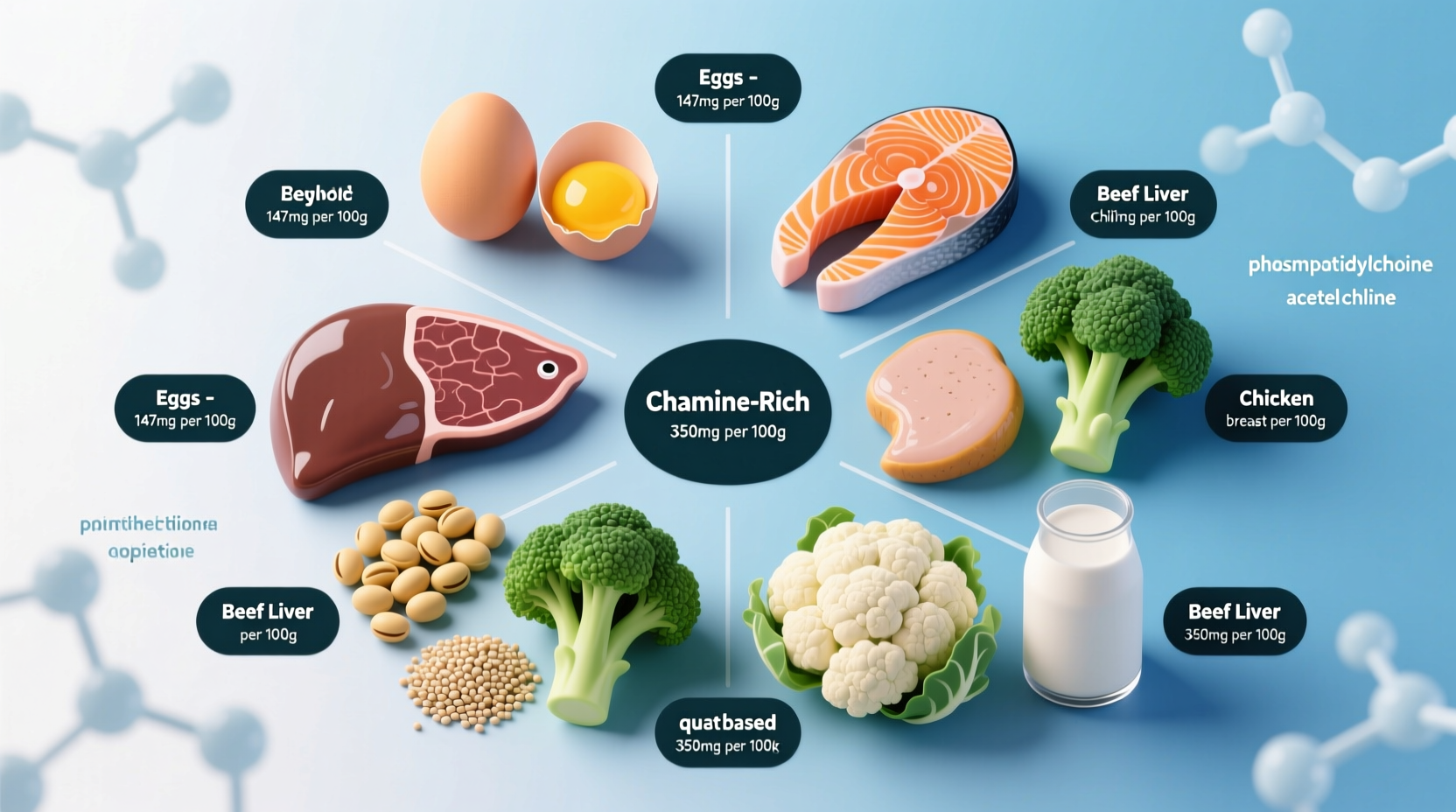
| Food Source | Serving Size | Choline (mg) | % Daily Value* |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beef liver | 3 ounces | 356 | 65% |
| Egg (whole) | 1 large | 147 | 27% |
| Salmon | 6 ounces | 242 | 44% |
| Soybeans (cooked) | ½ cup | 107 | 20% |
| Chicken breast | 3 ounces | 72 | 13% |
| Shiitake mushrooms | 1 cup | 73 | 13% |
*Based on 550mg daily value for men; 425mg for women

Special Considerations for Different Diets
Your choline needs change based on life stage and dietary preferences. Here's what research shows about specific scenarios:
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
During pregnancy, choline becomes critical for fetal brain development. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition reports that adequate choline intake reduces neural tube defect risk by 50%. Pregnant women need 450mg daily, increasing to 550mg while breastfeeding. Two eggs plus a serving of salmon meets nearly 80% of this requirement.
Plant-Based Diets
Vegetarians and vegans face unique challenges since animal products contain the most concentrated choline sources. Focus on these plant-based options:
- Soy products (tofu, tempeh, edamame)
- Quinoa (complete protein with decent choline)
- Broccoli and Brussels sprouts
- Shiitake mushrooms
- Legumes like kidney beans
Combine these strategically—try a tofu scramble with broccoli and mushrooms to boost your intake.
Athletes and Active Individuals
Physical activity increases choline turnover. Endurance athletes may need up to 20% more choline due to sweat loss and metabolic demands. Include choline-rich foods within 30 minutes post-workout for optimal muscle recovery.
Practical Meal Integration Strategies
Knowing choline sources is only half the battle. Here's how to incorporate them seamlessly into your routine:
Breakfast Solutions
Replace cereal with a vegetable omelet using two eggs (294mg choline). Add mushrooms and spinach for additional nutrients. This single meal provides over 50% of your daily requirement.
Lunch and Dinner Hacks
Meal prep smartly by batch-cooking quinoa and roasted chickpeas. Combine with steamed broccoli and a hard-boiled egg for a choline-rich salad. For dinner, try baked salmon with shiitake mushroom risotto using cauliflower rice.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Many people mistakenly believe all eggs are equal. The choline is primarily in the yolk—using only egg whites cuts your intake by 90%. Similarly, processed soy products like soy milk contain significantly less choline than whole soybeans.
Monitoring Your Choline Intake
Track your consumption for three days using a nutrition app. Most adults need 425-550mg daily, but requirements vary:
- Men 19+: 550mg
- Women 19+: 425mg
- Pregnant: 450mg
- Breastfeeding: 550mg
- Teens: 400-500mg
If you consistently fall short, consider adding one choline-dense food daily. Just two eggs covers more than half your requirement. Consult a registered dietitian before taking supplements, as excessive choline can cause fishy body odor and digestive issues.










 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4