Modern agriculture increasingly relies on specialized automation to address labor shortages and improve efficiency with delicate crops like peppers. Pepper Automated Handling Systems (AHS) represent a critical advancement in agricultural technology, combining robotics, computer vision, and gentle manipulation techniques to handle peppers throughout the production chain.
Understanding Pepper Automated Handling Systems
Pepper AHS technology has evolved significantly over the past decade to address the unique challenges of handling peppers, which are notably more fragile than many other crops. Unlike tomatoes or apples, peppers have thin skins and stems that easily detach, requiring specialized handling approaches.
These systems typically incorporate three key components: harvesting mechanisms that identify ripe peppers using spectral imaging, gentle grippers designed specifically for pepper morphology, and sorting algorithms that assess quality characteristics without physical contact. The most advanced pepper harvesting robots can distinguish between different pepper varieties and maturity levels with 95% accuracy.
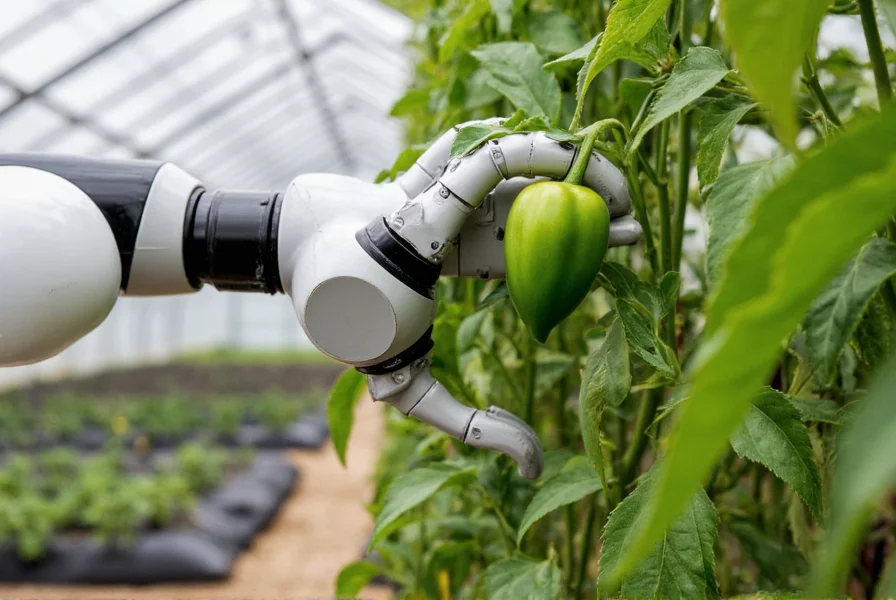

Technical Components of Modern Pepper AHS
Contemporary pepper automated handling systems integrate multiple sophisticated technologies working in concert:
| Component | Function | Technical Specifications |
|---|---|---|
| Computer Vision System | Identifies ripe peppers and assesses quality | Multi-spectral cameras, AI algorithms trained on 50,000+ pepper images |
| Gentle Gripping Mechanism | Harvests without damaging fruit | Soft robotics technology, pressure sensors (0.1-0.3N force range) |
| Conveyor System | Transports peppers with minimal contact | Food-grade silicone belts, variable speed control (0.5-2m/s) |
| Sorting Technology | Classifies by size, color, and defects | Hyperspectral imaging, machine learning classification |
Benefits of Implementing Pepper Handling Automation
Farmers adopting pepper AHS technology report substantial improvements across multiple operational metrics. The most significant advantages include:
- Labor cost reduction - Automated systems can operate continuously, addressing seasonal labor shortages that particularly affect pepper harvesting
- Reduced crop damage - Precision handling decreases bruising and stem detachment by up to 70% compared to manual harvesting
- Consistent quality control - Computer vision systems maintain uniform standards throughout the harvesting process
- Data collection capabilities - Modern systems generate valuable field data about crop health and yield patterns
- Extended harvesting windows - Automation allows for harvesting during optimal ripeness periods regardless of labor availability
Technical Challenges in Pepper Automation
Despite significant advancements, implementing pepper AHS presents several technical hurdles. The primary challenges include:
Pepper plants grow in irregular patterns with varying fruit orientations, making consistent robotic access difficult. The delicate nature of peppers requires extremely precise force control—too much pressure causes bruising while too little fails to detach the fruit properly. Environmental factors like changing light conditions in greenhouse settings can interfere with computer vision systems. Additionally, different pepper varieties (bell peppers, chili peppers, etc.) require customized handling approaches due to variations in size, shape, and stem attachment.
Implementation Considerations for Growers
Farmers considering pepper automated handling systems should evaluate several factors before investment. The initial capital expenditure for comprehensive pepper AHS ranges from $150,000 to $500,000 depending on scale and capabilities. Most systems achieve return on investment within 2-4 years through labor savings and reduced crop loss.
Successful implementation requires careful assessment of existing infrastructure compatibility, particularly greenhouse layout or field configuration. Training requirements for farm personnel to operate and maintain these systems typically ranges from 40-80 hours. Integration with existing farm management software provides additional value through data analytics capabilities.
When evaluating different pepper harvesting automation solutions, growers should prioritize systems with modular designs that can adapt to multiple pepper varieties and potentially other crops. The most effective implementations combine automation with strategic human oversight for quality control.
Future Developments in Pepper Handling Technology
Research in agricultural robotics continues to advance pepper AHS capabilities. Current development focuses on improving:
- Adaptive learning systems that improve performance throughout the growing season
- Energy efficiency to reduce operational costs
- Multi-crop compatibility to increase year-round utilization
- Real-time quality assessment that integrates with supply chain systems
- Collaborative robotics that work safely alongside human workers
Emerging technologies like soft robotics and advanced machine learning promise to further reduce crop damage while increasing harvesting speed. Some experimental systems now achieve harvesting rates of 8-10 peppers per minute per robotic arm, approaching the efficiency of experienced human workers while maintaining superior consistency.










 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4