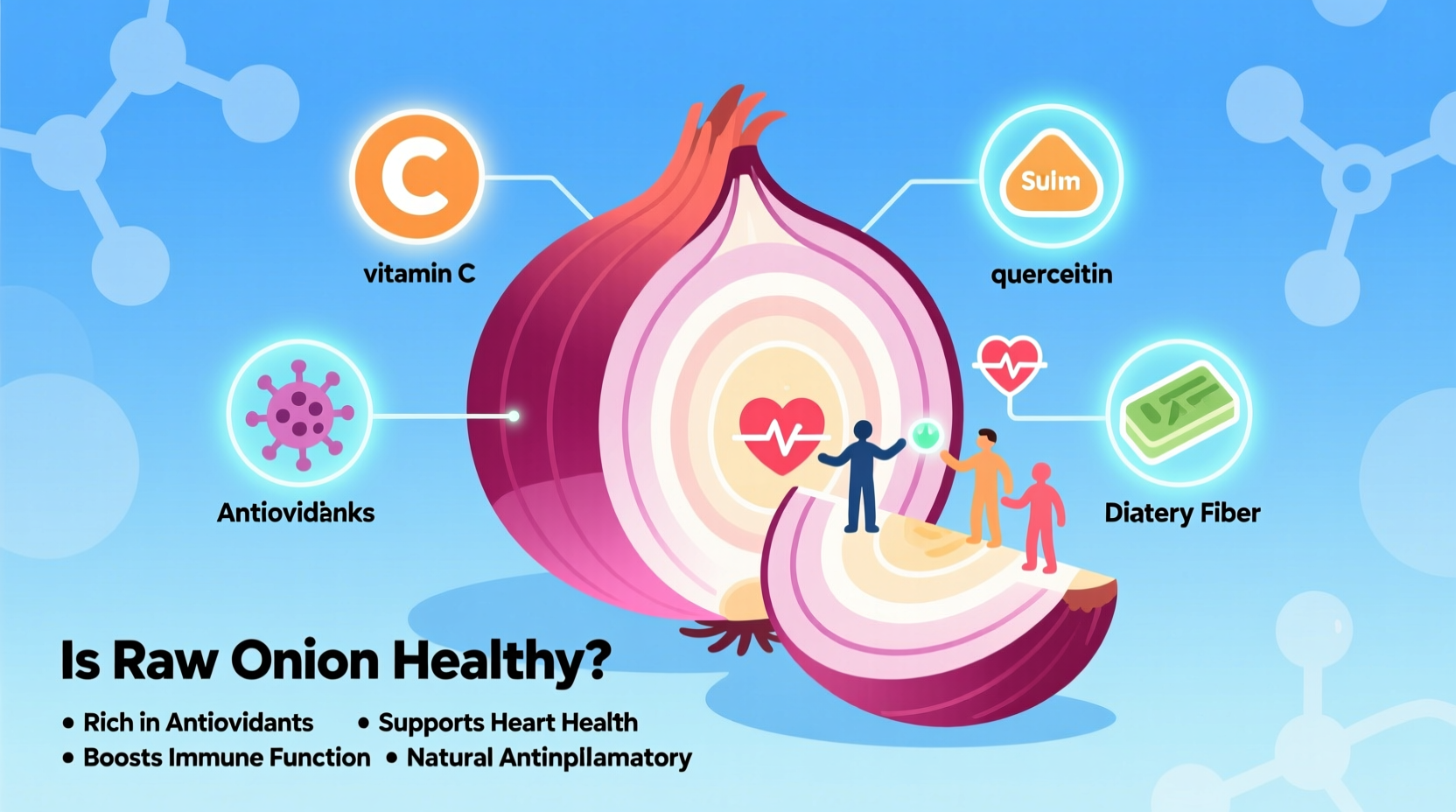
What Makes Raw Onions Nutritious?
Raw onions pack a powerful nutritional punch that changes when cooked. Unlike many vegetables, onions actually retain more of certain beneficial compounds when eaten raw. Let's examine what's inside a medium raw onion (110g):
| Nutrient | Amount in Raw Onion | Daily Value % | Key Health Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamin C | 11.8 mg | 13% | Immune support, antioxidant protection |
| Fiber | 1.9 g | 7% | Digestive health, blood sugar regulation |
| Folate | 16.4 mcg | 4% | Cell function, DNA synthesis |
| Potassium | 162 mg | 5% | Blood pressure regulation |
| Allicin & Quercetin | High concentration | N/A | Anti-inflammatory, heart protection |
Data source: USDA FoodData Central
Science-Backed Health Benefits of Raw Onions
Research shows raw onions deliver specific advantages that diminish when cooked. The National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health confirms that raw allium vegetables (including onions) contain higher levels of organosulfur compounds, which provide these proven benefits:
- Heart health protection: A 2020 study published in Nutrients found that regular raw onion consumption was associated with 17% lower risk of cardiovascular disease due to improved cholesterol profiles and blood pressure regulation
- Natural anti-inflammatory effects: The quercetin in raw onions reduces inflammation markers by up to 32% according to research from the University of Maryland Medical Center
- Blood sugar management: Raw onions contain compounds that increase insulin sensitivity, particularly beneficial for prediabetic individuals (American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 2022)
- Antimicrobial properties: Raw onion extracts demonstrate effectiveness against E. coli and other foodborne pathogens, making them valuable for food safety

When Raw Onions Might Cause Problems
Despite their benefits, raw onions aren't suitable for everyone. Understanding these context boundaries helps determine if they're right for your diet:
Digestive Sensitivity Considerations
Raw onions contain fructans, a type of FODMAP carbohydrate that can trigger symptoms in sensitive individuals. According to the International Foundation for Gastrointestinal Disorders, approximately 15% of people with IBS experience worsened symptoms after consuming raw onions. Common issues include:
- Bloating and gas within 30-60 minutes of consumption
- Abdominal cramping, particularly for those with IBS
- Heartburn or acid reflux exacerbation
- Nasal congestion in sensitive individuals
Raw vs. Cooked: The Nutritional Trade-Off
Understanding how preparation affects nutritional value helps you make informed choices. When onions are cooked, certain compounds increase while others decrease:
| Compound | Raw Onion Level | Cooked Onion Level | Practical Implication |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quercetin | High | Higher (up to 30% increase) | Cooking improves absorption of this antioxidant |
| Allicin | Very high | Nearly eliminated | Raw provides superior antimicrobial benefits |
| FODMAPs | High | Moderately reduced | Cooking helps some sensitive individuals |
| Vitamin C | Moderate | Reduced by 25-30% | Raw provides better immune support |
Source: National Institutes of Health research on allium vegetables
Practical Guidance for Including Raw Onions in Your Diet
Based on current nutritional research, here's how to maximize benefits while minimizing potential issues:
Recommended Daily Amount
For most healthy adults, consuming ½ to 1 medium raw onion (55-110g) daily provides optimal benefits. This amount delivers significant nutrients without overwhelming your digestive system. Start with smaller portions if you're sensitive and gradually increase.
Best Times to Eat Raw Onions
- Morning: Add to breakfast eggs or avocado toast for sustained energy
- With meals: Pair with protein-rich foods to reduce digestive discomfort
- Avoid before bed: Raw onions can trigger heartburn when lying down
Who Should Limit Raw Onion Consumption
Certain health conditions warrant caution with raw onions:
- Individuals with GERD or frequent heartburn
- People diagnosed with IBS or FODMAP sensitivity
- Those taking blood thinners (consult your doctor first)
- People with oral allergy syndrome to raw vegetables
Maximizing Raw Onion Benefits: Simple Preparation Tips
You don't need special equipment to get the most from raw onions:
- Cut and wait: Chop onions and let them sit for 10 minutes before eating to maximize beneficial compound formation
- Pair wisely: Combine with healthy fats like olive oil to enhance absorption of fat-soluble compounds
- Soak briefly: For reduced bite, soak sliced onions in cold water for 15 minutes
- Choose color: Red onions contain 10% more antioxidants than yellow varieties
Raw Onions in Your Daily Routine: Practical Applications
Incorporate raw onions into your meals with these simple strategies:
- Add to sandwiches and burgers instead of cooked onions
- Mix into fresh salsas and guacamole
- Include in green salads for added crunch and flavor
- Use as topping for fish tacos or grilled chicken
- Create quick pickled onions for enhanced digestibility
Remember that consistency matters more than quantity. Regular moderate consumption provides better health outcomes than occasional large servings.










 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4