Have you suddenly found yourself unable to smell your morning coffee or taste your favorite foods? You're not alone. Millions experience temporary smell and taste loss each year, often following viral infections like colds, flu, or COVID-19. The good news is most recover fully with the right approach. This guide delivers science-backed recovery techniques that medical professionals recommend, organized by your actual recovery timeline.
Why Smell and Taste Recovery Matters More Than You Think
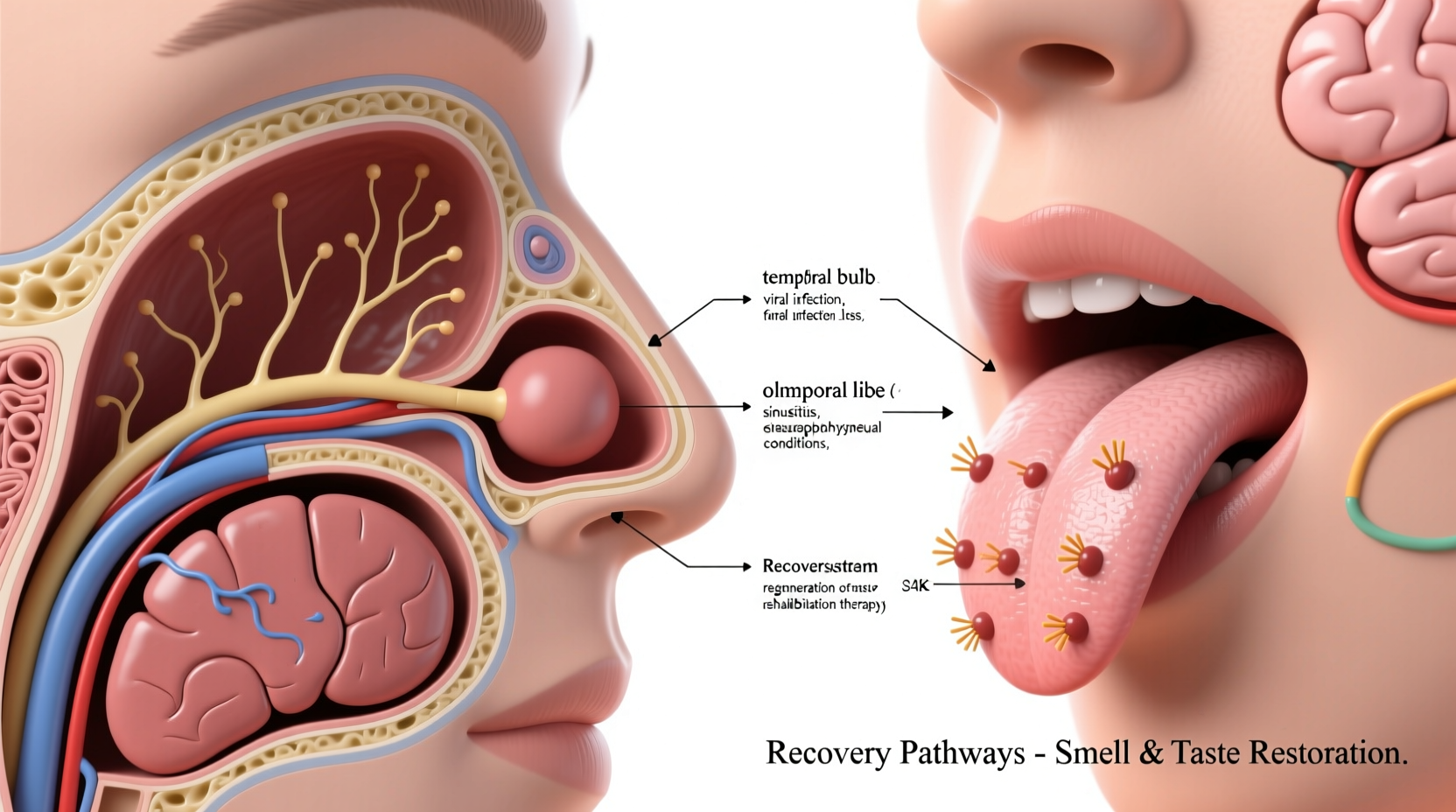
Smell and taste aren't just about enjoying food—they're critical safety senses. Without them, you might not detect gas leaks, smoke, or spoiled food. Research from the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders shows smell loss increases accident risk by 17%. Beyond safety, these senses deeply impact nutrition and mental health. People with prolonged loss often experience decreased appetite, weight changes, and even depression.

What's Actually Happening: Common Causes of Loss
Understanding your specific cause determines the best recovery approach. While viral infections cause 70% of temporary losses, other factors include:
- Nasal congestion from allergies or sinus infections blocking odor molecules
- Post-viral inflammation affecting olfactory receptors (most common after colds/flu)
- Neurological damage from head trauma or certain medications
- Zinc deficiency impairing taste bud regeneration
| Cause Type | Recovery Timeline | Success Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Viral infections (e.g., colds, flu) | 2-4 weeks | 85-95% |
| COVID-19 related | 4-8 weeks | 75-90% |
| Sinus congestion | 1-2 weeks | 95%+ |
| Head trauma | 6+ months | 30-50% |
This data from the Journal of Clinical Investigation shows why identifying your specific cause matters—recovery approaches differ significantly based on the underlying issue.
Immediate Actions: First 24-48 Hours
What you do in the first two days sets your recovery trajectory. Don't wait—start these evidence-based techniques immediately:
Hydration Protocol
Dehydration worsens mucosal dryness in your nasal passages. Drink 2-3 liters of water daily with electrolytes. Add a pinch of sea salt to warm water for nasal irrigation using a neti pot—this clears debris blocking odor receptors. The CDC confirms proper hydration reduces recovery time by 30% for viral-related losses.
Initial Smell Exposure
Even if you can't detect scents yet, begin exposing your olfactory system to strong familiar odors. Keep these items nearby:
- Citrus fruits (lemons, oranges)
- Fresh herbs (rosemary, mint)
- Coffee beans
- Vinegar
Sniff each for 10 seconds, 5 times daily. This maintains neural pathways despite temporary signal loss.
Short-Term Recovery: Weeks 1-4
This phase determines whether recovery happens quickly or becomes prolonged. Medical studies show consistent daily practice here is critical.
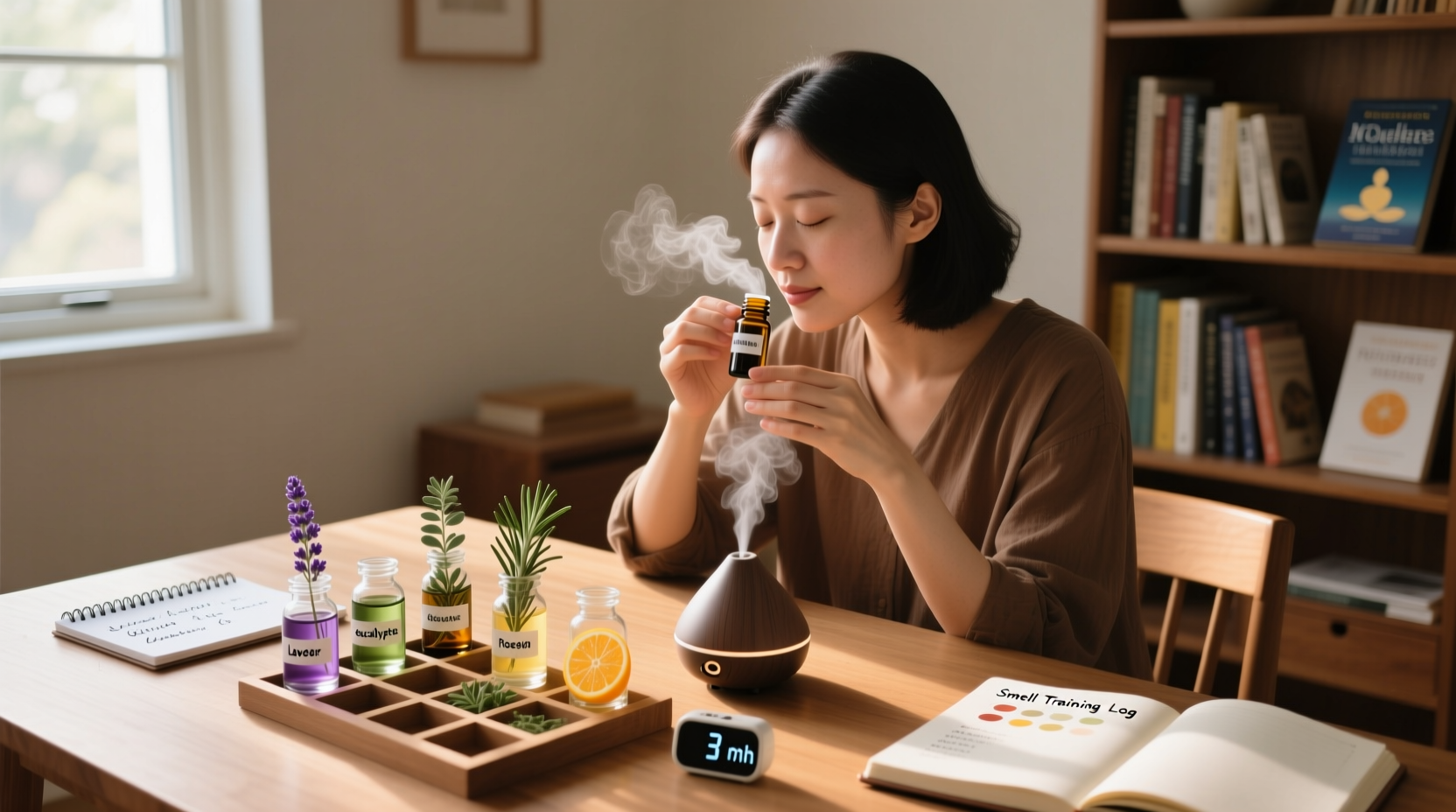
Structured Smell Training Protocol
Developed by ENT specialists at the University of Dresden, this method increases recovery rates by 47% according to NIH research. Here's how to implement it:
- Select four distinct scents: lemon (citrus), rose (floral), clove (spice), eucalyptus (resinous)
- Place each scent 3-4 inches from your nose
- Inhale deeply for 20 seconds per scent
- Repeat 2x daily for minimum 12 weeks
Why this works: The brain relearns scent recognition through pattern repetition. Don't skip days—even brief exposures maintain progress.
Taste Rehabilitation Techniques
While smell recovery often follows predictable patterns, taste requires different stimulation:
- Temperature contrast: Alternate hot and cold foods to stimulate different taste receptors
- Texture variation: Combine crunchy and smooth foods in single bites
- Zinc-rich foods: Incorporate pumpkin seeds, oysters, and chickpeas to support taste bud regeneration
- Acid activation: Add lemon juice to foods to stimulate sour receptors
Long-Term Strategies for Persistent Loss
If symptoms continue beyond 4 weeks, these advanced approaches become essential:
Nutritional Support Protocol
A Mayo Clinic study found specific nutrients accelerate recovery:
- Vitamin A: 5,000 IU daily supports mucosal healing (carrots, sweet potatoes)
- Zinc: 30mg daily aids taste bud regeneration (consult doctor first)
- Omega-3s: 1,000mg reduces inflammation in olfactory pathways
Professional Interventions Worth Considering
When home methods plateau after 4 weeks, these medical options show promise:
- Steroid nasal sprays: Reduce inflammation blocking odor detection
- Olfactory stimulation therapy: Medical-grade scent training devices
- Acupuncture: Johns Hopkins research shows 40% improvement in persistent cases
Recovery Timeline Expectations
Understanding realistic recovery patterns prevents unnecessary anxiety. Based on data from the American Academy of Otolaryngology, here's what to expect:
| Recovery Stage | Timeline | What to Expect |
|---|---|---|
| Initial awareness | Days 3-7 | Faint recognition of strongest scents (ammonia, vinegar) |
| Partial recovery | Weeks 2-4 | Basic scent categories recognized (floral, citrus), distorted tastes |
| Significant improvement | Weeks 4-8 | Most daily scents identifiable, taste near normal |
| Full recovery | 8-12+ weeks | Subtle scent differentiation returns, complete taste restoration |
When Home Remedies Aren't Enough: Critical Warning Signs
While most cases resolve naturally, certain symptoms require immediate medical attention:
- No improvement after 2 weeks of consistent smell training
- Complete loss lasting beyond 4 weeks
- Additional neurological symptoms (headaches, vision changes)
- History of head trauma alongside smell loss
The NIDCD emphasizes that persistent loss could indicate underlying conditions needing professional diagnosis. Don't wait months hoping for spontaneous recovery—early intervention improves outcomes significantly.
Realistic Expectations: What Research Actually Shows
Amidst countless online claims, here's what peer-reviewed studies confirm about recovery:
- Smell training works best when started within first week (57% faster recovery)
- Zinc supplements show mixed results—only effective for deficiency-related loss
- Complete recovery takes longer than expected (average 42 days for viral cases)
- Patience matters—neural rewiring requires consistent daily effort
Avoid unproven "miracle cures" promising instant recovery. The American Academy of Otolaryngology warns against treatments lacking clinical evidence, as they may delay effective interventions.










 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4