Planning your garden? Knowing exactly how long it takes to grow tomatoes helps you time your planting for maximum harvest. Whether you're a first-time gardener or looking to optimize your existing setup, understanding the tomato growth timeline ensures you'll enjoy fresh, homegrown tomatoes at their peak flavor.
Tomato Varieties and Their Growth Timelines
Not all tomatoes grow at the same pace. The "days to maturity" listed on seed packets refers to the time from transplanting outdoors to first harvest. Understanding these differences helps you select varieties that match your growing season.
| Tomato Type | Common Varieties | Days to Maturity | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Early Season | Stupice, Oregon Spring | 50-65 days | Short growing seasons |
| Mid-Season | Roma, Celebrity | 65-80 days | Balanced harvest timing |
| Late Season | Beefsteak, Brandywine | 80-100+ days | Long growing seasons |
| Cherry Tomatoes | Sun Gold, Sweet Million | 60-70 days | Continuous harvest |
This comparison of tomato growth duration by variety comes from data collected by the University of Minnesota Extension, which tracks performance across multiple growing zones. Determinate varieties (bush types) typically produce one large harvest, while indeterminate varieties (vining types) continue producing throughout the season.
Your Step-by-Step Tomato Growing Timeline
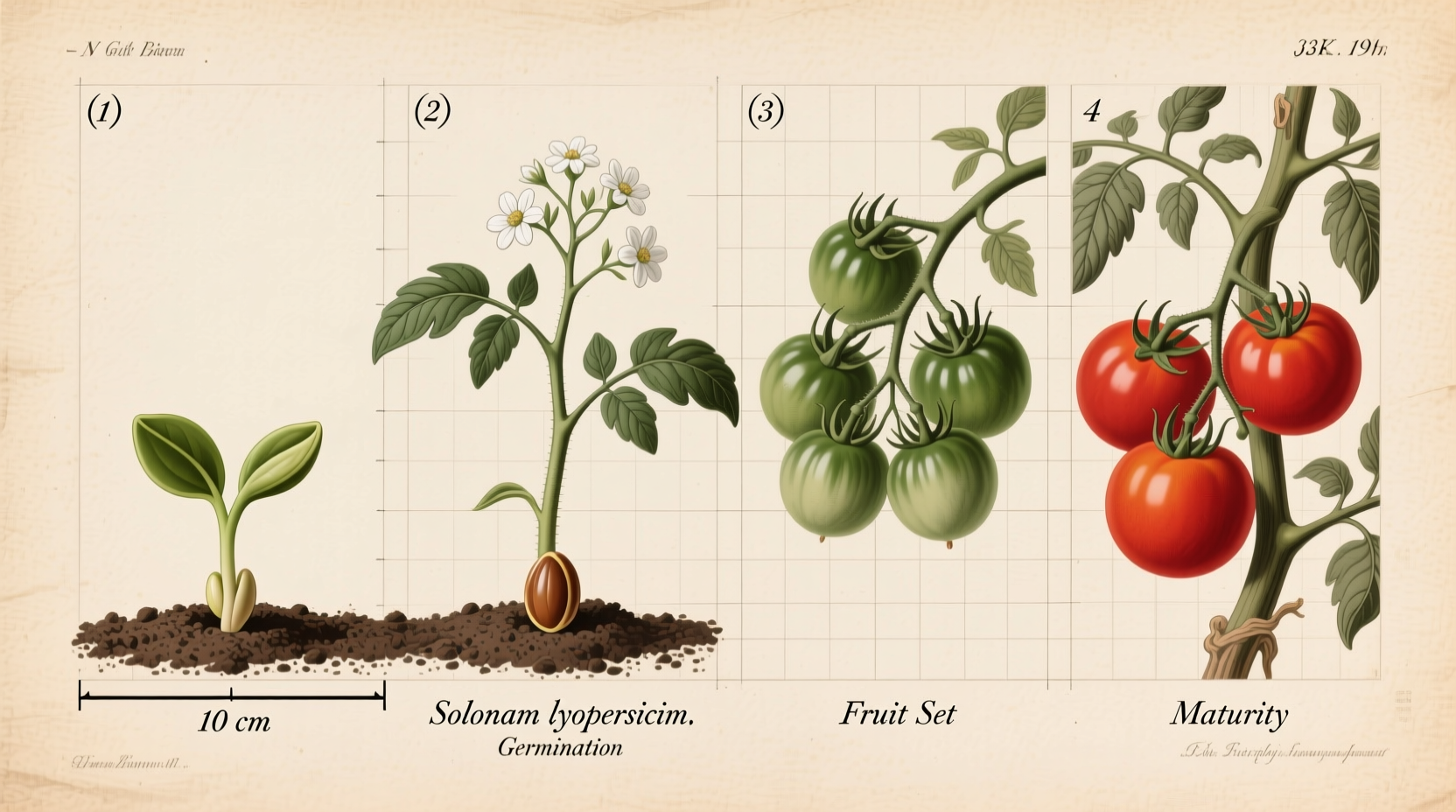
Understanding the complete journey from seed to harvest helps you anticipate each stage and provide proper care. Here's what to expect when growing tomatoes:
Weeks 1-6: Starting Seeds Indoors
Begin tomato seeds indoors 6-8 weeks before your last expected frost date. During this tomato seed germination period, maintain soil temperatures between 70-80°F (21-27°C) for optimal sprouting, which typically occurs within 5-10 days. Seedlings need 14-16 hours of light daily to prevent legginess.
Weeks 7-8: Hardening Off and Transplanting
Before moving plants outdoors, gradually acclimate them to outdoor conditions over 7-10 days—a process called hardening off. Transplant when soil temperatures consistently reach 60°F (15°C) at a 6-inch depth. Proper transplanting tomatoes for faster growth involves burying the stem up to the first set of leaves to encourage additional root development.
Weeks 9-12: Vegetative Growth and Flowering
After transplanting, tomatoes enter rapid vegetative growth. The first flowers typically appear 4-6 weeks after transplanting. During this critical tomato flowering stage duration, avoid excessive nitrogen which can promote leaf growth at the expense of flowers. Daytime temperatures between 70-85°F (21-29°C) optimize flower production.
Weeks 13-16+: Fruit Development and Ripening
From flower to ripe tomato takes approximately 25-60 days, depending on variety and conditions. The time from tomato flower to ripe fruit follows this progression: pollination (1-2 days), small green fruit (7-10 days), mature green stage (14-21 days), and ripening to color (7-14 days). Consistent watering during this phase prevents blossom end rot and cracking.

Factors That Impact Your Tomato's Growth Speed
Several environmental factors significantly affect how many days to harvest tomatoes. Understanding these helps you adjust your approach for faster, healthier plants.
Temperature Requirements for Optimal Growth
Tomatoes thrive in warm conditions but have specific temperature needs at different stages. According to research from Oregon State University Extension, tomatoes grow best when daytime temperatures range from 70-85°F (21-29°C) and nighttime temperatures stay above 55°F (13°C). Temperatures below 50°F (10°C) or above 95°F (35°C) significantly slow growth and can prevent fruit set.
Soil Quality and Preparation
Well-draining soil with a pH of 6.2-6.8 provides the ideal foundation for speeding up tomato growth naturally. Incorporate 3-4 inches of compost into your planting area to improve soil structure and nutrient content. Tomatoes are heavy feeders, requiring consistent access to nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium throughout their growth cycle.
Watering Practices That Make a Difference
Inconsistent watering is one of the most common reasons for delayed tomato harvest times. Provide 1-2 inches of water per week, watering deeply 2-3 times weekly rather than daily shallow watering. Mulching with straw or wood chips helps maintain consistent soil moisture and temperature, reducing stress on plants.
Troubleshooting Slow Tomato Growth
When your tomatoes aren't progressing as expected, these common issues might be the culprit:
- Nutrient deficiencies: Yellowing leaves often indicate nitrogen deficiency, while purple undersides suggest phosphorus shortage
- Poor pollination: Lack of flowers or fruit set may require manual pollination in enclosed spaces
- Disease pressure: Early blight or fusarium wilt can significantly slow growth and reduce yield
- Root bound plants: Container-grown tomatoes need adequate space for root development
For gardeners in shorter growing seasons, selecting varieties with fewer days to maturity and using season-extension techniques like wall o' waters or black plastic mulch can help achieve growing tomatoes in less time than expected.
Proven Strategies for Faster Tomato Harvests
Implement these research-backed techniques to optimize your tomato growing timeline from seed to harvest:
- Choose appropriate varieties: Match your climate with varieties bred for your region's growing season length
- Start seeds at the right time: Calculate backward from your last frost date for optimal indoor starting time
- Warm the soil: Use black plastic mulch 1-2 weeks before planting to raise soil temperature
- Provide consistent nutrition: Use balanced fertilizer with calcium to prevent blossom end rot
- Prune strategically: Remove suckers on indeterminate varieties to direct energy to fruit production
According to the Cornell University Gardeners' Resource, gardeners who implement these practices typically see harvests 7-14 days earlier than those using basic growing methods. Remember that while you can optimize conditions, rushing the natural tomato ripening process timeline often compromises flavor and quality.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does it take to grow tomatoes from seed to harvest?
From seed to harvest typically takes 95-130 days. This includes 6-8 weeks for seed starting indoors plus the days to maturity listed on your seed packet (usually 60-100 days from transplanting). Early varieties may be ready in as little as 85 days from seed, while heirloom varieties can take up to 120 days.
Why are my tomatoes taking longer to ripen than expected?
Several factors can delay ripening: cool temperatures below 60°F (15°C), excessive nitrogen fertilizer promoting leaf growth over fruit development, inconsistent watering causing stress, or selecting varieties not suited to your climate. Patience is often required, as tomatoes won't ripen properly off the vine if picked too early.
Can I speed up the tomato ripening process on the vine?
While you can't significantly accelerate natural ripening, you can optimize conditions: reduce watering slightly when fruits begin coloring, remove new flowers and small fruits late in the season to direct energy to existing fruit, and ensure plants receive at least 6-8 hours of direct sunlight daily. Never remove leaves that shade fruit, as this can cause sunscald.
How long after flowering do tomatoes appear?
Small green tomatoes typically appear 3-5 days after successful pollination. From flower to mature green fruit takes approximately 3-4 weeks, then an additional 1-2 weeks to ripen to full color. The complete process from flower to ripe tomato generally takes 45-60 days, depending on variety and growing conditions.










 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4