Ever found yourself staring at last night's steak wondering if it's still safe to eat? You're not alone. Millions of Americans question the shelf life of cooked meats weekly, risking foodborne illness when unsure. As a culinary safety expert with two decades of experience, I've seen how simple storage mistakes lead to unnecessary waste or, worse, food poisoning.
Why the 3-4 Day Rule Matters for Cooked Beef
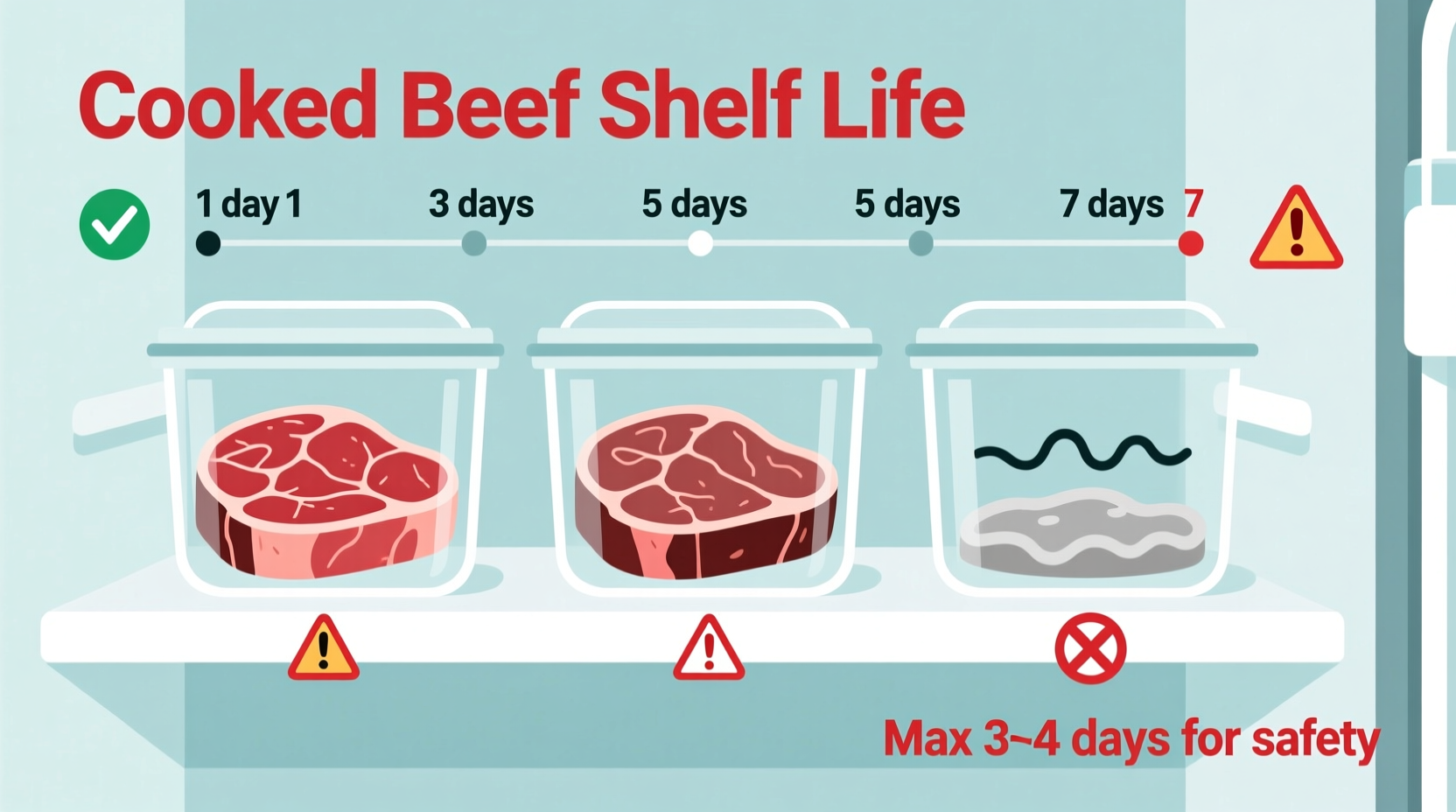
Understanding the science behind food spoilage transforms how you handle leftovers. Cooked beef enters what food safety experts call the "danger zone" between 40°F and 140°F (4°C-60°C), where bacteria multiply rapidly. The USDA's Food Safety and Inspection Service confirms that cooked beef stored at proper refrigerator temperatures (40°F or below) remains safe for consumption for 3-4 days.
This timeframe isn't arbitrary—it's based on bacterial growth studies. Pathogens like Staphylococcus aureus and Clostridium perfringens begin proliferating after the 4-day mark, significantly increasing food poisoning risks. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reports that improper food storage causes approximately 1 million foodborne illnesses annually in the United States.
Proper Storage Techniques That Extend Freshness
How you store cooked beef dramatically impacts its shelf life. Follow these professional kitchen-tested methods:
- Immediate cooling: Divide large portions into shallow containers (no deeper than 2 inches) to cool faster
- Airtight containers: Use glass or BPA-free plastic containers with tight-fitting lids
- Temperature control: Keep your refrigerator at 37-40°F (3-4°C) and verify with an independent thermometer
- Strategic placement: Store cooked beef on middle shelves, not in the door where temperatures fluctuate
According to research from the National Center for Home Food Preservation, properly stored cooked beef maintains quality up to 25% longer than haphazardly stored leftovers. Professional kitchens follow the "two-hour rule"—refrigerating cooked foods within two hours of cooking (one hour if ambient temperature exceeds 90°F/32°C).

When Cooked Beef Lasts Longer: Special Cases
Certain preparation methods extend cooked beef's refrigerator life. Understanding these variations prevents unnecessary waste:
| Preparation Method | Refrigerator Shelf Life | Key Preservation Factor |
|---|---|---|
| Plain cooked roast or steak | 3-4 days | Minimal moisture exposure |
| Beef in broth-based sauces | 3 days | Acidic components slow bacterial growth |
| Ground beef dishes | 1-2 days | Increased surface area accelerates spoilage |
| Beef with tomato-based sauces | 4-5 days | Natural acidity extends freshness |
This data aligns with USDA Food Safety guidelines, which note that acidic environments (like tomato sauces with pH below 4.6) create less hospitable conditions for bacteria. The University of Minnesota Extension confirms that ground meats spoil faster due to increased surface area exposed during processing.
Spoilage Warning Signs You Can't Ignore
Don't rely solely on dates—your senses provide critical safety information. Watch for these unmistakable spoilage indicators:
- Visual changes: Grayish color, slimy film, or visible mold (discard entire container)
- Odor changes: Sour, ammonia-like, or unpleasantly sweet smells
- Texture changes: Sticky or tacky surface even after washing
- Taste test (not recommended): Sour or "off" flavor indicates advanced spoilage
The Food and Drug Administration emphasizes that "when in doubt, throw it out" remains the golden rule of food safety. Never taste questionable meat to determine safety—pathogens like E. coli O157:H7 don't always produce noticeable odors but can cause severe illness.
Maximizing Safety When Reheating Leftover Beef
Proper reheating destroys surviving bacteria but requires specific temperature control. Follow these evidence-based practices:
- Reheat to internal temperature of 165°F (74°C) measured with a food thermometer
- Stir liquids and casseroles midway through reheating for even temperature distribution
- Refrigerate leftovers within two hours after reheating (one hour if room temperature exceeds 90°F)
- Avoid multiple reheating cycles—portion leftovers before initial refrigeration
Research published in the Journal of Food Protection confirms that reheating to 165°F eliminates common foodborne pathogens. The USDA Meat and Poultry Hotline reports that improper reheating causes 12% of foodborne illness cases linked to leftovers.
Freezing: Your Best Option for Long-Term Storage
When you can't consume cooked beef within 3-4 days, freezing preserves quality and safety. Follow these professional freezing techniques:
- Vacuum-seal portions for maximum shelf life (up to 3 months)
- Use heavy-duty freezer bags with air removed (2-3 months)
- Label containers with contents and date using freezer-safe markers
- Thaw in refrigerator—not at room temperature—to maintain safety
The National Center for Home Food Preservation confirms that frozen cooked beef maintains peak quality for 2-3 months. While technically safe indefinitely when frozen at 0°F (-18°C), quality deteriorates after this timeframe due to freezer burn and moisture loss.
Common Questions About Cooked Beef Storage
Can I eat cooked beef after 5 days in the refrigerator?
The USDA recommends discarding cooked beef after 4 days in the refrigerator. While some sources suggest 5-7 days, this increases foodborne illness risk significantly. Pathogens like Listeria monocytogenes can grow at refrigerator temperatures, making extended storage dangerous.
Does reheating cooked beef extend its refrigerator life?
No, reheating does not reset the clock on refrigerator storage. Each reheating cycle reduces quality and increases bacterial growth risk during the cooling period. The USDA Food Safety and Inspection Service states that leftovers should be consumed within 3-4 days regardless of reheating.
How can I tell if cooked beef has gone bad if it has no smell?
Some dangerous pathogens like E. coli don't produce noticeable odors. Check for visual changes (gray color, slimy texture), and when in doubt, discard the food. The CDC reports that 48 million Americans get sick from foodborne illnesses annually—many from consuming spoiled meat with no obvious warning signs.
Is cooked beef safe after the 'use by' date on the package?
'Use by' dates apply to uncooked meat. For cooked beef, the 3-4 day rule applies regardless of original packaging dates. The USDA explains that cooking resets the safety timeline—always count from the cooking date, not the purchase date.










 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4