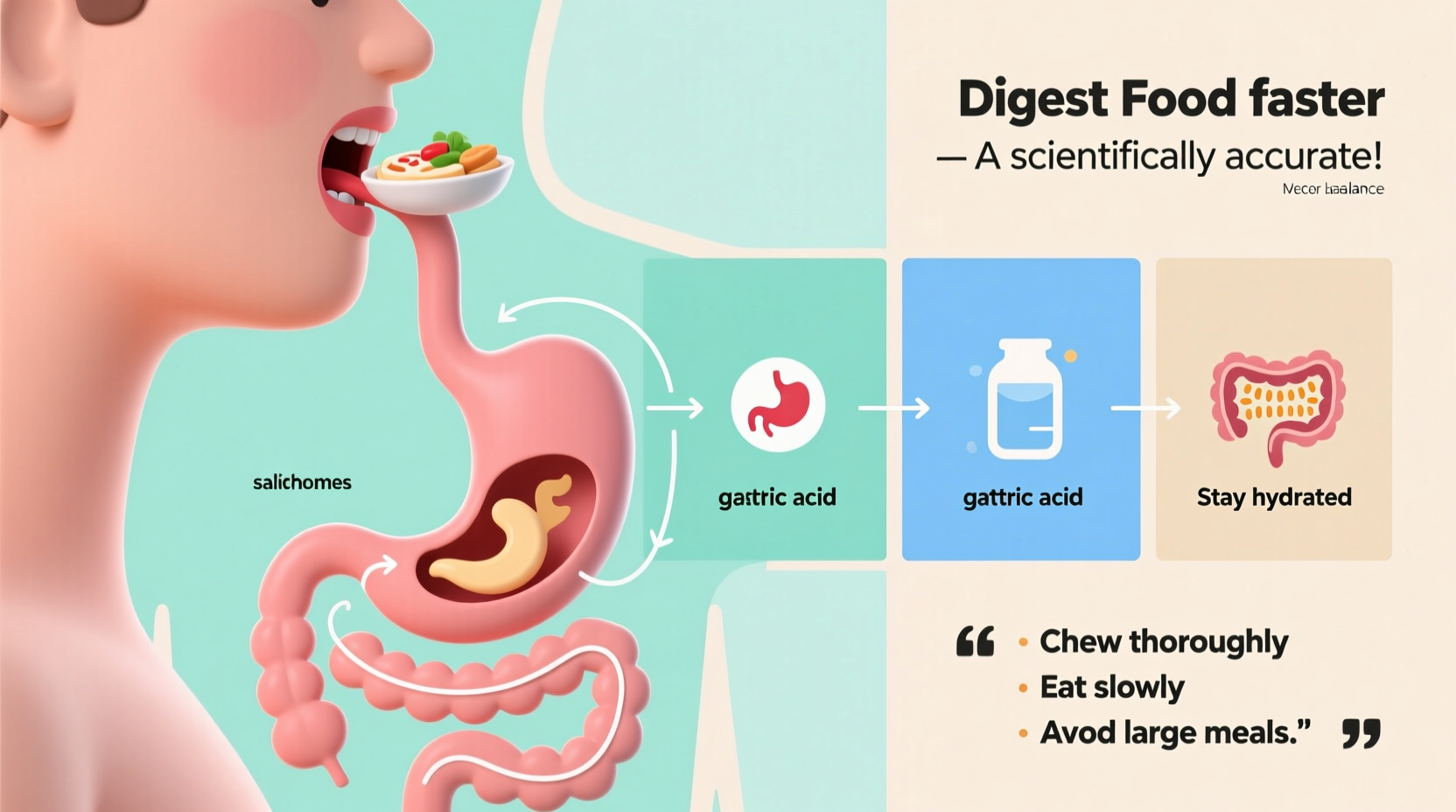
Understanding Your Digestive Timeline
Your digestive system processes food in stages, typically taking 24-72 hours from consumption to elimination. While you can't dramatically speed up this biological process overnight, certain evidence-based strategies can optimize your digestion efficiency. The key is enhancing your body's natural function rather than forcing unnatural acceleration that could lead to discomfort or health issues.
Immediate Actions for Better Digestion
When you need relief from that heavy, sluggish feeling after a meal, these practical steps deliver the fastest results:
Hydration Strategy That Works
Drinking water during meals has been misunderstood. Research from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases shows that moderate water intake with meals actually supports enzymatic activity. However, excessive fluids can dilute stomach acid. The optimal approach:
- Drink 4-6 ounces of room-temperature water with meals
- Wait 30 minutes after eating before consuming larger amounts
- Add lemon or apple cider vinegar (1 tablespoon in water) before meals to stimulate stomach acid production
Post-Meal Movement Protocol
Sitting still after eating slows gastric emptying. A 2019 study published in Nutrients found that light activity like walking for 10-15 minutes after meals improved gastric motility by 20% compared to remaining sedentary. The optimal post-meal timeline:
| Time After Eating | Recommended Activity | Digestive Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| 0-15 minutes | Sit upright, avoid reclining | Prevents acid reflux, maintains peristalsis |
| 15-30 minutes | Gentle walking (no more than 1.5 mph) | Stimulates gastric emptying without diverting blood flow |
| 30-60 minutes | Light stretching or seated twists | Massages digestive organs, improves circulation |
| 60+ minutes | Return to normal activity level | Allows complete gastric processing before exercise |
Dietary Adjustments for Daily Digestive Support
For lasting improvement in digestion speed, incorporate these evidence-based dietary practices:
The Ginger Advantage
Ginger contains gingerols that accelerate gastric emptying. According to research from the Mayo Clinic, consuming 1.2 grams of ginger before meals reduced digestion time by 25% in participants with functional dyspepsia. Implement this:
- 15 minutes before meals: 1/2 teaspoon grated ginger in warm water
- During meals: Include ginger in cooking (stir-fries, marinades)
- After meals: Ginger tea (avoid if you have acid reflux)
Strategic Food Combining
While strict food combining diets lack strong scientific backing, certain pairings do enhance digestion. The Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health recommends:
- Pair proteins with non-starchy vegetables (not heavy starches)
- Eat fruit separately from meals (best on empty stomach)
- Include healthy fats with vegetables to enhance nutrient absorption
- Limit liquid intake during protein-heavy meals
What Not to Do: Dangerous Digestion Myths
Certain popular "quick fixes" can damage your digestive system. The American Gastroenterological Association warns against:
- Overusing laxatives for "faster digestion" (leads to dependency)
- Excessive peppermint after meals (relaxes lower esophageal sphincter, causing reflux)
- Drinking ice-cold water with meals (constricts blood vessels in digestive tract)
- Over-supplementing with digestive enzymes (can reduce your body's natural production)
When Digestion Concerns Require Medical Attention
While occasional slow digestion is normal, these symptoms indicate you should consult a healthcare provider:
- Persistent bloating lasting more than 24 hours after eating
- Regular feelings of fullness after small meals
- Unintentional weight loss with digestive discomfort
- Nausea or vomiting accompanying slow digestion
These could indicate conditions like gastroparesis, GERD, or food intolerances that require professional diagnosis rather than home remedies.
Long-Term Digestive Health Practices
For sustained improvement in digestion efficiency, build these habits:
- Mindful eating: Chew each bite 20-30 times to begin mechanical digestion
- Stress management: High cortisol levels slow gastric emptying
- Regular meal timing: Helps regulate your digestive circadian rhythm
- Probiotic-rich foods: Sauerkraut, kimchi, and yogurt support gut microbiome

Conclusion: Sustainable Digestion Optimization
Improving digestion speed isn't about quick fixes but optimizing your body's natural processes. The most effective approach combines immediate relief strategies with sustainable daily habits that support your digestive system long-term. Remember that "faster" isn't always better—healthy digestion occurs at the right pace for your individual body. By implementing these science-backed methods consistently, you'll experience more comfortable digestion without resorting to harmful shortcuts.










 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4