For centuries, cultures worldwide have valued garlic not just for flavor but for its healing properties. Modern science is now validating what traditional medicine practitioners have known for generations: garlic possesses significant anti-inflammatory capabilities. But what exactly makes garlic effective, how much should you consume, and what does the research really say? Let's examine the evidence-based facts.
The Active Compounds Behind Garlic's Anti-Inflammatory Power
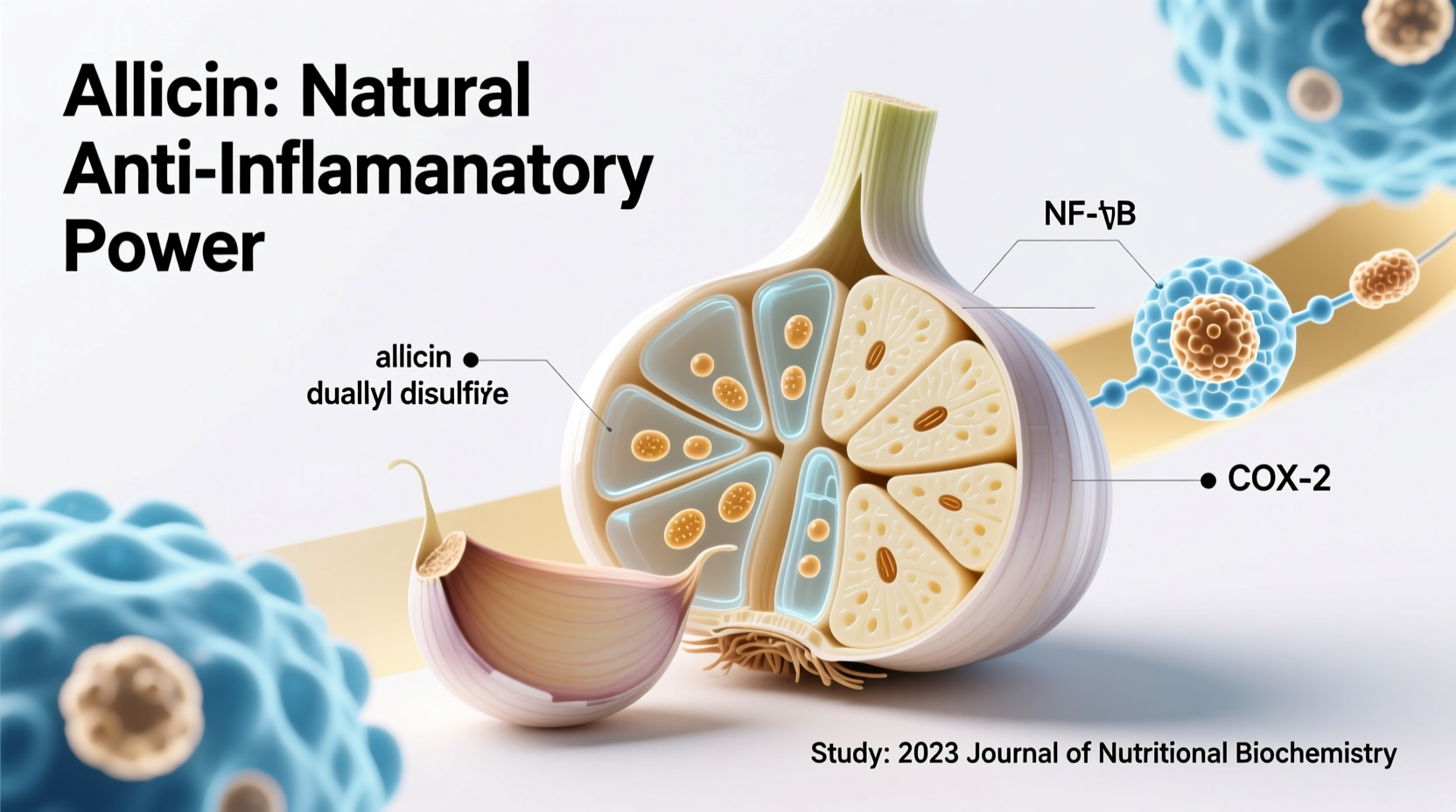
When you crush or chop fresh garlic, an enzyme called alliinase converts alliin into allicin—the compound responsible for garlic's distinctive smell and many health benefits. Allicin then breaks down into other organosulfur compounds that demonstrate powerful anti-inflammatory effects.
According to research published in the Journal of Nutrition, these compounds work by:
- Inhibiting NF-kB pathway activation (a key regulator of inflammation)
- Reducing production of pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α and IL-6
- Decreasing C-reactive protein (CRP) levels in the bloodstream
- Modulating immune cell activity to prevent excessive inflammatory responses

What Scientific Studies Actually Show About Garlic and Inflammation
A comprehensive review of 14 clinical trials involving over 700 participants, published in Nutrition Reviews, found that regular garlic consumption significantly reduced multiple inflammation markers. The most consistent benefits appeared with:
| Garlic Form | Daily Dosage | Observed Reduction in Inflammation Markers | Timeframe for Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fresh garlic | 2-3 cloves (4-6g) | 15-25% reduction in CRP | 8-12 weeks |
| Aged garlic extract | 600-1,200mg | 20-30% reduction in TNF-α | 12 weeks |
| Garlic powder | 600-900mg | 10-20% reduction in IL-6 | 12 weeks |
Researchers at the National Institutes of Health note that while these reductions are statistically significant, they represent modest improvements that work best as part of a comprehensive anti-inflammatory lifestyle—not as standalone treatments for serious inflammatory conditions.
Maximizing Garlic's Anti-Inflammatory Benefits: Practical Preparation Methods
The way you prepare garlic dramatically affects its anti-inflammatory potency. To maximize allicin production:
- Crush or chop first, wait 10 minutes before heating: This allows alliinase to fully convert alliin to allicin before heat deactivates the enzyme
- Avoid microwaving raw garlic: Studies in Food Chemistry show microwaving destroys 90% of potential allicin formation
- Pair with vitamin C-rich foods: Citrus or bell peppers enhance the stability of garlic's active compounds
- Use raw when possible: Raw garlic provides 3-5 times more allicin than cooked garlic
For those who can't tolerate raw garlic, aged garlic extract (available as supplements) provides stable anti-inflammatory compounds without the strong flavor or digestive side effects.
Realistic Expectations: Where Garlic Helps and Where It Doesn't
Understanding the context boundaries of garlic's anti-inflammatory effects prevents unrealistic expectations. Research shows garlic works best for:
- Mild, chronic inflammation associated with metabolic syndrome
- Exercise-induced muscle inflammation and recovery
- Early-stage cardiovascular inflammation markers
- Supporting overall immune regulation
Garlic is not sufficient for:
- Acute inflammatory conditions like severe arthritis flares
- Replacing prescribed anti-inflammatory medications
- Treating autoimmune disorders as a sole intervention
- Providing immediate relief from inflammation symptoms
The American Heart Association states that while garlic shows promise for cardiovascular health, "it should be considered a complementary approach rather than a replacement for evidence-based medical therapies."
Incorporating Garlic into an Effective Anti-Inflammatory Lifestyle
For maximum benefit, integrate garlic into a comprehensive anti-inflammatory approach:
- Morning routine: Add crushed raw garlic to lemon water (1 clove daily)
- Lunch enhancement: Mix minced garlic with olive oil and lemon juice for salad dressings
- Dinner preparation: Use the crush-and-wait method before adding to cooked dishes
- Supplement strategy: Consider aged garlic extract (600-1,200mg daily) if digestive sensitivity is an issue
Remember that garlic works synergistically with other anti-inflammatory foods. Pair it with omega-3 rich foods like salmon, leafy greens, berries, and turmeric for enhanced effects. The Mediterranean diet—which naturally incorporates these elements—provides the ideal framework for reducing inflammation through dietary patterns rather than isolated "superfoods."
Important Considerations and Potential Interactions
While generally safe, garlic can interact with certain medications. Consult your healthcare provider if you take:
- Blood thinners (garlic may increase bleeding risk)
- HIV medications (protease inhibitors)
- Some blood pressure medications
- Diabetes medications (garlic may enhance effects)
Pregnant women and those scheduled for surgery should discuss garlic consumption with their healthcare providers at least two weeks beforehand due to potential blood-thinning effects.










 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4