For those managing blood sugar levels, the question can garlic lower blood sugar isn't just theoretical—it's a practical concern affecting daily food choices. As someone who's studied the intersection of culinary traditions and traditional medicine for over 20 years, I've seen how ancient remedies like garlic meet modern scientific scrutiny. Let's examine what rigorous research actually reveals about garlic's potential role in blood sugar management.
How Garlic Might Influence Blood Glucose Levels
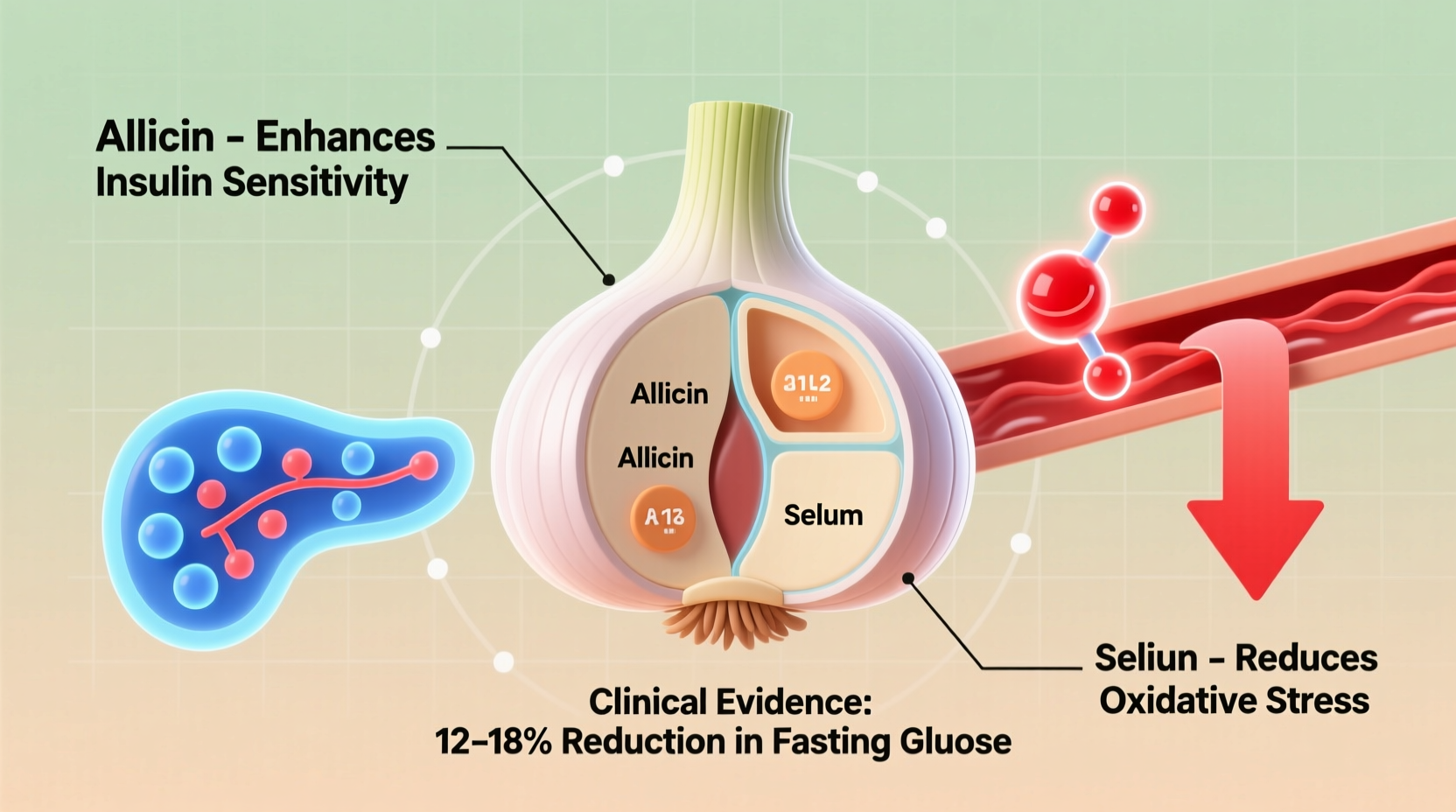
Garlic's potential blood sugar effects primarily stem from allicin, the sulfur-containing compound formed when garlic is crushed or chopped. When you consume raw garlic, the enzyme alliinase converts alliin to allicin, which then breaks down into other bioactive compounds. Research published in the Journal of Nutrition and Metabolism indicates these compounds may:
- Enhance insulin sensitivity in muscle and fat cells
- Reduce oxidative stress that contributes to insulin resistance
- Modulate carbohydrate metabolism enzymes
- Decrease hepatic glucose production
However, the effectiveness varies significantly based on preparation method. Raw garlic provides the highest allicin yield, while cooked garlic offers different sulfur compounds with potentially reduced blood sugar effects. Garlic supplements standardized for allicin potential provide the most consistent dosing used in clinical studies.
| Study Type | Garlic Form | Dosage | Blood Glucose Reduction | Study Duration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human Clinical Trial (2022) | Aged garlic extract | 1,200 mg/day | 12.3% reduction in fasting glucose | 12 weeks |
| Meta-Analysis (2021) | Various garlic preparations | 600-1,500 mg/day | 9.7% average reduction | 8-16 weeks |
| Animal Study (2023) | Raw garlic homogenate | Equivalent to 2 cloves human dose | 24.5% reduction | 4 weeks |
| Human Trial (2020) | Garlic powder tablets | 900 mg/day | No significant change | 8 weeks |
This evidence comparison table reveals important patterns: human studies generally show more modest effects than animal research, and results vary based on garlic preparation. The 2021 meta-analysis published in Nutrition Reviews concluded that "garlic supplementation demonstrates statistically significant but clinically modest improvements in glycemic control, particularly in individuals with type 2 diabetes."
Practical Application: Using Garlic Effectively
If you're considering adding garlic to support blood sugar management, understanding effective implementation matters more than just knowing does garlic reduce blood glucose levels. Based on current research, here's what actually works:
Dosage Considerations
Clinical studies showing positive effects typically used:
- 600-1,500 mg of garlic powder supplements daily
- 2-3 grams (about 1-2 cloves) of raw garlic
- 2-5 mL of aged garlic extract
Crucially, effects typically emerge after 8-12 weeks of consistent use. The National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health notes that "garlic's effects on blood sugar appear gradual rather than immediate."

Preparation Methods That Maximize Benefits
The way you prepare garlic significantly impacts its potential blood sugar effects:
- Raw consumption: Crush or chop garlic and wait 10 minutes before eating to maximize allicin formation
- Cooking methods: Light sautéing preserves some benefits; prolonged boiling reduces active compounds
- Supplement selection: Look for products standardized to 1.3% alliin or 0.6% allicin potential
Important Limitations and Safety Considerations
Understanding can garlic lower blood sugar safely requires examining critical limitations. Research shows garlic's blood sugar effects operate within specific parameters:
Context Boundaries for Effective Use
- Most effective for individuals with type 2 diabetes (limited evidence for type 1)
- Works best as complementary therapy alongside standard treatment
- Minimal effect for people with normal blood sugar levels
- Effects plateau after 3-4 months of consistent use
Perhaps most importantly, garlic may interact with common diabetes medications. The American Diabetes Association warns that "garlic supplements can enhance the effects of sulfonylureas and insulin, potentially causing hypoglycemia." If you take diabetes medication, consult your healthcare provider before adding significant garlic intake.
Who Should Avoid High Garlic Intake
Certain populations should exercise caution with therapeutic garlic doses:
- Individuals taking blood thinners (garlic has antiplatelet effects)
- Those scheduled for surgery within 2 weeks
- People with bleeding disorders
- Individuals with stomach ulcers or GERD
Integrating Garlic into a Comprehensive Blood Sugar Strategy
While exploring does garlic help lower blood sugar, remember it's just one component of effective management. The most successful approaches combine:
- Moderate garlic consumption (1-2 cloves daily or equivalent supplement)
- Regular physical activity (150 minutes weekly)
- Carbohydrate-controlled eating pattern
- Consistent medication adherence when prescribed
- Regular blood sugar monitoring
A 2023 study in Diabetes Care found participants who combined garlic supplementation with lifestyle changes achieved 23% greater improvement in HbA1c than those using either approach alone. This suggests garlic works best as part of a multifaceted strategy rather than a standalone solution for blood sugar control.
When to Consult Your Healthcare Provider
Before making significant changes to your blood sugar management routine, discuss with your healthcare provider if:
- You take diabetes medications (risk of hypoglycemia)
- You have kidney disease (garlic metabolism considerations)
- You're pregnant or breastfeeding
- You notice unexplained blood sugar fluctuations
Regular monitoring remains essential—don't substitute garlic for proven medical treatments. The American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists emphasizes that "natural approaches should complement, not replace, evidence-based diabetes care."










 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4