When you're wondering why is sweet potato good for you, the answer lies in its remarkable nutritional composition that supports multiple aspects of health. Unlike refined carbohydrates, sweet potatoes provide sustained energy while delivering essential vitamins and minerals your body needs to function optimally.
Nutritional Powerhouse: What Makes Sweet Potatoes Special
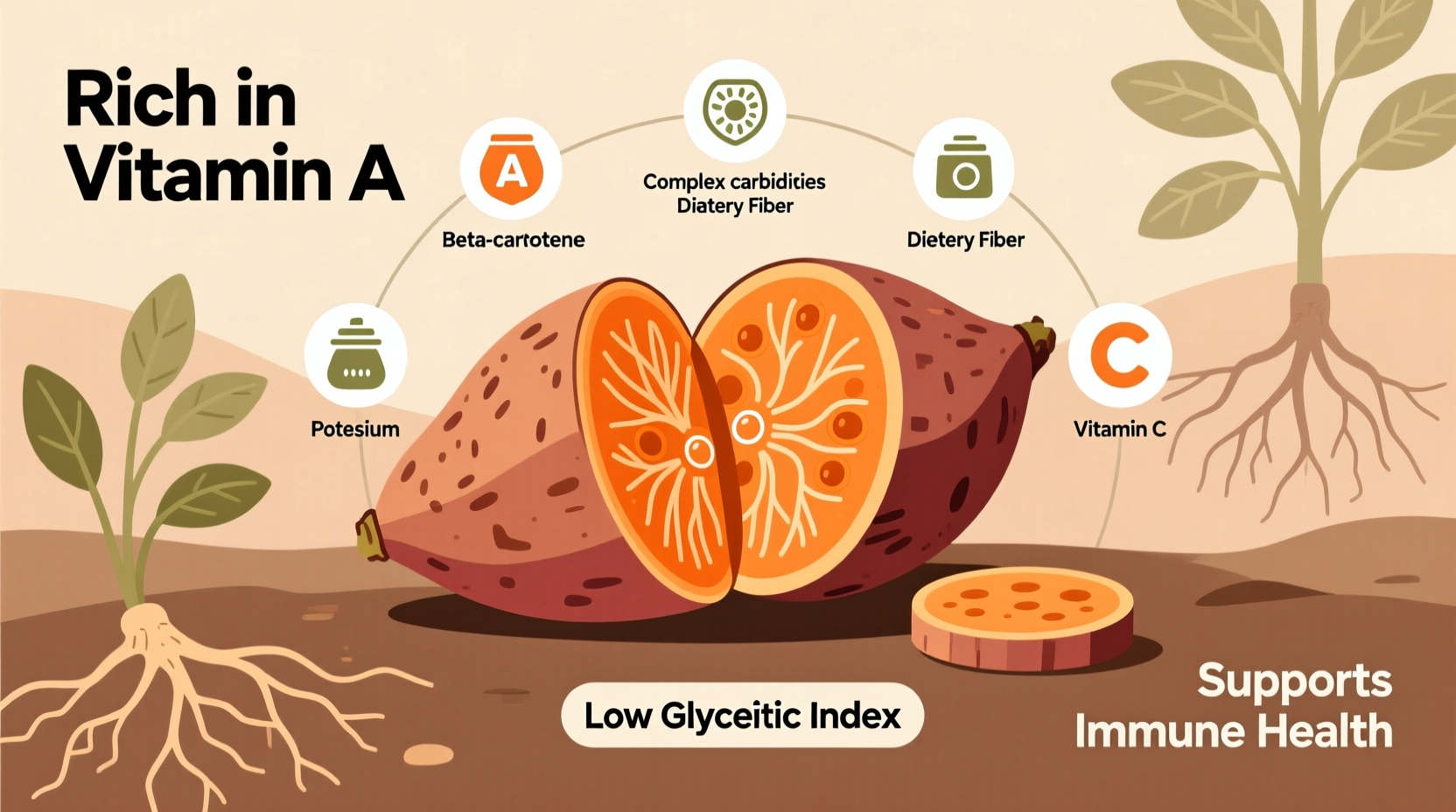
Sweet potatoes stand out among root vegetables for their exceptional nutrient density. A single medium sweet potato (about 130g) provides:
| Nutrient | Amount per Medium Sweet Potato | Daily Value % |
|---|---|---|
| Vitamin A (as beta-carotene) | 21,907 IU | 438% |
| Vitamin C | 22.3 mg | 25% |
| Fiber | 3.8 g | 15% |
| Potassium | 542 mg | 16% |
| Manganese | 0.6 mg | 28% |
According to USDA FoodData Central, sweet potatoes contain significantly more beta-carotene than white potatoes, which explains their vibrant orange color and exceptional vitamin A benefits. This nutrient profile makes sweet potatoes particularly valuable for those seeking natural ways to boost immune system function through diet.

Blood Sugar Management: Better Than You Think
Many people mistakenly believe that sweet potatoes will spike blood sugar, but research tells a different story. The glycemic index (GI) of sweet potatoes varies significantly based on preparation method:
- Boiled sweet potato: GI of 44 (low)
- Baked sweet potato: GI of 94 (high)
- Cooling boiled sweet potato: GI drops to 32 (very low)
This explains why sweet potatoes are good for blood sugar control when prepared properly. The American Diabetes Association notes that cooling cooked sweet potatoes increases their resistant starch content, which slows glucose absorption. This makes them an excellent carbohydrate choice for people managing diabetes when prepared as part of a balanced meal.
Vision Health: The Beta-Carotene Connection
The vibrant orange color of sweet potatoes comes from beta-carotene, which your body converts to vitamin A—essential for maintaining healthy vision. Just one medium sweet potato provides more than your entire daily requirement of vitamin A.
Research published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition shows that populations with higher beta-carotene intake have a 35% lower risk of developing age-related macular degeneration. This explains why sweet potatoes are good for eye health and why they've been traditionally valued in indigenous Latin American cultures where vision health was critical for survival.
Immune System Support: Beyond Vitamin C
While vitamin C often gets credit for immune support, sweet potatoes offer a more comprehensive approach. The combination of vitamin A, vitamin C, and antioxidants like anthocyanins (in purple varieties) creates a powerful defense system.
A study from the National Institutes of Health found that adequate vitamin A intake reduces the risk of respiratory infections by 24%. This is particularly relevant when considering why sweet potatoes are good for immune system function, especially during cold and flu season. The fiber content also supports gut health, which houses 70% of your immune system.
Digestive Health Benefits You Should Know
The fiber content in sweet potatoes works in two important ways for digestive health:
- Soluble fiber forms a gel-like substance that slows digestion and helps regulate blood sugar
- Insoluble fiber adds bulk to stool and promotes regular bowel movements
According to the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, consuming adequate fiber reduces the risk of diverticular disease by 40%. This explains why sweet potatoes are good for digestion and why they've been used traditionally in many cultures to support gut health. The resistant starch formed when cooled also serves as food for beneficial gut bacteria.
Heart Health Advantages Backed by Research
Sweet potatoes contribute to cardiovascular health through multiple mechanisms:
- Potassium content helps regulate blood pressure
- Fiber reduces LDL ("bad") cholesterol levels
- Antioxidants reduce inflammation in blood vessels
The American Heart Association recognizes potassium-rich foods like sweet potatoes as important components of a heart-healthy diet. Research shows that increasing potassium intake while reducing sodium can lower blood pressure by 4-5 mm Hg in hypertensive individuals. This is a key reason why sweet potatoes are good for heart health and overall cardiovascular function.
Practical Tips for Maximizing Sweet Potato Benefits
To get the most health benefits from sweet potatoes, consider these evidence-based preparation methods:
- Boil instead of bake to maintain a lower glycemic index
- Cool cooked sweet potatoes before eating to increase resistant starch
- Keep the skin on for extra fiber and nutrients (just wash thoroughly)
- Pair with healthy fats like olive oil to enhance absorption of fat-soluble vitamins
- Avoid excessive added sugars that negate blood sugar benefits
These preparation techniques address common concerns about why sweet potatoes might not be good for you when prepared improperly. The cooking method significantly impacts their nutritional profile and health effects.
Sweet Potato vs. Regular Potato: Making the Right Choice
When deciding between sweet potatoes and white potatoes, consider these nutritional differences:
| Nutrient | Sweet Potato (130g) | White Potato (130g) |
|---|---|---|
| Vitamin A | 438% DV | 0% DV |
| Vitamin C | 25% DV | 20% DV |
| Fiber | 15% DV | 10% DV |
| Glycemic Index (boiled) | 44 | 78 |
| Antioxidant Content | Very High | Moderate |
This comparison shows why sweet potatoes are better than regular potatoes for most health goals, particularly for blood sugar management and vitamin intake. Both can be part of a healthy diet, but sweet potatoes offer superior nutritional benefits for most people.
Addressing Common Sweet Potato Concerns
Some people worry about sweet potatoes being too high in carbohydrates, but the quality of these carbs matters significantly. The complex carbohydrates in sweet potatoes provide sustained energy without the blood sugar spikes associated with refined carbs.
For those concerned about weight management, sweet potatoes actually support healthy weight loss due to their high fiber content, which promotes satiety. A study in the Journal of Nutrition and Metabolism found that participants who included sweet potatoes in their diet reported greater fullness and consumed fewer calories throughout the day.










 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4