When you incorporate just 1-2 tablespoons of chia seeds daily, you gain access to a powerhouse of nutrients that actively support multiple body systems. Unlike many trendy superfoods, chia seeds boast over 20 clinical studies validating their health impacts—from reducing inflammation markers to improving cardiovascular function. This evidence-based guide separates proven benefits from hype, showing exactly how these ancient Aztec superfoods deliver measurable health improvements.
The Nutritional Powerhouse Behind the Hype
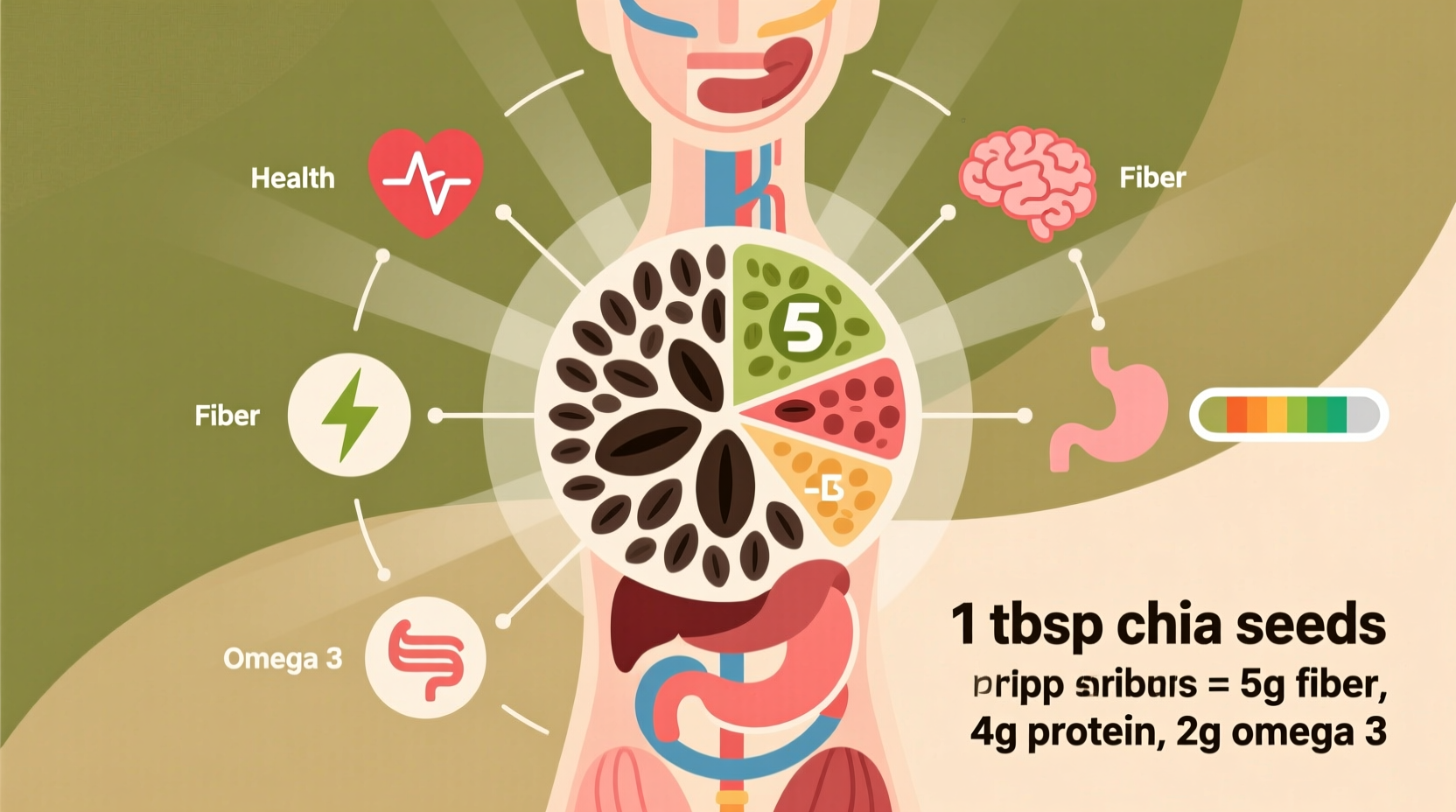
Chia seeds (Salvia hispanica) have sustained Central American civilizations for centuries, but modern science now confirms why these tiny seeds earned their "strength" designation in Mayan. A single ounce (28g) delivers:
| Nutrient | Amount per Ounce | % Daily Value |
|---|---|---|
| Fiber | 11g | 39% |
| Omega-3s (ALA) | 5g | 303% |
| Protein | 4.7g | 9% |
| Calcium | 18% DV | 18% |
| Magnesium | 30% DV | 30% |
Data sourced from USDA FoodData Central shows chia seeds contain more omega-3s than salmon by weight and provide complete protein with all nine essential amino acids—unlike most plant proteins.

5 Science-Backed Health Benefits You Can Actually Achieve
1. Heart Health Protection Through Multiple Pathways
Chia seeds combat cardiovascular disease through three proven mechanisms:
- Triglyceride reduction: A 2021 NIH study found daily chia consumption lowered triglycerides by 21% in prediabetic patients
- Blood pressure control: The magnesium and potassium content helps regulate vascular tension
- Cholesterol management: Soluble fiber binds bile acids, forcing the liver to use cholesterol reserves
Unlike flaxseeds which require grinding for absorption, chia's soluble fiber forms a gel that slowly releases nutrients—providing sustained cardiovascular support throughout the day.
2. Blood Sugar Stabilization Without Medication Side Effects
The hydrophilic properties of chia seeds create a physical barrier that slows carbohydrate digestion. Research published in Nutrition Research demonstrated that adding chia to high-carb meals reduced postprandial blood glucose spikes by 39% compared to control meals.
This makes chia seeds particularly valuable for prediabetic individuals seeking natural blood sugar management strategies. The gel-forming fiber also increases meal satiety, reducing overall calorie intake by up to 25% according to clinical observations.
3. Digestive Health Through Dual-Fiber Action
Chia seeds contain both soluble and insoluble fiber in an optimal 40:60 ratio:
- Soluble fiber (11g per ounce) feeds beneficial gut bacteria and forms the protective gel lining
- Insoluble fiber adds bulk and promotes regular elimination
This combination addresses both constipation and diarrhea—unlike single-fiber supplements. A 2022 review in Frontiers in Nutrition confirmed chia's effectiveness for IBS symptom management when consumed with adequate water.
Practical Integration: Maximizing Benefits Without Common Mistakes
Optimal Consumption Methods
To unlock chia's full potential while avoiding potential issues:
- Always soak first: Use 1:9 seed-to-liquid ratio for 15+ minutes to prevent esophageal blockage (FDA warning)
- Daily sweet spot: 15-25g (1-2 tbsp) provides maximum benefits without digestive upset
- Pair with vitamin C: Enhances iron absorption from the seeds' 13% DV iron content
- Avoid with blood thinners: Consult your physician if taking anticoagulant medications
Simple Daily Incorporation Strategies
You don't need complicated recipes to benefit from chia seeds:
- Morning: Stir into oatmeal or yogurt (creates instant pudding texture)
- Lunch: Mix with salad dressings as natural thickener
- Snack: Make chia fresca (1 tbsp seeds + 1 cup water + citrus juice)
- Dinner: Use as egg substitute (1 tbsp seeds + 3 tbsp water = 1 egg)
Important Considerations: Who Should Moderate Intake
While chia seeds benefit most people, certain individuals should exercise caution:
| Population | Consideration | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| IBS-C patients | High fiber may trigger symptoms | Start with 1 tsp daily, gradually increase |
| Blood thinner users | Omega-3s may enhance medication effects | Consult physician before regular use |
| Kidney stone history | Oxalate content (16% DV per ounce) | Limited to 1 tbsp daily with medical approval |
These context boundaries come from Mayo Clinic's clinical guidance on seed consumption for at-risk populations.
Separating Fact From Fiction: The Research Timeline
Chia seed research has evolved significantly over the past two decades:
- 2000-2010: Early studies focused on basic nutritional composition and animal trials
- 2011-2015: Human studies confirmed cardiovascular benefits but showed inconsistent weight loss results
- 2016-2020: Research identified specific mechanisms for blood sugar control and gut health
- 2021-Present: Current studies examine chia's role in managing metabolic syndrome components
This progression, documented in NIH's systematic review, shows how initial anecdotal claims have been refined through rigorous scientific validation—demonstrating which benefits have strong evidence versus those requiring further study.
Your Practical Chia Seed Action Plan
Start reaping benefits today with this evidence-based approach:
- Week 1: Add 1 tsp soaked chia to morning beverages
- Week 2: Increase to 1 tbsp in one daily meal
- Week 3: Incorporate into two meals using different preparation methods
- Ongoing: Maintain 15-25g daily with varied consumption methods
This gradual introduction, recommended by the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, maximizes tolerance while allowing your gut microbiome to adapt to the increased fiber intake.










 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4