Discover exactly which vitamins power this nutritional powerhouse and how they benefit your health. Whether you're blending it into smoothies, sautéing it with garlic, or adding it to salads, understanding spinach's vitamin profile helps you maximize its health benefits in your daily diet.
Vitamin Breakdown: What Vitamins Are in Spinach?
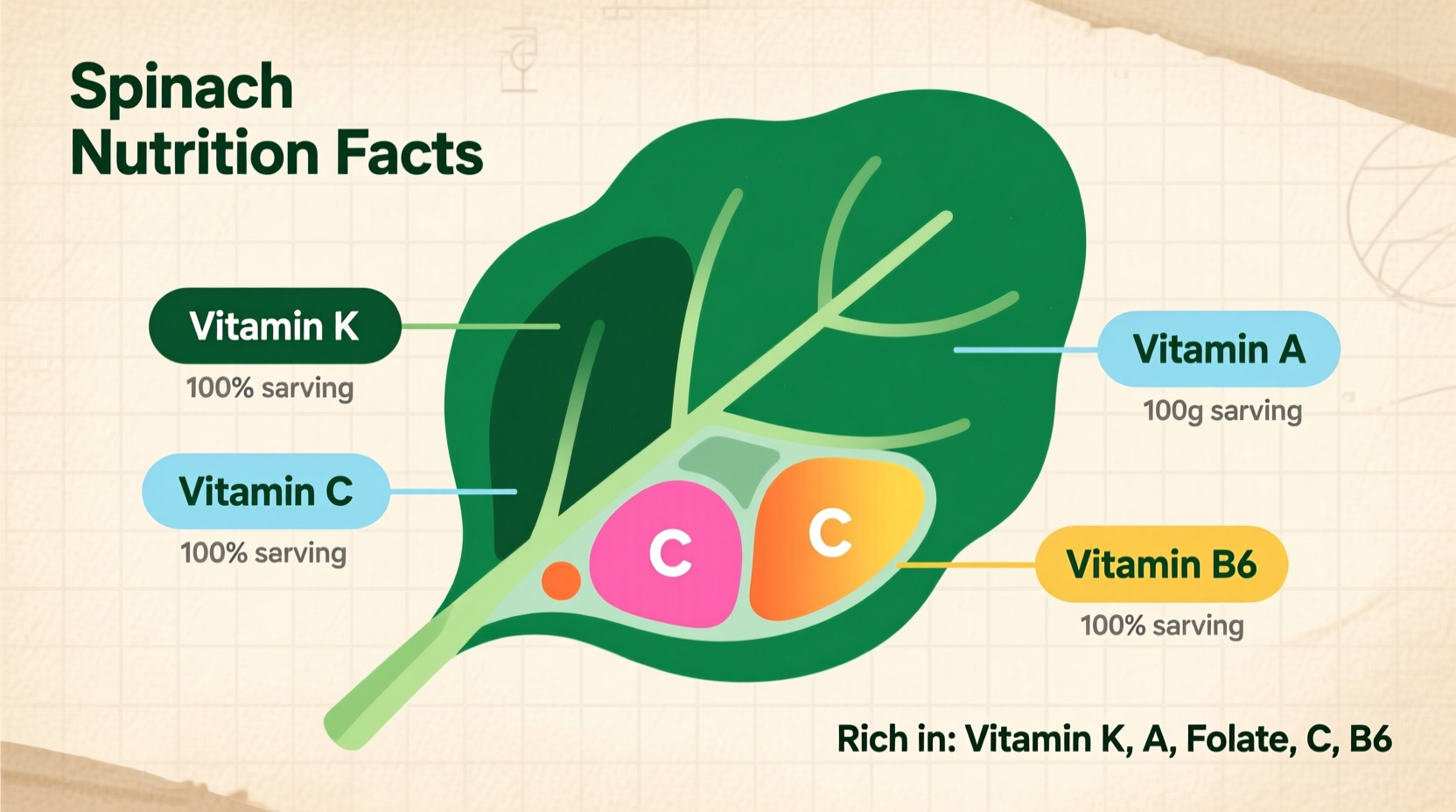
Spinach earns its "superfood" status through an impressive vitamin profile. According to USDA FoodData Central, a 100g serving of raw spinach contains:
| Vitamin | Amount per 100g | % Daily Value |
|---|---|---|
| Vitamin K1 | 482.9 mcg | 402% |
| Vitamin A (RAE) | 469 mcg | 52% |
| Folate (B9) | 194 mcg | 49% |
| Vitamin C | 28.1 mg | 31% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.195 mg | 11% |
| Vitamin E | 2.03 mg | 13% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.189 mg | 14% |
These values come from the USDA FoodData Central, the authoritative source for U.S. nutrient composition data. Notice how vitamin K1 dominates spinach's nutritional profile—that's why it's particularly valuable for bone health and blood clotting.

Why Spinach's Vitamin Profile Stands Out
When comparing spinach to other leafy greens, its vitamin density becomes even more impressive:
| Vitamin | Spinach (per 100g) | Kale (per 100g) | Romaine (per 100g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamin K | 482.9 mcg | 389.6 mcg | 102.5 mcg |
| Vitamin A | 469 mcg RAE | 680 mcg RAE | 209 mcg RAE |
| Vitamin C | 28.1 mg | 93.4 mg | 12.1 mg |
| Folate | 194 mcg | 141 mcg | 136 mcg |
This comparison, based on NIH Office of Dietary Supplements data, shows spinach's unique nutritional advantages. While kale contains more vitamin C, spinach provides significantly more vitamin K and folate than its cruciferous counterpart.
Vitamin K: Spinach's Superpower
Spinach contains more vitamin K per serving than almost any other food. This fat-soluble vitamin plays several critical roles:
- Essential for proper blood clotting (coagulation)
- Supports bone mineralization and density
- May help prevent arterial calcification
A single cup (30g) of raw spinach provides over 100% of your daily vitamin K requirement. For those on blood thinners like warfarin, consistent daily intake is crucial—sudden increases or decreases can interfere with medication effectiveness. The National Institutes of Health recommends discussing dietary changes with your healthcare provider if you're taking anticoagulants.
Maximizing Vitamin Absorption from Spinach
How you prepare spinach dramatically affects vitamin availability. Understanding these context boundaries helps you get the most nutritional value:
Cooking Methods Matter
- Raw spinach: Best for preserving vitamin C (which degrades with heat)
- Lightly cooked spinach: Increases bioavailability of vitamins A and K (cooking breaks down cell walls)
- Sautéed with healthy fats: Fat-soluble vitamins (A, E, K) absorb better when consumed with fats
Research published in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry confirms that steaming spinach preserves more nutrients than boiling. When boiled, water-soluble vitamins like vitamin C and folate leach into the cooking water.
Smart Food Pairings
Combine spinach with these foods to boost vitamin absorption:
- Lemon juice or vinegar: The acidity increases non-heme iron absorption
- Olive oil or avocado: Enhances absorption of fat-soluble vitamins
- Vitamin C-rich foods: Like bell peppers or citrus, which improve iron uptake
Practical Ways to Incorporate Spinach for Maximum Vitamin Benefits
Knowing what vitamins are in spinach is only valuable if you can effectively include them in your diet. Here's how to optimize your spinach consumption:
Daily Vitamin Targets
To meet daily vitamin requirements through spinach alone:
- Vitamin K: Just 15g (½ cup raw) meets 100% of daily needs
- Vitamin A: Approximately 100g (3.5oz raw) provides 52% of daily needs
- Folate: About 50g (1.8oz raw) delivers 25% of daily needs
Simple Preparation Tips
- Add raw spinach to smoothies (vitamin C preservation)
- Sauté with garlic and olive oil for enhanced vitamin K absorption
- Use in omelets—eggs provide fat for better nutrient uptake
- Make spinach pesto instead of traditional basil pesto
- Add to soups during the last 2 minutes of cooking to preserve nutrients
Spinach Nutrition Through the Seasons
Spinach's vitamin content varies slightly depending on growing conditions and season:
- Spring spinach: Typically higher in folate and vitamin C
- Winter spinach: Often contains more vitamin K due to slower growth
- Frozen spinach: Nutrient levels remain stable and may even exceed fresh spinach in some vitamins due to flash-freezing at peak ripeness
A study from the USDA Agricultural Research Service found that properly frozen spinach retains 90-95% of its vitamin content for up to 12 months, making it a reliable year-round option.










 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4