When you're wondering what nutrients are in celery, you're tapping into one of nature's most underrated nutritional powerhouses. This crisp, refreshing vegetable offers far more than just crunch—it delivers essential vitamins, minerals, and plant compounds that contribute significantly to overall wellness. Understanding celery's complete nutritional profile helps you make informed dietary choices that support hydration, inflammation management, and cellular protection.
The Complete Nutritional Breakdown of Celery
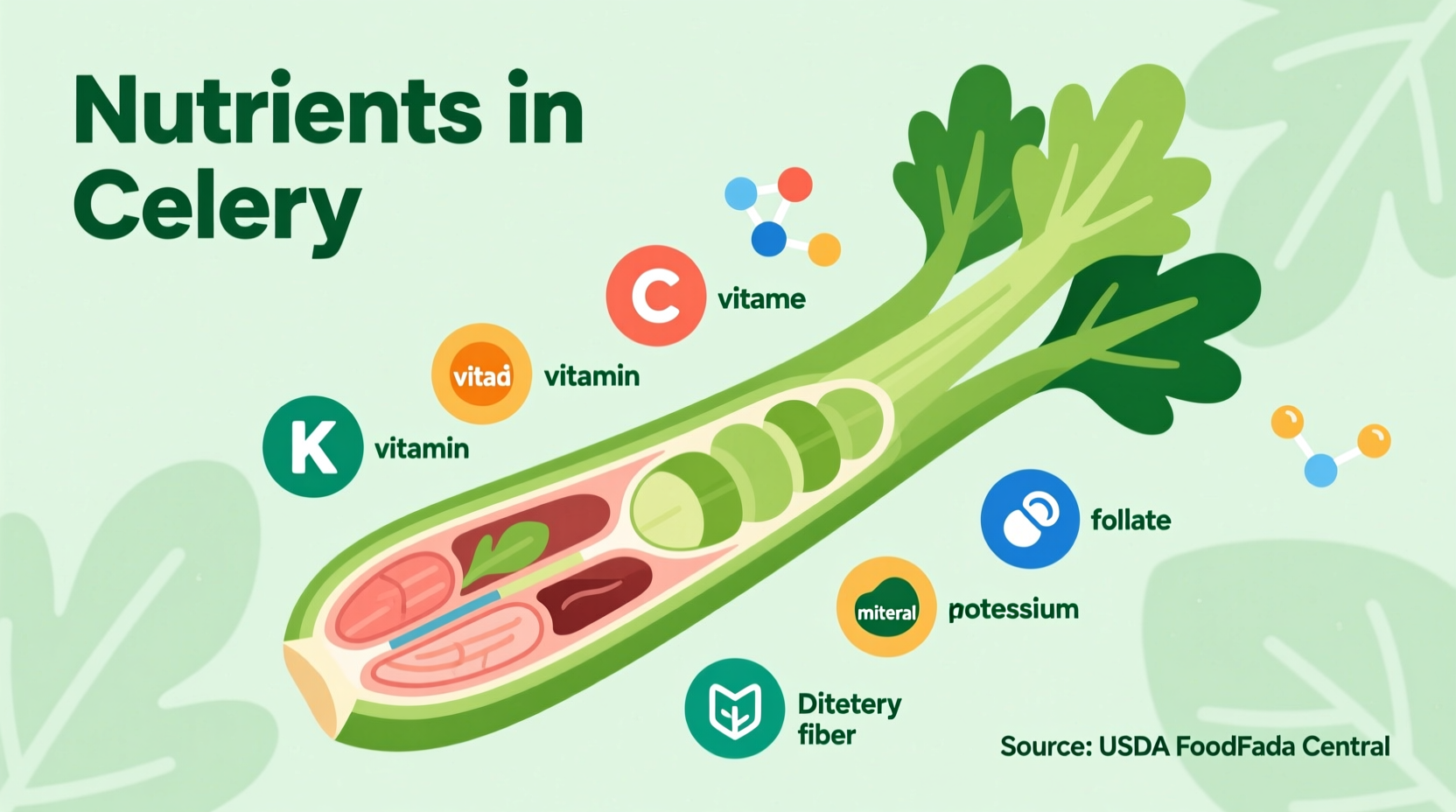
Let's examine exactly what you get when you add celery to your plate. The USDA FoodData Central provides the most current, scientifically verified nutritional information for raw celery. This data represents one cup (101g) of chopped celery—the perfect serving size for snacks, salads, or cooking.
| Nutrient | Amount per Cup | Daily Value % | Key Health Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calories | 16 | 1% | Low-energy density for weight management |
| Vitamin K | 32.2 mcg | 27% | Bone health and blood clotting regulation |
| Vitamin A | 453 IU | 9% | Eye health and immune function support |
| Vitamin C | 3.2 mg | 5% | Antioxidant protection and collagen synthesis |
| Folate | 36.4 mcg | 9% | Cellular function and DNA synthesis |
| Potassium | 260 mg | 7% | Blood pressure regulation and muscle function |
| Fiber | 1.6 g | 6% | Digestive health and satiety enhancement |
This nutritional profile comes with celery's remarkable 95% water content, making it an exceptional hydrating food. Unlike many vegetables, celery maintains its crisp texture while delivering these essential nutrients with minimal caloric impact—perfect for those seeking nutrient-dense, low-calorie options.
Unique Phytonutrients That Set Celery Apart
Beyond standard vitamins and minerals, celery contains specialized plant compounds that contribute to its health-promoting properties. Research published in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry identifies several key phytonutrients:
- Apigenin—a flavonoid with demonstrated anti-inflammatory properties that may support cellular health
- Luteolin—another flavonoid showing promise in laboratory studies for its antioxidant effects
- Phthalides—unique compounds responsible for celery's distinctive aroma that may support healthy blood pressure levels
These compounds work synergistically with the vitamins and minerals in celery, creating what nutrition researchers call the "food matrix effect"—where the complete nutritional package delivers greater benefits than isolated nutrients alone.

Practical Applications: Maximizing Celery's Nutritional Benefits
Knowing what nutrients are in celery is just the beginning—you'll want to incorporate it effectively into your diet. Here's how to get the most from this versatile vegetable:
Preserving Nutrient Content During Preparation
Celery's water-soluble vitamins (like vitamin C and folate) can leach out when exposed to excessive water or heat. To maximize retention:
- Wash celery just before use rather than soaking it
- Use the leaves! They contain higher concentrations of nutrients than the stalks
- When cooking, use minimal water and shorter cooking times
- Pair with healthy fats (like olive oil) to enhance absorption of fat-soluble vitamins
Creative Ways to Include More Celery
Move beyond basic snacks with these nutritionist-approved suggestions:
- Add finely chopped celery to tuna or chicken salad for crunch without extra calories
- Blend celery leaves into green smoothies for added nutrients without strong flavor
- Use celery stalks as edible utensils for hummus or nut butter dips
- Include in vegetable broth for depth of flavor and additional nutrients
- Try celery juice as part of a balanced morning routine (though whole celery provides more fiber)
Contextual Considerations: When Celery Fits Your Needs
While celery offers impressive nutritional benefits, it's important to understand its limitations within a balanced diet. Unlike leafy greens such as spinach or kale, celery doesn't provide significant amounts of iron or calcium. Its vitamin C content, while present, is substantially lower than citrus fruits or bell peppers.
For individuals managing certain health conditions, celery's natural sodium content (about 80mg per cup) might require consideration, though this remains significantly lower than processed foods. Those on blood thinners should maintain consistent vitamin K intake, which celery contributes to significantly.
Evolution of Nutritional Understanding
Our appreciation of celery's nutritional value has evolved considerably. Historically valued primarily as a flavor enhancer, modern analytical techniques have revealed its complex phytochemical profile. Research published in Nutrients journal shows that early nutritional analyses focused mainly on basic vitamins and minerals, while contemporary science recognizes the importance of celery's unique phthalides and flavonoids.
This progression mirrors broader shifts in nutritional science—from isolating individual nutrients to understanding whole-food synergies. What was once considered merely a low-calorie filler now earns recognition as a functional food with specific health-promoting properties.
How Celery Compares to Similar Vegetables
Understanding what nutrients are in celery becomes more valuable when compared to similar vegetables. While celery shares characteristics with other crunchy vegetables, its nutritional profile has distinctive features:
- Compared to cucumbers: Celery provides significantly more vitamin K and potassium, though both are excellent hydrating options
- Compared to bell peppers: Peppers offer much higher vitamin C, but celery provides more consistent vitamin K across varieties
- Compared to carrots: Carrots excel in beta-carotene, while celery offers superior hydration with fewer calories
This comparative perspective helps you strategically incorporate celery into your diet based on specific nutritional goals rather than viewing it as a generic vegetable option.
Answering Common Questions About Celery Nutrition
Many people have specific questions about incorporating celery into their nutrition plans. Let's address some frequent inquiries with evidence-based information.










 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4