Your Complete Guide to Keto-Friendly Foods
If you're starting a ketogenic diet, knowing exactly what foods support ketosis is crucial for success. This science-backed guide delivers a comprehensive, practical food list that helps you maintain ketosis while enjoying delicious, satisfying meals. No confusing jargon—just clear information you can use immediately.
Why Food Selection Matters on Keto
The ketogenic diet works by shifting your body from burning glucose to burning fat for energy—a state called ketosis. To maintain this metabolic state, you need to limit carbohydrates to 20-50 grams per day. This strict carb limit means every food choice counts. Unlike other diets, keto requires precise food selection based on macronutrient composition rather than just calories.

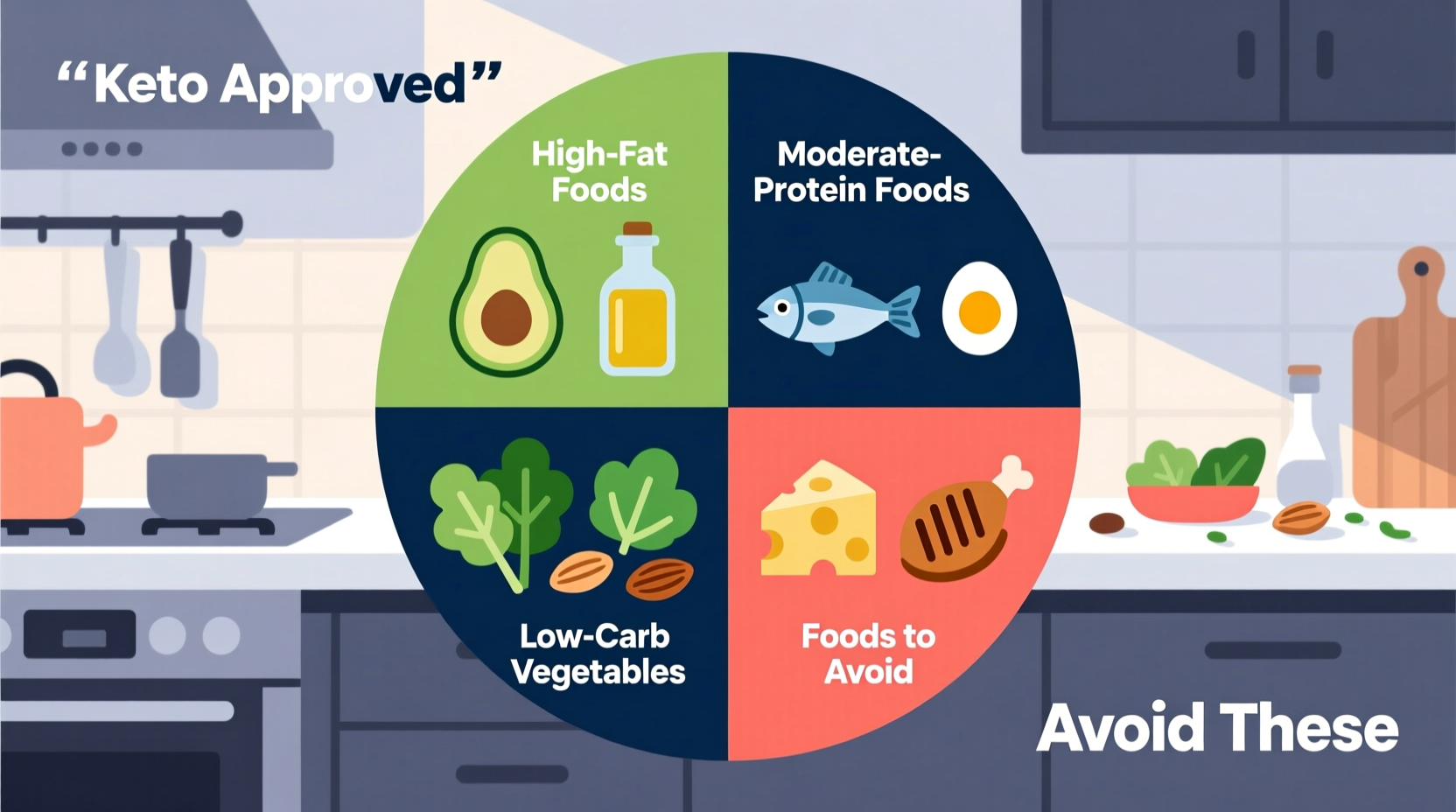
Keto Food Categories: What to Eat
| Food Category | Keto-Friendly Options | Carb Count (per 100g) |
|---|---|---|
| Proteins | Beef, chicken, pork, lamb, turkey | <1g |
| Fatty Fish | Salmon, mackerel, sardines, herring | <0g |
| Low-Carb Veggies | Spinach, broccoli, asparagus, zucchini | 1-5g |
| Healthy Fats | Olive oil, avocado oil, butter, ghee | 0g |
| Dairy | Hard cheeses, heavy cream, full-fat yogurt | 1-4g |
This comparison reflects standard nutritional data from the USDA FoodData Central, the authoritative source for nutrient composition information. The carb counts shown represent net carbs (total carbs minus fiber), which is the measurement that matters for keto dieters.
Building Balanced Keto Meals
Creating satisfying keto meals follows a simple formula: 70-80% of calories from fat, 20-25% from protein, and 5-10% from carbohydrates. A practical approach is to fill half your plate with low-carb vegetables, one-quarter with quality protein, and one-quarter with healthy fats.
For example, a perfect keto dinner might include:
- Grilled salmon (protein)
- Asparagus sautéed in butter (vegetable + fat)
- Side salad with olive oil dressing (additional fat)
Foods That Will Break Ketosis
Certain foods contain hidden carbohydrates that can quickly exceed your daily limit. Be especially careful with:
- Sugary foods: soda, fruit juice, cake, candy
- Grains: wheat, rice, oats, cereal
- Starchy vegetables: potatoes, sweet potatoes, peas
- Most fruits: bananas, apples, oranges (berries in moderation are acceptable)
- "Low-fat" products that often contain added sugars
Many processed "keto-friendly" products on the market contain sugar alcohols or artificial ingredients that may affect individuals differently. Always check nutrition labels for total carbohydrates and serving size.
Practical Keto Shopping Strategy
Streamline your grocery shopping with this perimeter approach: focus on the outer aisles of the store where fresh foods are located. Fill your cart with:
- Meat and seafood counter items
- Fresh low-carb vegetables
- Dairy section items like cheese and heavy cream
- Healthy oils and vinegars from the condiment aisle
Minimize time in the center aisles where processed foods dominate. When you do venture there, stick to specific items like canned fish, olives, or nuts—always checking carb content.
When Keto Might Not Be Appropriate
While effective for many people, the ketogenic diet isn't suitable for everyone. According to the Mayo Clinic, individuals with certain medical conditions should avoid keto or consult their physician first:
- People with pancreatitis
- Those with liver failure
- Individuals with disorders of fat metabolism
- People with kidney disease
- Those with a history of eating disorders
Pregnant or breastfeeding women should also consult healthcare providers before starting keto, as nutritional requirements change during these periods.
Common Keto Food Mistakes to Avoid
Even experienced keto dieters sometimes make these critical errors:
- Overeating protein: Excess protein can convert to glucose through gluconeogenesis
- Neglecting electrolytes: Low-carb diets cause increased excretion of sodium, potassium, and magnesium
- Forgetting hidden carbs: Sauces, dressings, and processed meats often contain sugar
- Not drinking enough water: Keto has a natural diuretic effect requiring increased hydration
Tracking your food intake for the first few weeks helps identify unexpected carb sources and ensures you're hitting your macronutrient targets.
Making Keto Sustainable Long-Term
The most successful keto dieters focus on whole, unprocessed foods rather than relying on specialty products. Incorporate variety by rotating different protein sources and experimenting with new low-carb vegetables each week. Meal prepping helps maintain consistency, especially during busy workweeks.
Remember that keto isn't just about restriction—it's about embracing delicious, nutrient-dense foods that support your health goals. With proper planning, you can enjoy satisfying meals while maintaining ketosis.










 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4