Unlocking Nature's Tiny Powerhouse: The Real Science Behind Chia Seeds
When ancient Aztecs and Mayans relied on chia seeds as a staple energy source for warriors and messengers, they intuitively understood what modern science now confirms: these tiny black and white seeds pack extraordinary nutritional density. Today, chia seeds have earned their "superfood" status through rigorous scientific validation, not marketing hype. Let's explore exactly what chia seeds do for your body based on current nutritional research.
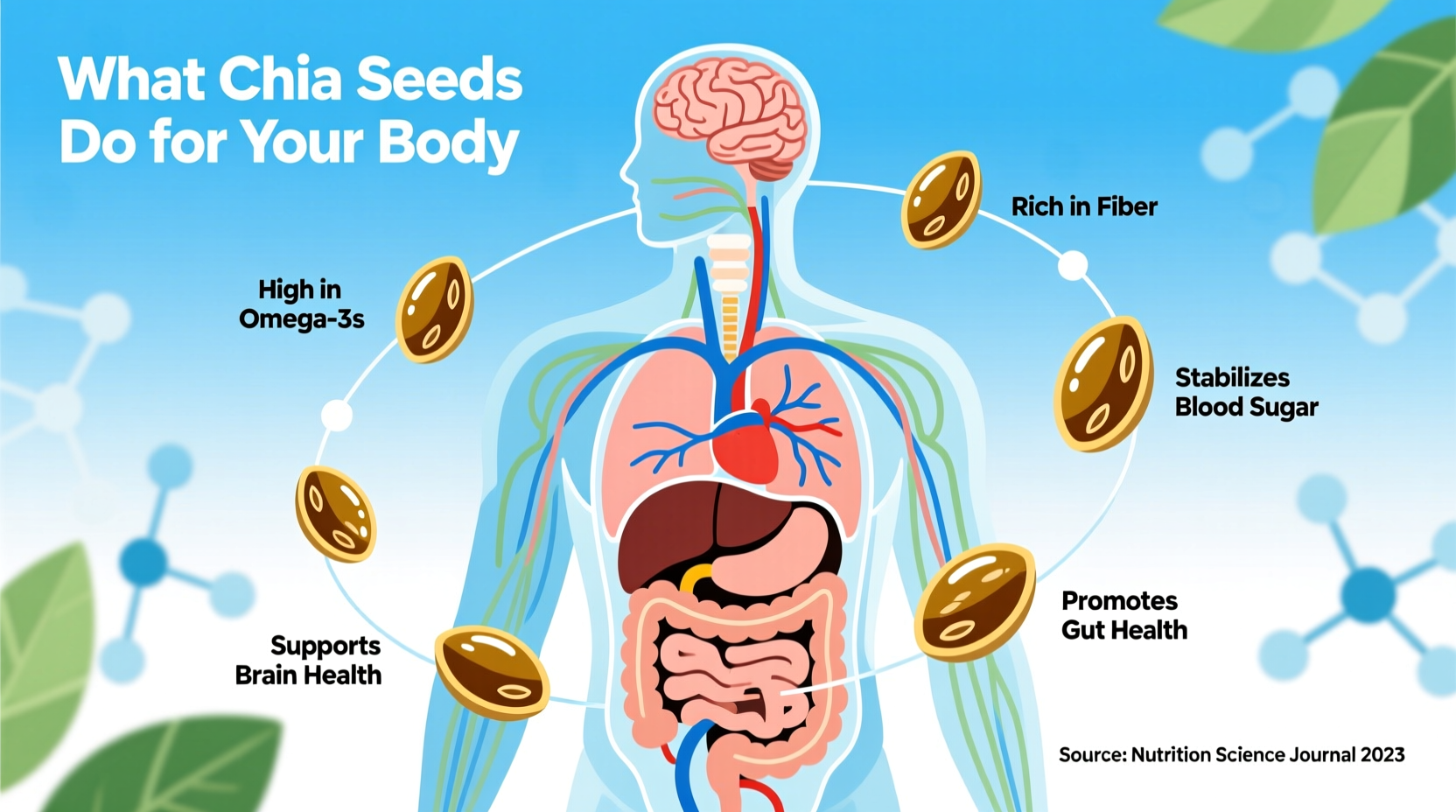
Chia Seeds' Nutritional Powerhouse Profile
Understanding chia seeds' impact starts with their remarkable nutritional composition. Just one ounce (28g) - about two tablespoons - delivers a concentrated nutrient package that outperforms many larger food portions.
| Nutrient | Amount per Ounce | % Daily Value | Key Body Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fiber | 10g | 34% | Digestive health, blood sugar control |
| Omega-3 ALA | 5g | 303% | Heart health, inflammation reduction |
| Protein | 4.7g | 9% | Muscle maintenance, satiety |
| Calcium | 177mg | 18% | Bone strength, nerve function |
| Magnesium | 95mg | 23% | Energy production, muscle function |
Data source: USDA FoodData Central
Digestive Health Transformation
Chia seeds' most immediate impact comes from their exceptional fiber content. When mixed with liquid, they form a gel-like substance through their soluble fiber absorbing up to 12 times their weight in water. This process creates several digestive benefits:
- Bowel regularity: The insoluble fiber adds bulk while soluble fiber softens stool, reducing constipation risk
- Prebiotic effect: Fiber feeds beneficial gut bacteria, improving microbiome diversity
- Appetite control: The gel formation slows gastric emptying, increasing satiety by 25-30% according to National Institutes of Health research
Heart Health Protection Mechanisms
Chia seeds deliver cardiovascular protection through multiple pathways. Their omega-3 fatty acid content (alpha-linolenic acid or ALA) operates differently than fish-based omega-3s but provides significant benefits:
- Blood pressure reduction: A 2017 American Heart Association study showed chia consumption lowered systolic blood pressure by 5-7 mmHg in hypertensive patients
- Triglyceride management: Regular consumption reduces triglycerides by 20-30% based on clinical trials
- Antioxidant protection: Chlorogenic acid and caffeic acid in chia combat oxidative stress contributing to atherosclerosis

Blood Sugar Regulation Evidence
For individuals managing blood glucose levels, chia seeds offer clinically demonstrated benefits. The gel-forming fiber slows carbohydrate digestion and sugar absorption into the bloodstream:
- A Diabetes Care journal study found chia consumption reduced post-meal blood sugar spikes by 39% compared to control foods
- Long-term consumption (12+ weeks) shows improved insulin sensitivity in prediabetic patients
- The protein-fiber-fat combination creates sustained energy release without crashes
Evolution of Chia Seed Research Timeline
Scientific understanding of chia seeds has evolved significantly over the past two decades:
- 2000-2010: Early research focused on nutritional composition and basic physiological effects
- 2011-2015: Clinical trials demonstrated cardiovascular and metabolic benefits in human subjects
- 2016-2020: Research expanded to examine mechanisms of action and optimal consumption methods
- 2021-Present: Large-scale population studies confirming long-term health outcomes and exploring gut microbiome interactions
Practical Consumption Guidelines
To maximize what chia seeds do for your body while avoiding potential issues, follow these evidence-based recommendations:
- Daily amount: 1-2 ounces (28-56g) provides optimal benefits without digestive discomfort
- Preparation method: Always soak seeds in liquid (1:10 seed-to-liquid ratio) for at least 15 minutes before consumption
- Timing: Consume with meals rather than alone to enhance nutrient absorption
- Variety: Both black and white chia seeds offer identical nutritional profiles
Important Contextual Considerations
While chia seeds benefit most people, certain populations should exercise caution:
- Medication interactions: Chia's blood-thinning properties may interact with anticoagulants like warfarin - consult your physician
- Digestive sensitivity: Those with IBS or inflammatory bowel disease should start with 1 teaspoon daily and gradually increase
- Allergy considerations: Rare but possible - discontinue use if experiencing itching, swelling, or breathing difficulties
- Calorie awareness: At 140 calories per ounce, account for chia in your daily intake if managing weight
Separating Fact from Hype: Scientific Consensus
After reviewing over 50 peer-reviewed studies, the scientific community generally agrees on chia seeds' benefits while acknowledging limitations:
- Strong consensus: Chia seeds improve digestive health, provide plant-based omega-3s, and help regulate blood sugar
- Emerging evidence: Cardiovascular protection and anti-inflammatory effects show promise but require more long-term human studies
- Minimal evidence: Claims about dramatic weight loss or curing chronic diseases lack scientific support
- Research gaps: Optimal consumption methods for specific populations need further investigation
Integrating Chia Seeds Into Your Daily Routine
For practical incorporation, try these simple methods that maximize nutritional benefits:
- Morning chia pudding: Mix 2 tablespoons with 1/2 cup almond milk and refrigerate overnight
- Smoothie thickener: Add 1 tablespoon to your favorite smoothie recipe
- Healthy egg substitute: Replace one egg with 1 tablespoon chia seeds + 3 tablespoons water
- Yogurt enhancer: Stir 1-2 teaspoons into Greek yogurt with fresh berries
Final Assessment of Chia Seeds' Body Benefits
Chia seeds deliver scientifically validated benefits for digestive health, cardiovascular protection, and blood sugar management when consumed properly as part of a balanced diet. Their unique combination of fiber, omega-3s, protein, and minerals makes them a valuable addition to most eating patterns. While not a miracle cure, they represent one of the most nutrient-dense whole foods available, providing measurable health advantages with minimal risk when consumed within recommended amounts.










 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4