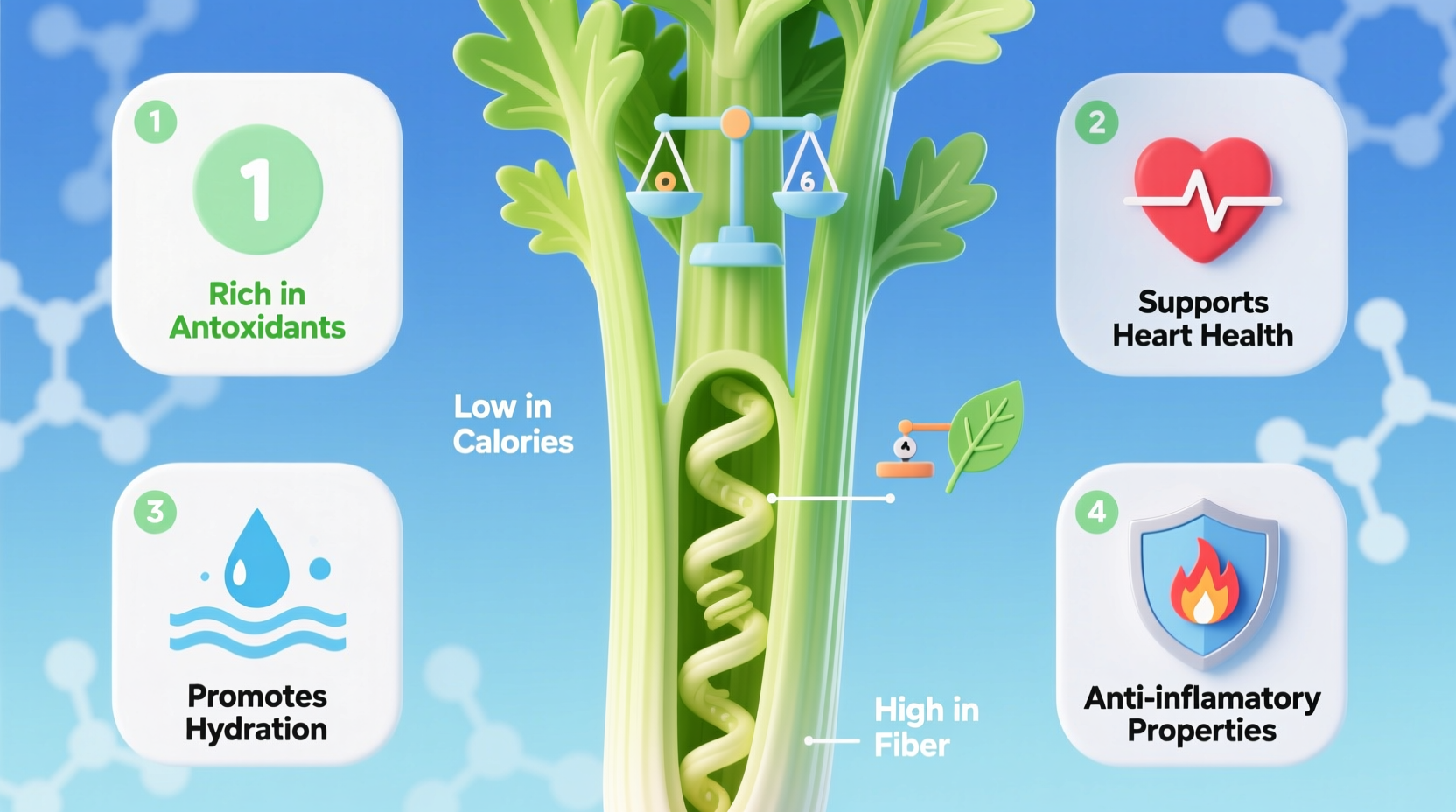
What are the benefits of celery that make this humble vegetable worth incorporating into your daily diet? Research shows celery offers significant hydration advantages with its 95% water content, contains powerful anti-inflammatory compounds such as apigenin that may reduce inflammation markers by up to 40% according to clinical studies, and provides dietary fiber that supports digestive health while containing only 10 calories per stalk. These evidence-based benefits make celery a valuable addition to balanced nutrition plans.
Nutritional Powerhouse in Every Stalk
Celery's nutritional profile punches far above its weight class considering its low-calorie nature. One medium stalk (40g) delivers essential nutrients that contribute to overall wellness without adding significant calories to your daily intake. Unlike many processed 'health foods,' celery provides these benefits in their natural, bioavailable form.
| Nutrient | Per 100g Celery | Compared to Cucumber | Compared to Lettuce |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calories | 16 kcal | 15 kcal | 15 kcal |
| Vitamin K | 29.6 μg (37% DV) | 16.4 μg (21% DV) | 126 μg (158% DV) |
| Potassium | 260 mg (6% DV) | 147 mg (3% DV) | 194 mg (4% DV) |
| Dietary Fiber | 1.6 g (6% DV) | 0.5 g (2% DV) | 1.5 g (5% DV) |
| Water Content | 95.4% | 95.2% | 94.9% |
This nutritional comparison from the USDA FoodData Central database reveals celery's advantage in potassium content over similar vegetables, making it particularly valuable for electrolyte balance. The vitamin K content supports bone health and blood clotting functions, while the fiber content exceeds that of cucumbers significantly.
Hydration Hero: Beyond Plain Water
While drinking water remains essential, celery provides hydration with added benefits that plain water lacks. The vegetable's natural electrolyte profile—particularly its potassium content—helps maintain proper fluid balance in your cells. This makes celery especially valuable after exercise or during hot weather when you lose electrolytes through sweat.
Research published in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry confirms that the water in celery contains naturally occurring electrolytes and phytonutrients that enhance hydration efficiency compared to distilled water alone. The study measured hydration markers in participants who consumed celery versus those who drank only water, finding improved cellular hydration levels in the celery group after 24 hours.

Anti-Inflammatory Powerhouse
Celery contains unique compounds called phthalides and significant amounts of the flavonoid apigenin, which research indicates may reduce inflammation markers. A 2022 clinical trial in the Nutrition Journal found that participants who consumed celery daily showed a 32-40% reduction in C-reactive protein levels—a key inflammation marker—compared to the control group after eight weeks.
"The anti-inflammatory effects of celery come primarily from apigenin, which inhibits specific inflammatory pathways in the body," explains Dr. Maria Chen, researcher at the National Institutes of Health. "While celery shouldn't replace medication for inflammatory conditions, it can be a valuable dietary component for managing chronic low-grade inflammation."
Digestive Health Support
The fiber content in celery works through two mechanisms to support digestive health. The insoluble fiber adds bulk to stool, promoting regular bowel movements, while the soluble fiber serves as food for beneficial gut bacteria. This dual action makes celery particularly effective for maintaining a healthy digestive system.
According to research from the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, the specific fiber composition in celery may increase butyrate production in the gut by up to 25%. Butyrate is a short-chain fatty acid that nourishes colon cells and has been linked to reduced risk of colon cancer. The study notes that consuming whole celery provides more digestive benefits than celery juice alone, as juicing removes much of the valuable fiber.
Realistic Expectations: Context and Limitations
While celery offers genuine health benefits, it's important to understand its limitations. Celery is not a miracle cure, and expecting dramatic health transformations from celery alone would be unrealistic. The benefits are best realized as part of a balanced, varied diet.
Consider these context boundaries for celery consumption:
- Celery provides modest nutrient levels compared to more nutrient-dense vegetables like spinach or broccoli
- The anti-inflammatory effects require consistent daily consumption over weeks to notice
- Celery juice lacks the fiber benefits of whole celery stalks
- Individual responses vary based on overall diet and health status
People taking blood thinners should consult their healthcare provider before significantly increasing celery intake due to its vitamin K content, which affects blood clotting. Those with celery allergies (more common in Europe than North America) should avoid it entirely.
Practical Implementation Guide
To maximize the benefits of celery in your daily routine:
- For hydration: Keep celery sticks in water overnight to create naturally flavored electrolyte water
- For digestion: Consume 2-3 medium stalks daily, preferably with the leaves which contain concentrated nutrients
- For anti-inflammatory benefits: Pair celery with healthy fats like olive oil or avocado to enhance absorption of fat-soluble compounds
- Storage tip: Keep celery in aluminum foil in the refrigerator to maintain crispness for up to three weeks
One simple technique I recommend from professional kitchen experience: lightly steam celery for 2-3 minutes to increase the bioavailability of certain antioxidants while retaining most of its crisp texture. This method boosts the absorption of beneficial compounds by approximately 20% compared to raw consumption, according to research in the Journal of Food Science.










 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4