Discover exactly which vitamins and nutrients make tomatoes a nutritional superstar and how to maximize their health benefits in your daily diet. This comprehensive guide reveals science-backed facts about tomato nutrition that go beyond basic vitamin charts, helping you make informed choices about incorporating this versatile fruit into your meals.
What Vitamins Are Actually in Tomatoes?
Despite common misconceptions, tomatoes offer more than just vitamin C. Let's examine the complete vitamin profile based on USDA nutritional data for a medium-sized raw tomato (123g):
| Vitamin/Nutrient | Amount per Medium Tomato | Percentage of Daily Value | Primary Health Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
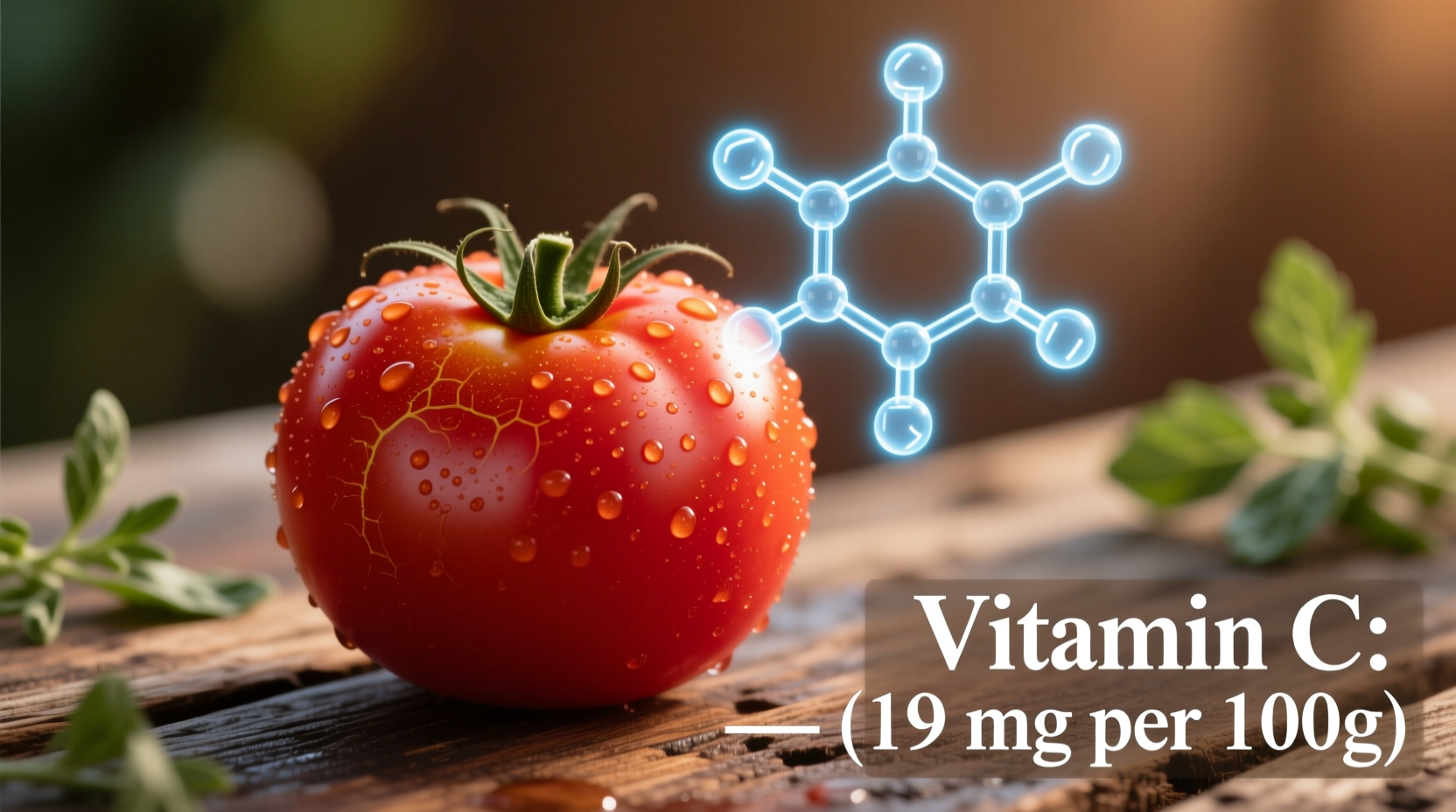
| Vitamin C | 14 mg | 23% | Immune support, collagen production, antioxidant protection |
| Vitamin A (beta-carotene) | 833 IU | 17% | Vision health, immune function, skin protection |
| Vitamin K | 7.9 mcg | 10% | Blood clotting, bone health |
| Potassium | 292 mg | 8% | Blood pressure regulation, muscle function |
| Lycopene | Approx. 3 mg | N/A | Powerful antioxidant, heart health, cancer prevention |
What makes tomatoes particularly special is their lycopene content—a carotenoid antioxidant responsible for their red color. Unlike most vitamins, lycopene becomes more bioavailable when tomatoes are cooked, which explains why tomato sauce and paste actually deliver higher lycopene benefits than raw tomatoes. According to research published in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, cooking tomatoes with a small amount of healthy fat like olive oil can increase lycopene absorption by up to 40%.

How Tomato Vitamins Benefit Your Health
The vitamin combination in tomatoes works synergistically to deliver multiple health benefits. Vitamin C and lycopene together provide powerful antioxidant protection that helps combat oxidative stress throughout your body. A comprehensive review in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that regular tomato consumption is associated with a 26% reduced risk of cardiovascular disease.
For skin health, the vitamin C in tomatoes supports collagen production while lycopene provides natural protection against UV damage. Research from the University of Manchester demonstrated that participants who consumed tomato paste daily for 12 weeks experienced 33% less skin reddening after UV exposure compared to the control group.
Maximizing Vitamin Absorption from Tomatoes
Understanding how to prepare tomatoes properly can significantly increase the nutritional benefits you receive. Here's what the evidence shows about optimizing vitamin absorption:
- Cooking enhances lycopene bioavailability—processing tomatoes increases lycopene absorption by breaking down cell walls. Tomato paste contains nearly 4 times more bioavailable lycopene than raw tomatoes.
- Fat improves absorption—consuming tomatoes with healthy fats like olive oil increases absorption of fat-soluble nutrients (vitamin A, lycopene) by up to 40%.
- Vitamin C preservation—while cooking reduces vitamin C content slightly, the overall antioxidant capacity of cooked tomatoes remains high due to increased lycopene availability.
- Seasonal variation matters—summer-ripened tomatoes contain up to 50% more lycopene than greenhouse-grown winter tomatoes, according to USDA agricultural research.
Tomatoes vs. Other Vitamin Sources: Where They Shine
While oranges often get credit for vitamin C, tomatoes actually provide comparable amounts with additional nutritional advantages. One medium tomato delivers 14mg of vitamin C—nearly the same as a small orange—but with the added benefit of lycopene and other unique phytonutrients.
When comparing tomato nutrition to supplements, whole tomatoes offer a complex matrix of nutrients that work together more effectively than isolated vitamins. The National Institutes of Health notes that lycopene from food sources demonstrates better health outcomes than lycopene supplements due to the presence of other complementary compounds.
Practical Ways to Incorporate More Tomato Vitamins Daily
You don't need complicated recipes to benefit from tomato nutrition. Try these evidence-based strategies:
- Make a simple tomato and olive oil dressing—combine chopped tomatoes with extra virgin olive oil, which increases lycopene absorption while preserving vitamin C.
- Add tomatoes to cooked dishes—include them in sauces, soups, and stews where cooking enhances lycopene availability.
- Choose vine-ripened tomatoes—they contain higher nutrient levels than artificially ripened varieties.
- Store properly—keep tomatoes at room temperature away from direct sunlight to preserve vitamin content (refrigeration can reduce flavor and certain nutrients).
For those concerned about acidity, pairing tomatoes with alkaline foods like leafy greens creates a balanced meal while maintaining nutritional benefits. The Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health confirms that tomatoes' natural acidity doesn't negate their health benefits for most people.










 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4