The Complete Nutritional Profile of Spinach
Spinach stands as one of nature's most nutrient-dense foods, offering remarkable nutritional value with minimal calories. According to the USDA FoodData Central database, a single cup (30g) of raw spinach contains just 7 calories while delivering essential vitamins and minerals that support multiple bodily functions.
| Nutrient | Raw Spinach (1 cup/30g) | % Daily Value | Cooked Spinach (½ cup/85g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calories | 7 | - | 41 |
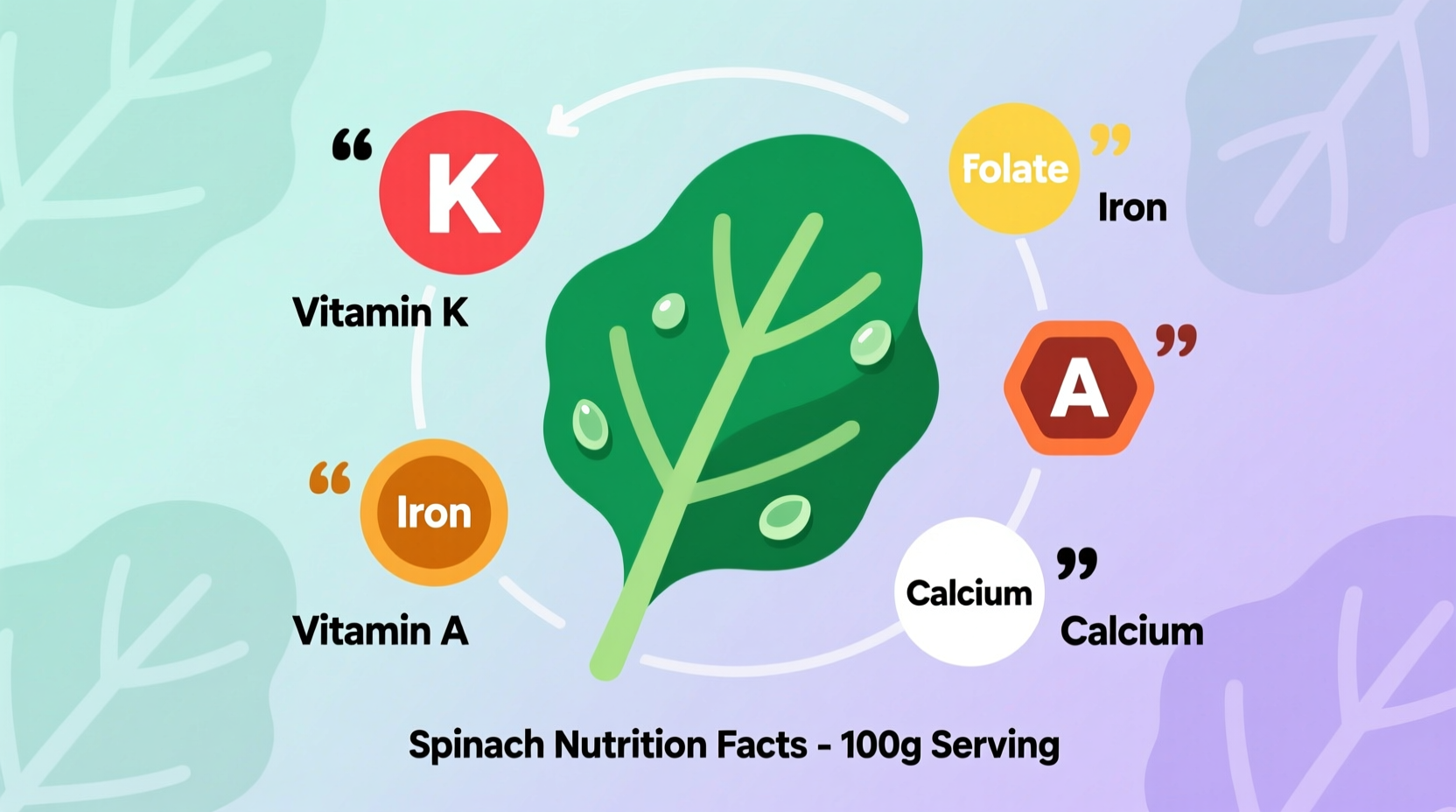
| Vitamin K | 145 mcg | 121% | 889 mcg (740%) |
| Vitamin A | 141 mcg | 18% | 573 mcg (64%) |
| Folate | 58 mcg | 15% | 131 mcg (33%) |
| Vitamin C | 8.4 mg | 14% | 8.4 mg (14%) |
| Iron | 0.8 mg | 4% | 3.2 mg (18%) |
Notice how cooking concentrates nutrients by reducing water content? This explains why cooked spinach appears more nutrient-dense. However, some heat-sensitive nutrients like vitamin C remain relatively stable during brief cooking.
Science-Backed Health Benefits of Spinach
Research published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition confirms spinach's role in supporting eye health through its high lutein and zeaxanthin content. These carotenoids accumulate in the retina, filtering harmful blue light and reducing the risk of age-related macular degeneration. A study from the National Eye Institute found that people with the highest dietary intake of these compounds had a 43% lower risk of developing advanced macular degeneration.
Bone health receives significant support from spinach's exceptional vitamin K content. According to research from the Framingham Heart Study, adequate vitamin K intake correlates with higher bone mineral density and reduced fracture risk. Just one cup of raw spinach provides more than your entire daily requirement of this crucial bone-supporting nutrient.
The nitrates in spinach offer cardiovascular benefits by improving blood vessel function. A 2020 study in Hypertension demonstrated that consuming nitrate-rich vegetables like spinach lowered blood pressure by an average of 3-4 mmHg in just 24 hours. This effect occurs through the conversion of dietary nitrates to nitric oxide, which relaxes blood vessels.
The Popeye Iron Myth: Separating Fact from Fiction
Many believe spinach contains extraordinary iron levels thanks to the Popeye cartoon character. This misconception originated from a 1930s decimal point error in nutritional data that claimed spinach contained 35mg of iron per 100g (actually 3.5mg). While spinach does contain iron, its bioavailability is limited by oxalic acid content.
Research from the National Institutes of Health shows that the body absorbs only about 2-5% of the iron in raw spinach compared to 15-35% from animal sources. However, you can significantly improve absorption by:
- Pairing spinach with vitamin C-rich foods (citrus, bell peppers, strawberries)
- Cooking spinach to reduce oxalate content by up to 87%
- Avoiding calcium-rich foods in the same meal (calcium inhibits iron absorption)

Maximizing Nutrient Retention: Preparation Methods That Work
Your preparation method dramatically affects spinach's nutritional value. According to agricultural research from the University of California, Davis, different cooking techniques yield varying nutrient retention:
- Raw consumption: Best for preserving vitamin C and folate, but limits iron absorption due to oxalates
- Light steaming (2-3 minutes): Reduces oxalates by 5-15% while preserving most water-soluble vitamins
- Boiling (5 minutes): Decreases oxalates by 30-87% but leaches some water-soluble nutrients into cooking water
- Sautéing: Preserves fat-soluble vitamins (A, E, K) while reducing volume for greater nutrient density per bite
For optimal nutrition, try this chef-recommended technique: quickly wilt spinach in a hot pan with olive oil and garlic, then finish with a squeeze of lemon juice. The fat enhances absorption of fat-soluble vitamins, while the vitamin C dramatically improves iron uptake.
Practical Daily Incorporation Strategies
You don't need large quantities to benefit from spinach's nutrition. The Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommend 1-2 cups of dark leafy greens daily. Here's how to incorporate spinach seamlessly into your routine:
- Add 1 cup raw spinach to smoothies (vitamin C from fruits enhances iron absorption)
- Use as a base for salads with citrus dressing and pumpkin seeds
- Stir into soups, stews, and pasta sauces during the last few minutes of cooking
- Create spinach pesto by blending with basil, garlic, pine nuts, and olive oil
- Make spinach omelets or frittatas with vitamin C-rich bell peppers
Storage matters too! Keep fresh spinach in airtight containers with a paper towel to absorb excess moisture. Properly stored, it maintains nutrient levels for 5-7 days in the refrigerator. Avoid freezing unless necessary, as this can degrade certain nutrients.
When Spinach Consumption Requires Caution
While spinach offers tremendous benefits, certain individuals should moderate intake:
- People on blood thinners: Vitamin K's blood-clotting properties require consistent intake (sudden increases/decreases can interfere with medication)
- Kidney stone formers: High oxalate content may contribute to calcium oxalate stones in susceptible individuals
- Infants under 6 months: Nitrates can cause methemoglobinemia ("blue baby syndrome")
If you have these conditions, consult your healthcare provider about appropriate spinach consumption. For most people, however, the benefits far outweigh potential concerns when consumed as part of a balanced diet.










 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4