Many cultures have used onion juice and honey as traditional remedies for centuries, particularly for hair growth and respiratory issues. While generally considered safe in culinary quantities, understanding the potential side effects is crucial before using this combination as a treatment. This guide provides evidence-based information about the risks associated with onion juice and honey applications.
Why People Use Onion Juice and Honey Together
This natural combination has gained popularity for several traditional applications:
- Hair growth stimulation - Many believe the sulfur compounds in onions combined with honey's antibacterial properties can improve scalp health
- Sore throat relief - The mixture is often used as a home remedy for coughs and throat irritation
- Skin treatments - Some apply it topically for acne or minor skin irritations
| Application Method | Most Common Uses | Typical Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Topical (scalp/skin) | Hair growth, acne treatment | 15-30 minutes before washing |
| Oral consumption | Sore throat relief, immune support | 1-2 teaspoons daily |
Documented Side Effects of Onion Juice and Honey
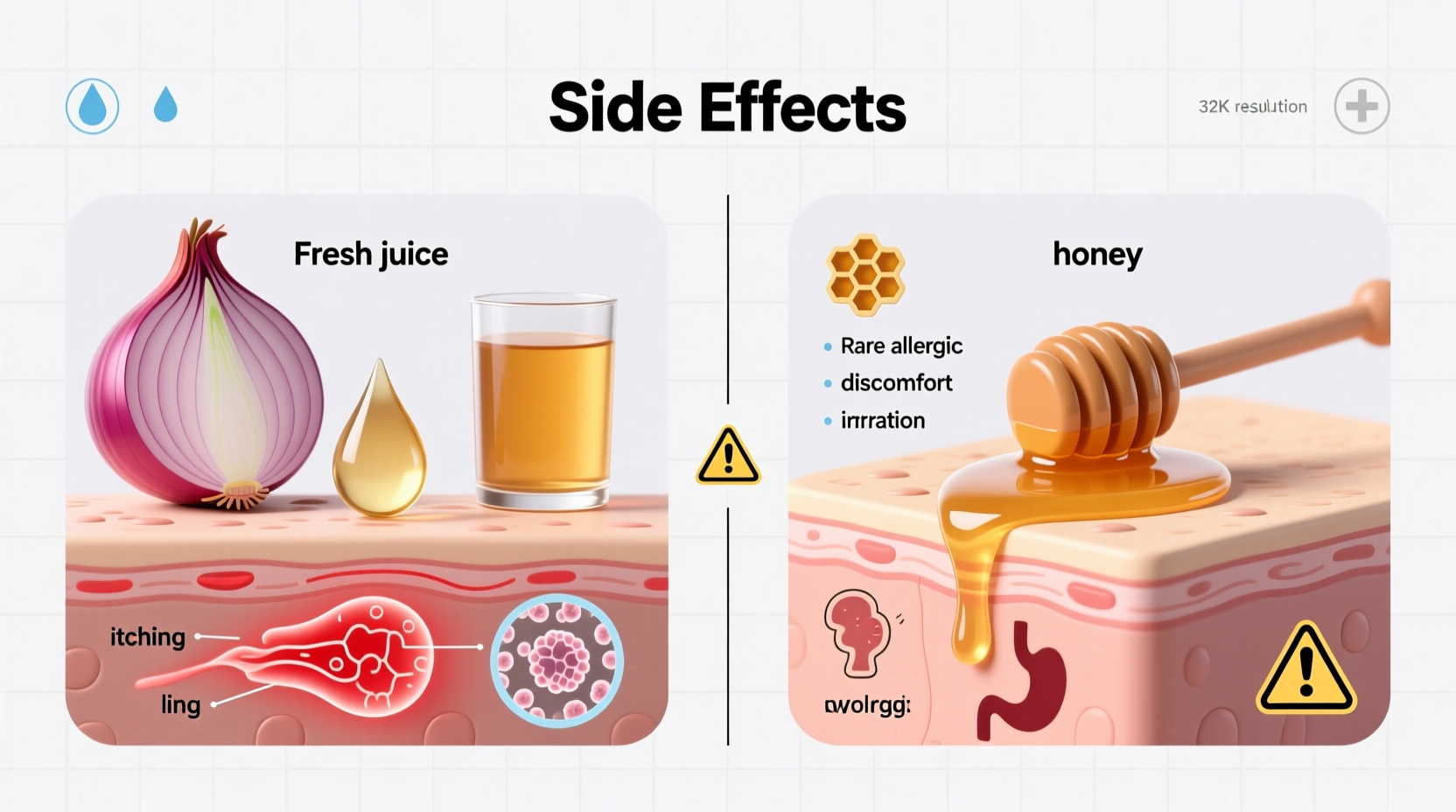
Skin Reactions from Topical Application
When applied to the skin or scalp, onion juice can cause:
- Burning or stinging sensation - Particularly on sensitive or broken skin
- Redness and inflammation - According to a 2020 study in Contact Dermatitis, onion extracts can cause irritant contact dermatitis in approximately 15% of test subjects
- Allergic contact dermatitis - Characterized by itching, swelling, and blistering
- Temporary skin discoloration - Yellowish tint that usually fades within hours
The American Academy of Dermatology notes that "allium vegetables like onions contain compounds that can be irritating to the skin, especially when used in concentrated forms like juice." (aad.org)
Digestive Side Effects from Consumption
When consumed orally, potential issues include:
- Heartburn or acid reflux - Onions are known FODMAP foods that can trigger digestive issues
- Stomach discomfort - Particularly in individuals with sensitive digestive systems
- Diarrhea - When consumed in large quantities
Specific Concerns with Honey
Honey presents unique risks that many people overlook:
- Infant botulism - The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) strictly warns against giving honey to children under 12 months due to Clostridium botulinum spores that can cause life-threatening botulism in infants (cdc.gov)
- Blood sugar impact - Honey contains significant sugars that can affect blood glucose levels
- Allergic reactions - Though rare, some individuals may react to pollen or other components in honey
Who Should Avoid Onion Juice and Honey Treatments
Certain populations face higher risks and should exercise caution or avoid this combination entirely:
| Population | Risk Level | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Infants under 1 year | High risk | Avoid honey completely due to botulism risk |
| Pregnant or breastfeeding women | Moderate caution | Consult healthcare provider before use |
| People with onion allergy | High risk | Avoid all onion products |
| Diabetics | Moderate risk | Monitor blood sugar carefully if consuming |
When to Seek Medical Attention
Contact a healthcare professional if you experience:
- Severe skin reactions that persist after washing off the mixture
- Difficulty breathing or swallowing after consumption
- Signs of infection at application sites
- Persistent digestive issues lasting more than 24 hours
- For infants: constipation, weakness, or feeding difficulties after honey exposure
Safer Application Practices
If you choose to use onion juice and honey, follow these evidence-based safety guidelines:
- Perform a patch test - Apply a small amount to your inner forearm and wait 24 hours before full application
- Dilute onion juice - Mix with water (1:1 ratio) to reduce irritation potential
- Limit application time - Don't leave on skin longer than 30 minutes
- Use raw, unpasteurized honey - For consumption, though this doesn't eliminate botulism risk for infants
- Wash thoroughly - After topical application to prevent prolonged skin exposure

Scientific Evidence vs. Anecdotal Claims
It's important to distinguish between scientifically supported facts and traditional beliefs:
- Documented benefits - Honey has proven antibacterial properties recognized by the National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- Limited evidence - While some small studies suggest onion extracts may support hair growth, robust clinical evidence is lacking
- Common misconceptions - Many claimed benefits are based on traditional use rather than scientific validation
The NIH's National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health states: "While some traditional remedies show promise in preliminary studies, consumers should be cautious about claims that aren't supported by rigorous scientific research." (nccih.nih.gov)
Conclusion: Weighing Benefits Against Risks
Onion juice and honey can be part of a natural health regimen for many adults when used appropriately, but awareness of potential side effects is essential. The most significant risks involve skin irritation from topical use and the serious botulism risk for infants from honey. Always consult with a healthcare provider before using this combination to treat medical conditions, especially if you have underlying health issues or are taking medications.










 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4