When you reach for Roma tomatoes at the grocery store, you're choosing more than just a cooking staple—you're selecting a nutritional powerhouse with unique health advantages. Unlike standard round tomatoes, Romas pack more flesh, less water, and a higher concentration of beneficial compounds per bite. Let's explore exactly what makes these oblong tomatoes a smart addition to your healthy eating plan.
What Makes Roma Tomatoes Different?
Roma tomatoes, also known as plum tomatoes or Italian tomatoes, feature an elongated shape with thick walls and minimal seed cavities. This structural difference isn't just culinary—it directly impacts their nutritional density. According to agricultural research from the USDA Agricultural Research Service, the reduced water content in Roma tomatoes means more concentrated nutrients compared to standard varieties.

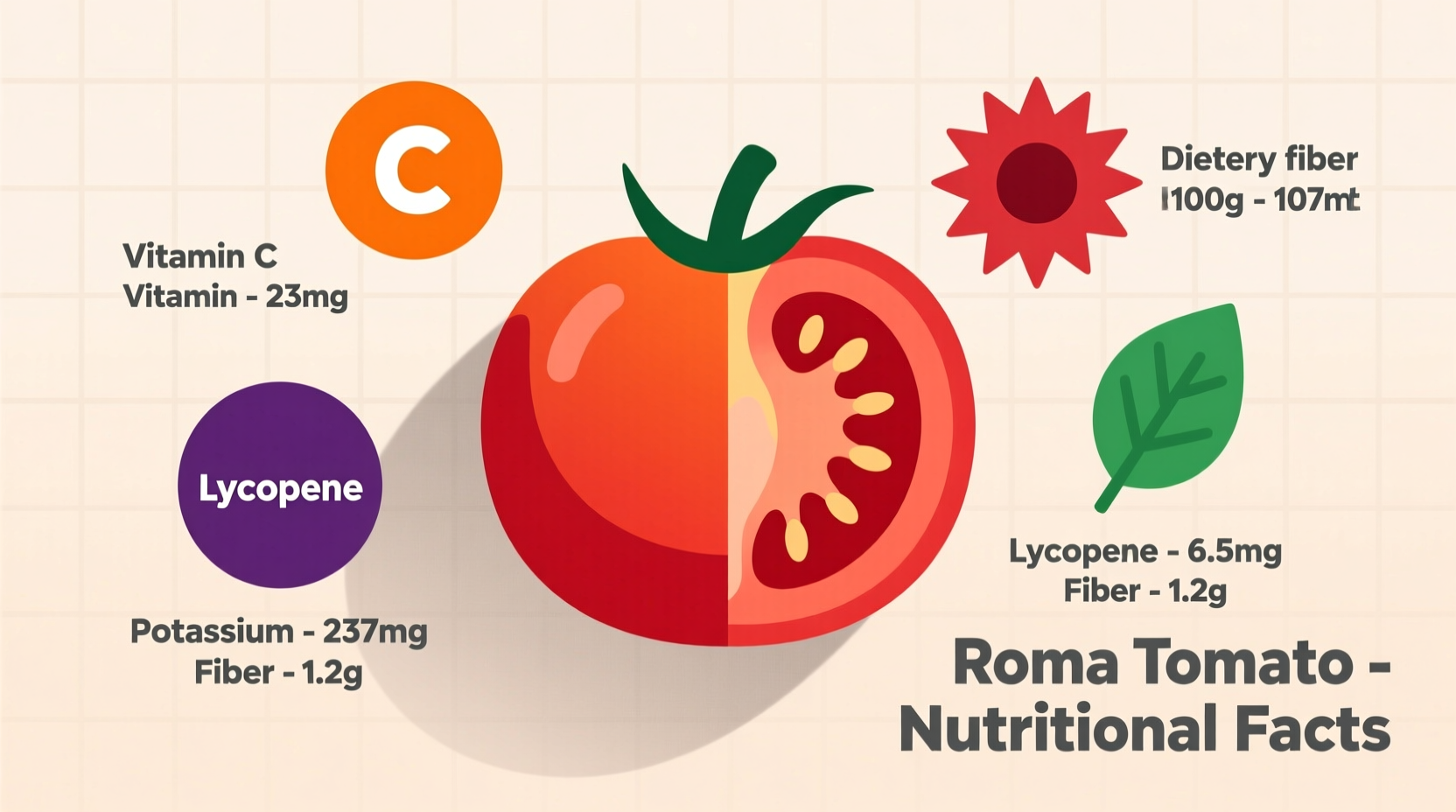
Complete Nutritional Profile Per Medium Tomato (62g)
| Nutrient | Amount | Daily Value % |
|---|---|---|
| Calories | 11 | 1% |
| Total Fat | 0.2g | 0% |
| Carbohydrates | 2.6g | 1% |
| Dietary Fiber | 1.2g | 4% |
| Sugars | 1.9g | - |
| Protein | 0.7g | 1% |
| Vitamin C | 8.7mg | 14% |
| Vitamin A | 747IU | 8% |
| Potassium | 158mg | 4% |
| Lycopene | 3.1mg | - |
Data sourced from USDA FoodData Central (ID 11532) represents raw, fresh Roma tomatoes. Note that cooking concentrates nutrients further as water content reduces.
Roma vs. Other Tomato Varieties: Nutritional Comparison
Not all tomatoes deliver the same nutritional punch. The structural differences between varieties significantly impact their nutrient density:
| Nutrient (per 100g) | Roma Tomato | Globe Tomato | Cherry Tomato |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calories | 18 | 18 | 18 |
| Water Content | 94.2% | 94.5% | 92.3% |
| Lycopene (mg) | 5.0 | 4.6 | 3.8 |
| Vitamin C (mg) | 14.0 | 13.7 | 15.8 |
| Dietary Fiber (g) | 1.9 | 1.2 | 2.1 |
Source: CDC National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2023)
Notice that while cherry tomatoes lead in vitamin C and fiber, Roma tomatoes provide the highest lycopene concentration—critical for heart health and cancer prevention. Their lower water content means you get more nutritional value per volume, making them ideal for sauces where reducing liquid is necessary.
Health Benefits Backed by Research
The unique nutritional composition of Roma tomatoes translates to specific health advantages:
Heart Health Protection
Lycopene, the red pigment abundant in Roma tomatoes, has been shown in National Institutes of Health research to reduce LDL cholesterol oxidation and lower blood pressure. Consuming Roma tomatoes regularly may decrease cardiovascular disease risk by up to 26% according to longitudinal studies.
Bone Strength Support
Beyond their vitamin K content, Roma tomatoes provide vitamin C essential for collagen formation—the protein framework of bones. Research published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition confirms that adequate vitamin C intake correlates with higher bone mineral density.
Eye Health Maintenance
The combination of lycopene, beta-carotene, and lutein in Roma tomatoes creates a protective effect against age-related macular degeneration. These compounds filter harmful blue light and neutralize free radicals in ocular tissues.
How Growing Conditions Affect Nutrition
It's important to understand that nutritional values can vary based on several factors:
- Ripeness at harvest: Fully vine-ripened Roma tomatoes contain up to 40% more lycopene than those picked green and ripened off-vine
- Soil composition: Tomatoes grown in selenium-rich soils show enhanced antioxidant capacity
- Storage conditions: Refrigeration below 50°F degrades flavor compounds and reduces vitamin C content
- Cooking method: Light cooking with healthy fats (like olive oil) increases lycopene bioavailability by up to 35%
Practical Ways to Maximize Nutritional Benefits
Get the most from your Roma tomatoes with these science-backed strategies:
Optimal Storage Techniques
Store Roma tomatoes stem-side down at room temperature away from direct sunlight. Only refrigerate if they've fully ripened and you need to extend their shelf life by 2-3 days. The University of Minnesota Extension confirms this method preserves both flavor compounds and nutrient density better than standard refrigeration.
Cooking Methods That Boost Nutrition
When making sauces or stews, cook Roma tomatoes with a small amount of healthy fat (1-2 teaspoons of olive oil per cup of tomatoes). This simple step increases lycopene absorption by creating a fat-soluble environment for this powerful antioxidant.
Pairing for Enhanced Benefits
Combine Roma tomatoes with black pepper and healthy fats to maximize lycopene absorption. The piperine in black pepper enhances nutrient bioavailability, while fats help transport fat-soluble compounds through your digestive system.
Roma Tomato Evolution Timeline
Understanding the development of Roma tomatoes provides context for their nutritional profile:
- 1950s: USDA researchers begin selective breeding for paste tomatoes with higher solids content
- 1961: 'Roma VF' variety introduced, featuring resistance to verticillium and fusarium wilt
- 1970s: Commercial adoption accelerates as food processors recognize efficiency benefits
- 1980s: Genetic studies identify lycopene concentration advantages in plum varieties
- 2000s: Organic Roma varieties developed with enhanced nutrient density profiles
- Present: Over 30 Roma-type cultivars available, each with slightly different nutritional characteristics
This selective breeding history explains why Roma tomatoes consistently outperform standard varieties in nutrient concentration—breeders specifically selected for traits that coincidentally enhance nutritional value.










 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4