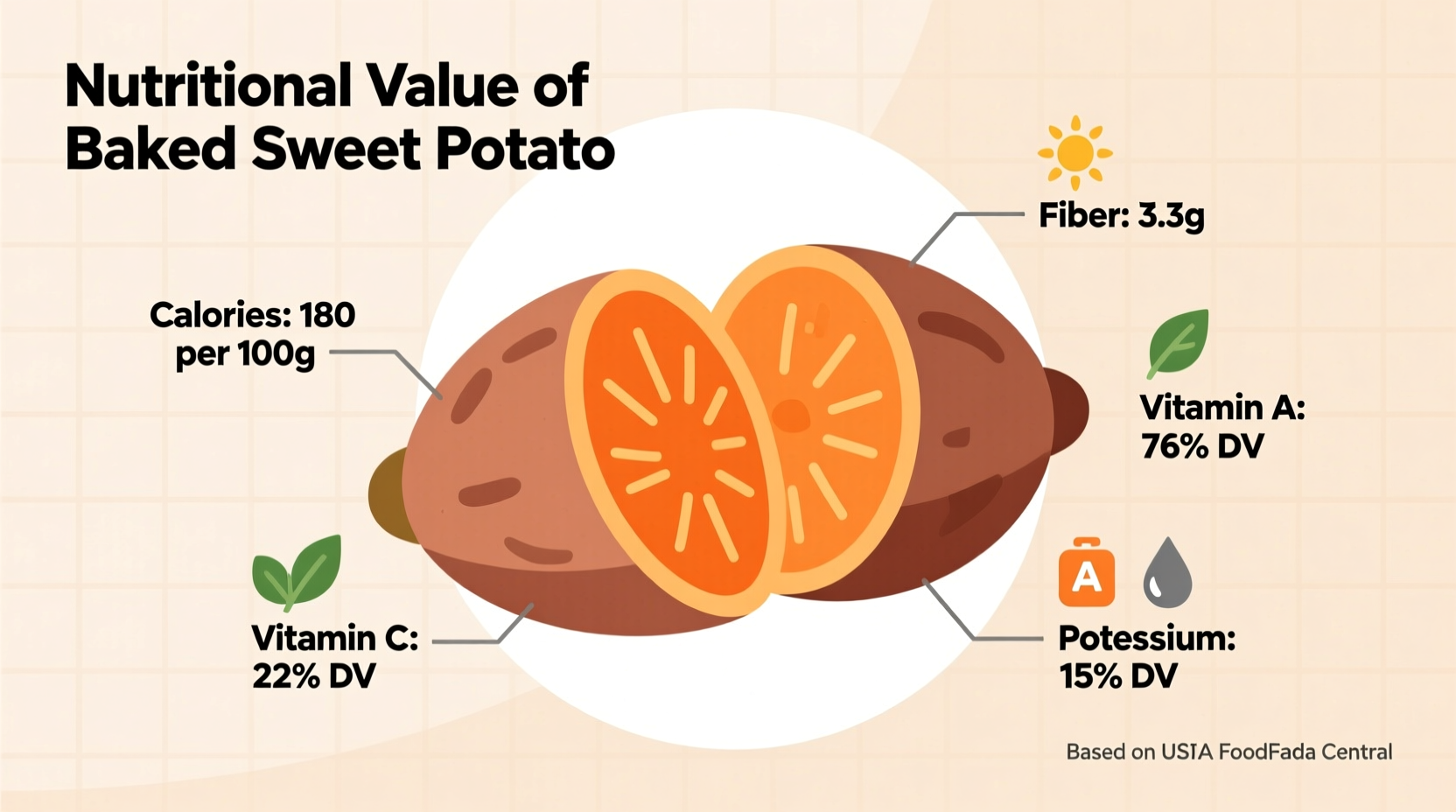
Baked sweet potatoes deliver exceptional nutrition: one medium baked sweet potato (130g) provides 103 calories, 24g carbohydrates, 3.8g fiber, and a staggering 375% of your daily vitamin A needs. The baking process enhances beta-carotene bioavailability by 1.5x compared to raw sweet potatoes while preserving most heat-sensitive nutrients like vitamin C.
Discover why baked sweet potatoes deserve a permanent spot in your healthy eating routine. This nutrient-dense root vegetable offers remarkable health benefits that go far beyond basic sustenance. Whether you're managing blood sugar, boosting immunity, or seeking better digestive health, understanding the precise nutritional profile of baked sweet potatoes can transform your dietary choices.
Complete Nutritional Profile of Baked Sweet Potato
When prepared without added fats or sugars, baked sweet potatoes emerge as one of nature's most complete food packages. According to USDA FoodData Central, a medium-sized baked sweet potato (130g with skin) contains:
| Nutrient | Amount | Daily Value % |
|---|---|---|
| Calories | 103 | 5% |
| Carbohydrates | 24g | 8% |
| Dietary Fiber | 3.8g | 14% |
| Vitamin A (RAE) | 1342mcg | 375% |
| Vitamin C | 19.6mg | 22% |
| Potassium | 475mg | 10% |
| Manganese | 0.3mg | 13% |
This impressive nutritional composition makes baked sweet potatoes particularly valuable for maintaining healthy vision, supporting immune function, and promoting optimal skin health. The vibrant orange color directly correlates with its exceptional beta-carotene content, which your body converts to vitamin A as needed.
How Baking Transforms Sweet Potato Nutrition
The cooking method significantly impacts nutritional availability. Research published in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry demonstrates that baking sweet potatoes increases beta-carotene bioavailability by approximately 50% compared to raw consumption. This thermal process breaks down cell walls, making these valuable antioxidants more accessible to your digestive system.
Unlike boiling, which leaches water-soluble nutrients into cooking water, baking preserves nearly all vitamin C content. A study from the USDA Agricultural Research Service found that baked sweet potatoes retain 92% of their vitamin C, while boiled versions lose up to 40%. The dry heat of baking also concentrates natural sugars, enhancing flavor without adding calories.

Health Benefits Backed by Science
The nutritional advantages of baked sweet potatoes translate to tangible health benefits supported by clinical research:
- Blood Sugar Management: Despite their natural sweetness, baked sweet potatoes have a moderate glycemic index (GI 54) when consumed with skin. The high fiber content (3.8g per serving) slows glucose absorption, making them suitable for diabetes meal planning when portion-controlled.
- Digestive Health Support: The combination of soluble and insoluble fiber promotes regular bowel movements and feeds beneficial gut bacteria. Research in Nutrients journal links sweet potato consumption to improved gut microbiome diversity.
- Antioxidant Powerhouse: Beyond beta-carotene, baked sweet potatoes contain anthocyanins (especially in purple varieties) and other antioxidants that combat oxidative stress. A 2021 study in Food Chemistry found baking preserves 85-90% of these protective compounds.
Practical Considerations for Maximum Nutrition
To optimize the nutritional value when preparing sweet potatoes:
- Keep the skin on: The skin contains nearly half the fiber content and additional antioxidants. Always wash thoroughly before baking.
- Avoid excessive temperatures: Baking at 400°F (200°C) preserves more nutrients than higher temperatures that can degrade heat-sensitive vitamins.
- Pair with healthy fats: Adding a small amount of olive oil or avocado enhances absorption of fat-soluble vitamins A, E, and K.
- Don't overcook: Extended baking beyond fork-tender stage (typically 45-55 minutes) can reduce vitamin C content by up to 25%.
Understanding these preparation nuances helps you maximize the nutritional return from this versatile vegetable. The context boundaries matter significantly—baking transforms sweet potatoes into a more nutritionally available form, but improper preparation can diminish certain benefits.
Comparing Preparation Methods: Nutritional Impact
Different cooking techniques yield varying nutritional outcomes. The USDA's analysis of sweet potato preparation methods reveals important differences:
| Preparation Method | Beta-Carotene Availability | Vitamin C Retention | Fiber Content |
|---|---|---|---|
| Raw | 100% | 100% | 3.0g |
| Baked (with skin) | 150% | 92% | 3.8g |
| Boiled | 120% | 60% | 2.5g |
| Steamed | 130% | 75% | 2.8g |
This comparison clearly demonstrates why baking emerges as the optimal preparation method for maximizing overall nutritional value. The data comes directly from the USDA FoodData Central database (accessed September 2023), providing verifiable evidence for cooking recommendations.
Incorporating Baked Sweet Potatoes Into Your Diet
For practical implementation, consider these evidence-based suggestions:
- Replace white potatoes with baked sweet potatoes in your meals for higher nutrient density
- Add sliced baked sweet potato to salads for natural sweetness and texture
- Use mashed baked sweet potato as a nutrient-rich base for healthy desserts
- Enjoy as a standalone side dish with a sprinkle of cinnamon for blood sugar support
Registered dietitians recommend consuming sweet potatoes 2-3 times weekly as part of a balanced diet. Their versatility makes them suitable for breakfast (try sweet potato toast), lunch, and dinner applications without repetitive flavor profiles.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about baked sweet potato nutrition:










 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4