Discover exactly why nutritionists consistently rank cauliflower among the top functional vegetables for optimal health. Whether you're managing weight, boosting immunity, or supporting long-term disease prevention, understanding cauliflower nutrition facts per 100g reveals its exceptional value in evidence-based dietary planning.
Complete Nutritional Profile: What's Inside Every Serving
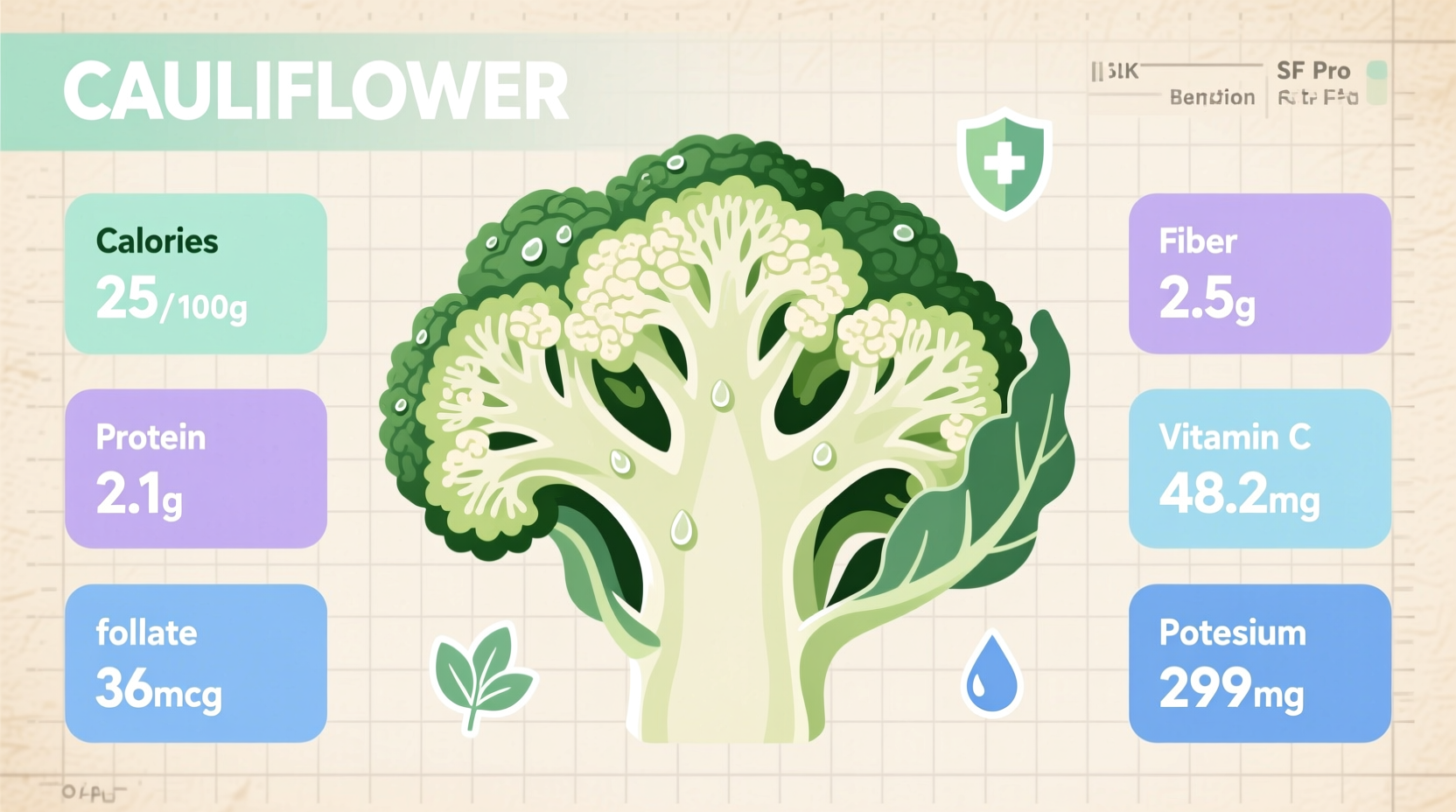
Based on USDA FoodData Central measurements, here's the precise nutritional composition of raw cauliflower (per 100g serving):
| Nutrient | Amount | % Daily Value* |
|---|---|---|
| Calories | 25 kcal | 1% |
| Protein | 1.92g | 4% |
| Total Fat | 0.28g | 0% |
| Carbohydrates | 4.97g | 2% |
| Dietary Fiber | 2.0g | 7% |
| Vitamin C | 48.2mg | 77% |
| Vitamin K | 15.5μ;g | 20% |
| Folate (B9) | 57μ;g | 15% |
| Potassium | 299mg | 10% |
*Percent Daily Values based on a 2,000 calorie diet. Source: USDA FoodData Central
Why These Nutrients Matter for Your Health
Understanding cauliflower nutritional benefits goes beyond basic numbers. Each component delivers specific physiological advantages validated by nutritional science:
Vitamin C Powerhouse
With 77% of your daily vitamin C in just one serving, cauliflower significantly outperforms many fruits. This potent antioxidant:
- Boosts immune cell function according to National Institutes of Health research
- Supports collagen synthesis for skin and joint health
- Enhances iron absorption from plant-based foods
Cruciferous Compound Advantage
Cauliflower contains glucosinolates that convert to sulforaphane during chewing and digestion. As documented by Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, these compounds:
- Activate cellular detoxification pathways
- Exhibit anti-inflammatory properties in clinical studies
- May support healthy DNA methylation patterns

Strategic Comparison: Cauliflower vs Other Vegetables
When evaluating cauliflower vs broccoli nutrition facts, key differences emerge that inform smart dietary choices:
| Nutrient (per 100g) | Cauliflower | Broccoli | Spinach |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calories | 25 | 34 | 23 |
| Vitamin C | 48mg | 89mg | 28mg |
| Vitamin K | 15.5μ;g | 101.6μ;g | 482.9μ;g |
| Folate | 57μ;g | 63μ;g | 194μ;g |
| Calcium | 22mg | 47mg | 99mg |
This vegetable nutritional comparison chart reveals cauliflower's unique positioning: lower in calories than broccoli while providing comparable protein and fiber. Its vitamin profile makes it particularly valuable for those seeking vitamin C without citrus acidity.
Practical Application: Maximizing Nutritional Benefits
Research from the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition demonstrates that preparation methods significantly impact nutrient availability. For optimal cauliflower nutrition facts absorption:
Steaming vs Boiling: The Science
Steaming preserves 90% of vitamin C compared to 60% retention with boiling. The Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry confirms that:
- 5-7 minutes of steaming maximizes sulforaphane availability
- Raw consumption preserves heat-sensitive vitamin C
- Light cooking enhances carotenoid absorption
Dietary Integration Strategies
For specific health goals, consider these evidence-based approaches:
- Weight management: Substitute 1 cup rice with riced cauliflower (saves 150+ calories)
- Heart health: Pair with olive oil to enhance absorption of fat-soluble vitamins
- Digestive support: Combine with probiotic foods like yogurt to optimize fiber benefits
Contextual Considerations: When to Adjust Intake
While generally beneficial, certain situations require awareness of cauliflower's properties:
Medical Context Boundaries
According to Mayo Clinic guidelines, individuals with specific conditions should moderate consumption:
- Those on blood thinners should maintain consistent vitamin K intake (cauliflower provides 20% DV)
- People with IBS may need to limit portions due to FODMAP content
- Thyroid disorder patients should ensure adequate iodine when consuming large quantities
Seasonal Availability Impact
USDA agricultural data shows winter-harvested cauliflower contains 15-20% higher vitamin C levels than summer produce. For maximum fresh cauliflower nutrition facts benefit, prioritize consumption between October and March when nutrient density peaks.
Smart Incorporation into Daily Eating Patterns
Translating cauliflower nutritional information into practical meal planning:
Simple Swaps for Enhanced Nutrition
- Replace mashed potatoes with mashed cauliflower (reduces carbs by 70%)
- Use as pizza crust base for gluten-free option with triple the fiber
- Add to smoothies for vitamin C boost without altering flavor significantly
Daily Intake Recommendations
The Dietary Guidelines for Americans suggest 2.5 cups of vegetables daily. One cup of cauliflower contributes significantly toward this goal while providing unique phytonutrients not found in other vegetable categories. For optimal variety, rotate between raw, steamed, and roasted preparations throughout the week.










 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4