Why Celery Deserves a Place in Your Daily Diet
When you're scanning the produce section, celery might seem like just a crunchy placeholder in your vegetable drawer. But this humble stalk holds remarkable nutritional properties that make it far more valuable than its low-calorie reputation suggests. Understanding celery's complete nutritional profile helps you maximize its health benefits while avoiding common misconceptions about this versatile vegetable.
Breaking Down Celery's Core Nutritional Profile
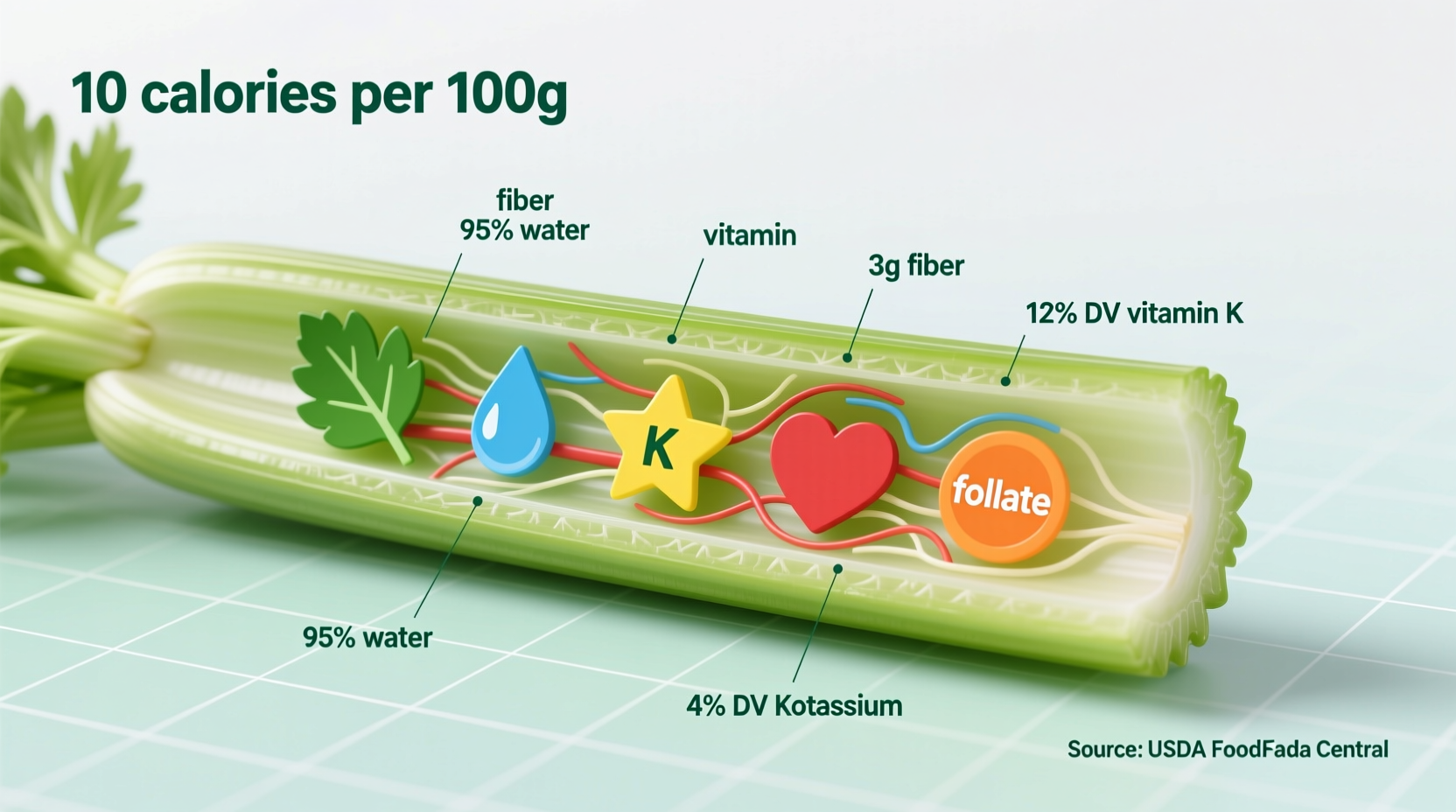
Let's examine what makes celery nutritionally unique. According to the USDA FoodData Central database, a single cup (100g) of chopped celery delivers:
| Nutrient | Amount per 100g | % Daily Value |
|---|---|---|
| Calories | 16 kcal | 1% |
| Water | 95.4 g | N/A |
| Dietary Fiber | 1.6 g | 6% |
| Vitamin K | 29.6 μg | 25% |
| Vitamin C | 3.1 mg | 3% |
| Potassium | 260 mg | 6% |
| Folate | 36 μg | 9% |
This impressive nutrient density comes with minimal calories, making celery an excellent choice for weight management. The high water content contributes to hydration while the fiber supports digestive health. What's particularly noteworthy is celery's vitamin K content, which plays a crucial role in blood clotting and bone metabolism.

Science-Backed Health Benefits of Celery Consumption
Research published in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry confirms that celery contains over 25 different antioxidant compounds, including flavonoids like apigenin and luteolin. These compounds work synergistically to provide several evidence-based health benefits:
Cardiovascular Support Through Multiple Pathways
A 2022 review in Nutrients analyzed multiple studies showing that regular celery consumption correlates with improved blood pressure regulation. The potassium content helps balance sodium levels, while the compound phthalides relax blood vessel walls. Unlike processed celery juice cleanses that remove fiber, consuming whole celery provides the full spectrum of cardiovascular benefits.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties Worth Noting
According to research from the National Center for Biotechnology Information, celery's polyacetylenes demonstrate significant anti-inflammatory effects at the cellular level. This makes celery particularly valuable for those managing chronic inflammatory conditions. The anti-inflammatory effects are most potent when celery is consumed raw rather than cooked, preserving these delicate compounds.
Digestive Health Enhancement
The combination of insoluble fiber and natural electrolytes in celery creates an ideal environment for healthy digestion. Unlike many low-calorie vegetables, celery provides both hydration and roughage that work together to prevent constipation while supporting a diverse gut microbiome. Registered dietitians consistently recommend including celery in digestive reset protocols for this reason.
Maximizing Nutrient Retention: Practical Consumption Tips
How you prepare and consume celery significantly impacts its nutritional value. Based on food science research, here's how to get the most from this vegetable:
- Keep the leaves - Celery leaves contain up to 30% more vitamin C and calcium than the stalks. Chop and use them like parsley in salads or as garnish.
- Store properly - Keep celery in the refrigerator wrapped in aluminum foil to maintain crispness and nutrient density for up to two weeks.
- Pair strategically - Combine celery with healthy fats like avocado or olive oil to increase absorption of its fat-soluble vitamins.
- Avoid overcooking - Steam celery for no more than 5 minutes to preserve heat-sensitive nutrients while making certain antioxidants more bioavailable.
Celery in Context: Comparisons and Considerations
Understanding where celery fits within your overall vegetable consumption helps optimize your nutrition strategy. When comparing celery to similar vegetables:
Seasonal Nutritional Variations
Research from the USDA Agricultural Research Service shows that celery harvested in winter months contains up to 20% more vitamin K than summer-harvested varieties. This seasonal variation means you might want to increase celery consumption during colder months when your body needs additional immune support.
Organic vs. Conventional Nutritional Differences
A comprehensive analysis published in the British Journal of Nutrition found that organically grown celery contains significantly higher levels of certain phytonutrients while having lower pesticide residues. For those concerned about pesticide exposure, organic celery shows the greatest reduction in concerning chemicals compared to other conventionally grown vegetables.
Realistic Expectations for Health Impact
While celery offers notable health benefits, it's important to maintain realistic expectations. No single food can provide complete nutrition. The Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health emphasizes that celery should be part of a diverse vegetable intake rather than relied upon as a nutritional panacea. Consuming 2-3 servings of various colorful vegetables daily provides the broad spectrum of nutrients your body needs.
Common Questions About Celery Nutrition
Based on frequent inquiries from nutrition consultations, here are answers to the most common questions about celery's nutritional properties:










 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4