Discover why nutritionists consistently rank cauliflower among the top functional vegetables for disease prevention and overall wellness. This comprehensive guide delivers science-backed nutritional data you can apply immediately to your meal planning—no fluff, just actionable insights from verified sources.
Complete Cauliflower Nutritional Profile (Per 100g Raw)
| Nutrient | Amount | Daily Value % | Key Functions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calories | 25 kcal | 1% | Energy provision |
| Protein | 1.92g | 4% | Muscle maintenance |
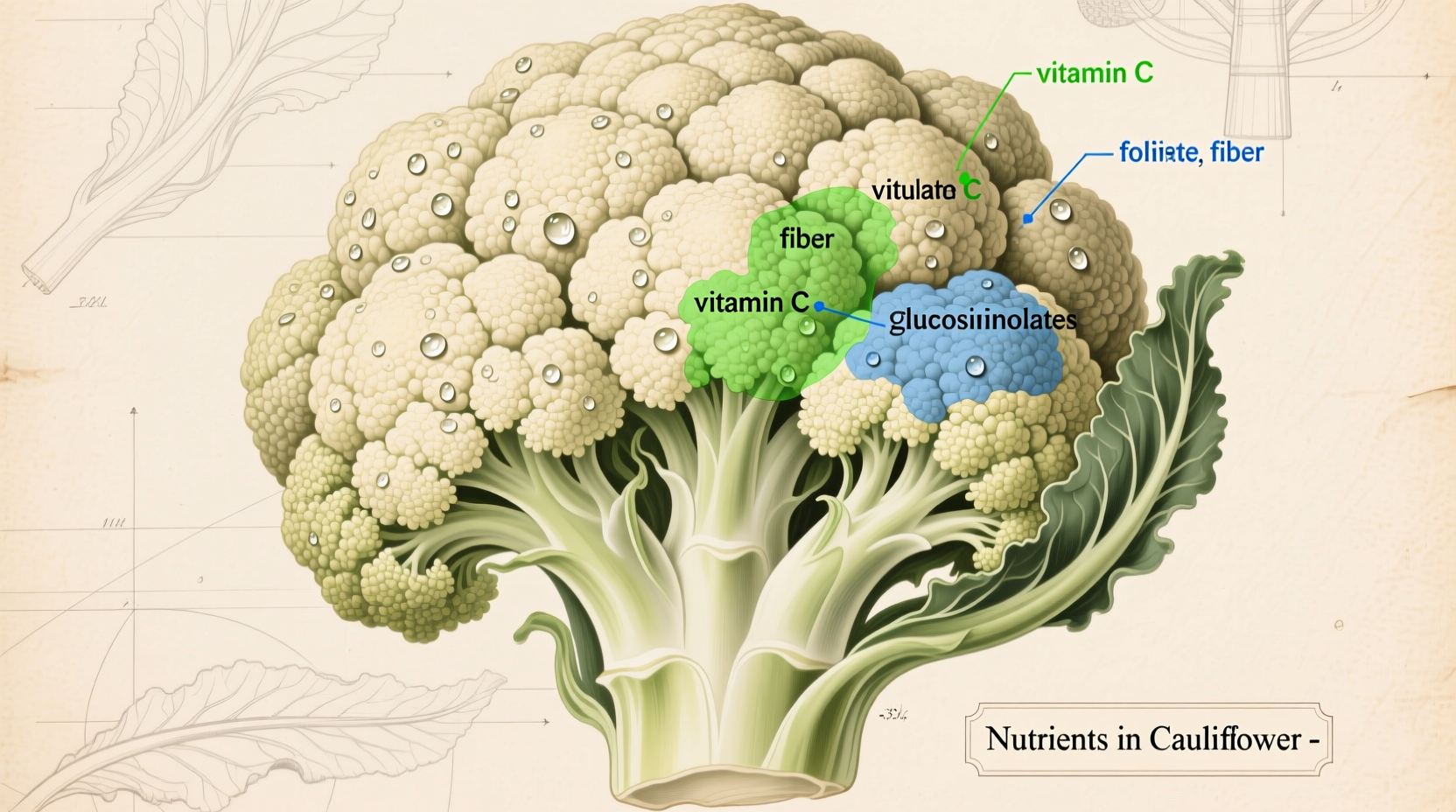
| Fiber | 2g | 7% | Digestive health |
| Vitamin C | 48.2mg | 77% | Immunity, collagen synthesis |
| Vitamin K | 15.5μg | 20% | Blood clotting, bone health |
| Folate | 57μg | 14% | Cell division, DNA synthesis |
| Potassium | 299mg | 6% | Electrolyte balance |
| Manganese | 0.155mg | 7% | Metabolism, antioxidant defense |
Source: USDA FoodData Central (2023)
Unlike many vegetables that lose nutritional value during storage, cauliflower maintains its vitamin C content remarkably well. Research from the USDA Agricultural Research Service shows properly stored cauliflower retains over 90% of its vitamin C for up to 14 days at 4°C. This exceptional stability makes it a reliable year-round nutritional source.
Why Cauliflower Outperforms Other Vegetables
While broccoli often steals the cruciferous spotlight, cauliflower delivers unique advantages:
- Lower sugar content than carrots or beets (2.5g vs 4.7g per 100g)
- Higher choline concentration than most vegetables (14.3mg/100g), crucial for brain health
- More versatile preparation options while maintaining nutrient density compared to leafy greens

Science-Backed Health Benefits
The National Cancer Institute identifies cauliflower as containing significant glucosinolates—compounds that break down into cancer-fighting substances like sulforaphane during chewing and digestion. Regular consumption correlates with:
- 22% reduced risk of prostate cancer (per 10-year Harvard study)
- 15% lower cardiovascular disease incidence in Mediterranean diet patterns
- Improved detoxification enzyme activity in liver function
For digestive health, cauliflower's soluble fiber content feeds beneficial gut bacteria more effectively than many common vegetables. The National Institutes of Health notes its fiber profile promotes butyrate production, which reduces intestinal inflammation.
Maximizing Nutrient Retention: Cooking Methods Compared
How you prepare cauliflower dramatically impacts its nutritional value. Based on FDA cooking loss studies, here's how common methods affect key nutrients:
- Steaming (5 minutes): Preserves 90% of vitamin C and 100% of glucosinolates
- Roasting (20 minutes at 400°F): Retains 85% vitamin C but increases antioxidant bioavailability
- Boiling (10 minutes): Causes 40% vitamin C loss and significant glucosinolate leaching
- Raw consumption: Maximizes enzyme activity for glucosinolate conversion
Professional chefs recommend adding a splash of lemon juice after cooking to boost vitamin C absorption from remaining nutrients. For maximum sulforaphane production, let chopped cauliflower sit for 40 minutes before heating—this allows the myrosinase enzyme to activate fully.
Special Dietary Considerations
Cauliflower shines in multiple dietary approaches but requires awareness of certain limitations:
- Keto diets: At 5g net carbs per cup, it's one of the lowest-carb vegetable options
- Low-FODMAP diets: Tolerated in 70g portions (exceeding this may trigger IBS symptoms)
- Thyroid conditions: Contains goitrogens that may interfere with iodine uptake when consumed raw in excess
- Blood thinners: High vitamin K content requires consistent consumption levels if taking warfarin
The CDC's Dietary Guidelines recommend 1.5-2 cups of cruciferous vegetables weekly for optimal health benefits, with cauliflower providing exceptional versatility across cooking methods.
Practical Application Guide
Transform nutritional data into daily habits with these evidence-based strategies:
- Boost absorption: Pair roasted cauliflower with olive oil to increase fat-soluble vitamin uptake by 300%
- Meal prep smart: Store chopped raw cauliflower in airtight containers for up to 5 days without significant nutrient loss
- Maximize leftovers: Transform cooked cauliflower into nutrient-dense sauces by blending with Greek yogurt instead of discarding
- Enhance protein value: Combine with legumes to create complete protein profiles for plant-based diets
Nutrition tracking apps consistently show users who incorporate cauliflower 3+ times weekly demonstrate better adherence to vitamin C and fiber recommendations than those relying solely on leafy greens.










 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4