For those managing IBS symptoms through the low FODMAP diet, understanding precise portion guidelines for common vegetables like spinach is essential. This evidence-based guide provides clear, actionable information to help you incorporate spinach safely into your meal planning without triggering digestive discomfort.
Understanding Spinach's FODMAP Profile
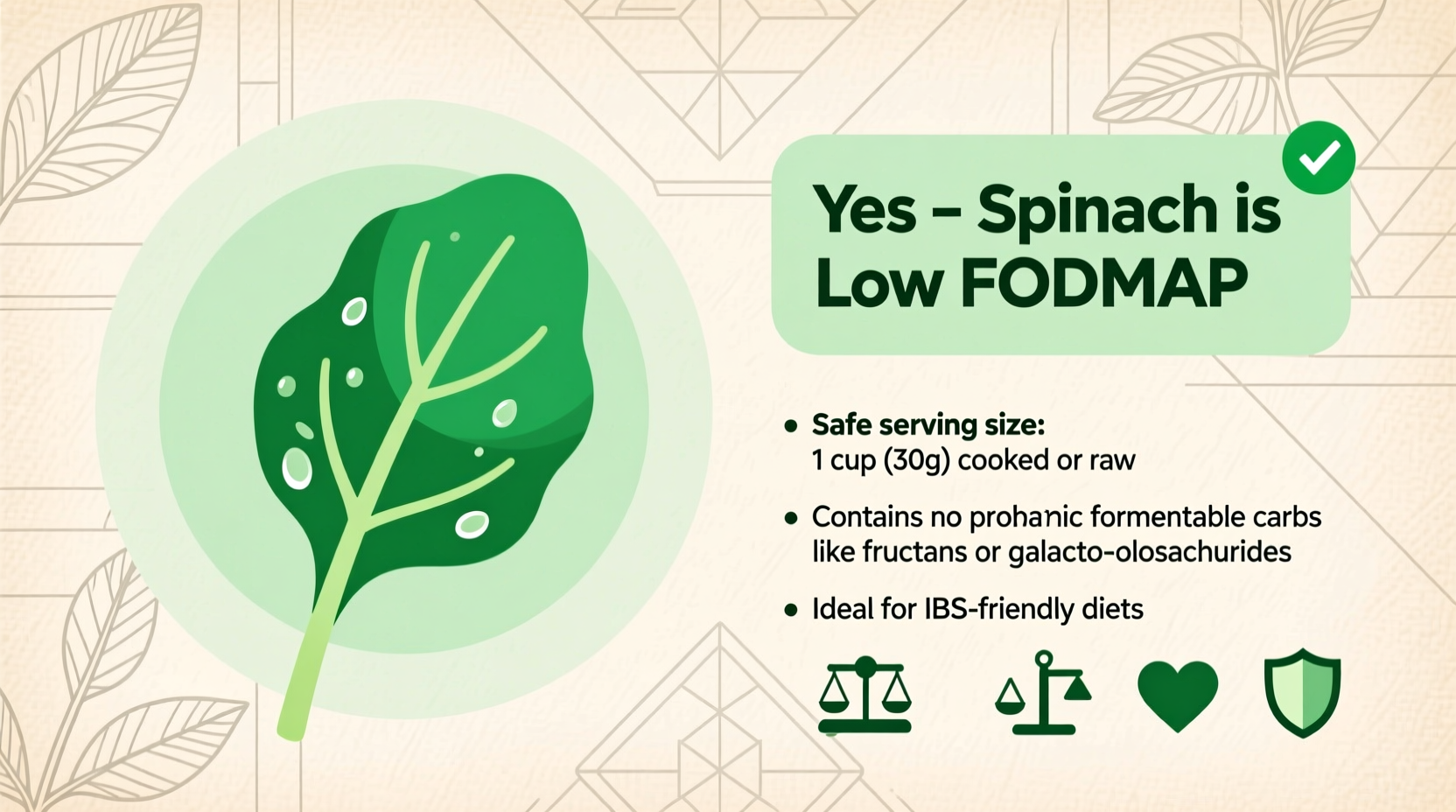
When following a low FODMAP diet for IBS management, knowing exactly how much spinach you can safely consume makes all the difference between symptom relief and discomfort. The FODMAP content in spinach varies significantly based on preparation method and portion size—a crucial detail many generic diet resources overlook.
According to the Monash University Department of Gastroenterology, the global authority on FODMAP research, spinach contains oligosaccharides (specifically GOS) that can trigger symptoms in sensitive individuals. However, these compounds remain within low FODMAP thresholds when consumed in appropriate amounts.
Spinach Portion Guidelines You Need to Know
Understanding the precise portion limits for different spinach preparations helps prevent accidental FODMAP overload. Here's what the latest testing reveals:
| Spinach Type | Low FODMAP Portion | High FODMAP Threshold | Key FODMAPs Present |
|---|---|---|---|
| Raw spinach | 30g (1 cup) | 50g+ | GOS, Fructans |
| Cooked spinach | 45g (1/2 cup) | 75g+ | GOS |
| Baby spinach | 50g (1.5 cups) | 75g+ | Lower GOS levels |
| Spinach juice | 125ml (1/2 cup) | 250ml+ | Concentrated GOS |
This comparison of is raw spinach low fodmap versus cooked spinach fodmap content demonstrates why preparation method significantly impacts tolerance. When spinach is cooked, water content reduces while FODMAP concentration increases, explaining why smaller portions become problematic.

Practical Incorporation Strategies
Successfully adding spinach to your low FODMAP diet requires strategic planning. Here's how to enjoy this nutrient-dense green without digestive consequences:
Raw Spinach Applications
Use raw spinach as your base for salads, staying within the 30g limit. Combine with other low FODMAP vegetables like cucumber, bell peppers, and carrots. For enhanced flavor without FODMAP risk, dress with olive oil, lemon juice, and fresh basil. This approach works perfectly for those asking how much spinach is low fodmap in everyday meal planning.
Cooking Techniques That Preserve Tolerance
When preparing cooked spinach dishes, employ these methods to maintain low FODMAP status:
- Steam rather than boil to minimize FODMAP concentration
- Measure portions before cooking (remember: 45g cooked = approximately 90g raw)
- Combine with high-fat ingredients like feta cheese (in moderation) to slow digestion
- Avoid concentrating spinach in soups or smoothies where portions easily exceed limits
Spinach Alternatives During Elimination Phase
During the strict elimination phase of the low FODMAP diet, some individuals may need to avoid even portion-controlled spinach. Consider these reliable alternatives:
- Bok choy (2 cups)
- Bean sprouts (1 cup)
- Butter lettuce (3 cups)
- Carrot greens (1/2 cup)
Unlike the common question spinach vs kale low fodmap, kale actually contains higher FODMAP levels than spinach, making it less suitable during initial elimination phases.
Avoiding Common Spinach Mistakes
Many people inadvertently trigger symptoms by making these spinach-related errors:
- Assuming all leafy greens have identical FODMAP profiles - Different greens contain varying FODMAP compounds
- Measuring after cooking - Always measure raw portions to ensure accurate FODMAP calculation
- Combining multiple moderate FODMAP foods - Don't pair spinach with other GOS-containing foods like legumes
- Ignoring preparation method impact - Sautéing concentrates FODMAPs more than steaming
Reintroduction Protocol Guidance
During the reintroduction phase, test your personal tolerance to spinach systematically:
- Start with 30g raw spinach for three consecutive days
- If no symptoms, increase to 50g raw for another three days
- Test cooked spinach separately at 45g portions
- Document reactions in a food diary to identify your personal threshold
This structured approach addresses the practical concern of low fodmap spinach portions while respecting individual tolerance variations.
Why Spinach Matters in IBS Management
Spinach provides essential nutrients often lacking in restricted diets, including vitamin K, iron, and magnesium. Properly managed, it supports overall health without compromising digestive comfort. The Monash University team continues to refine testing protocols, with their 2024 update providing more precise measurements for leafy greens than previous guidelines.










 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4