When you're exploring natural ways to manage your weight, celery often appears as a popular recommendation. But is there real science behind the hype? Let's examine what makes this crunchy vegetable a smart addition to weight management strategies—and where the limitations lie.
The Science Behind Celery and Weight Management
Celery's reputation in weight loss circles stems from three key properties that work together to support healthy eating habits:
Minimal Calorie Impact With Maximum Volume
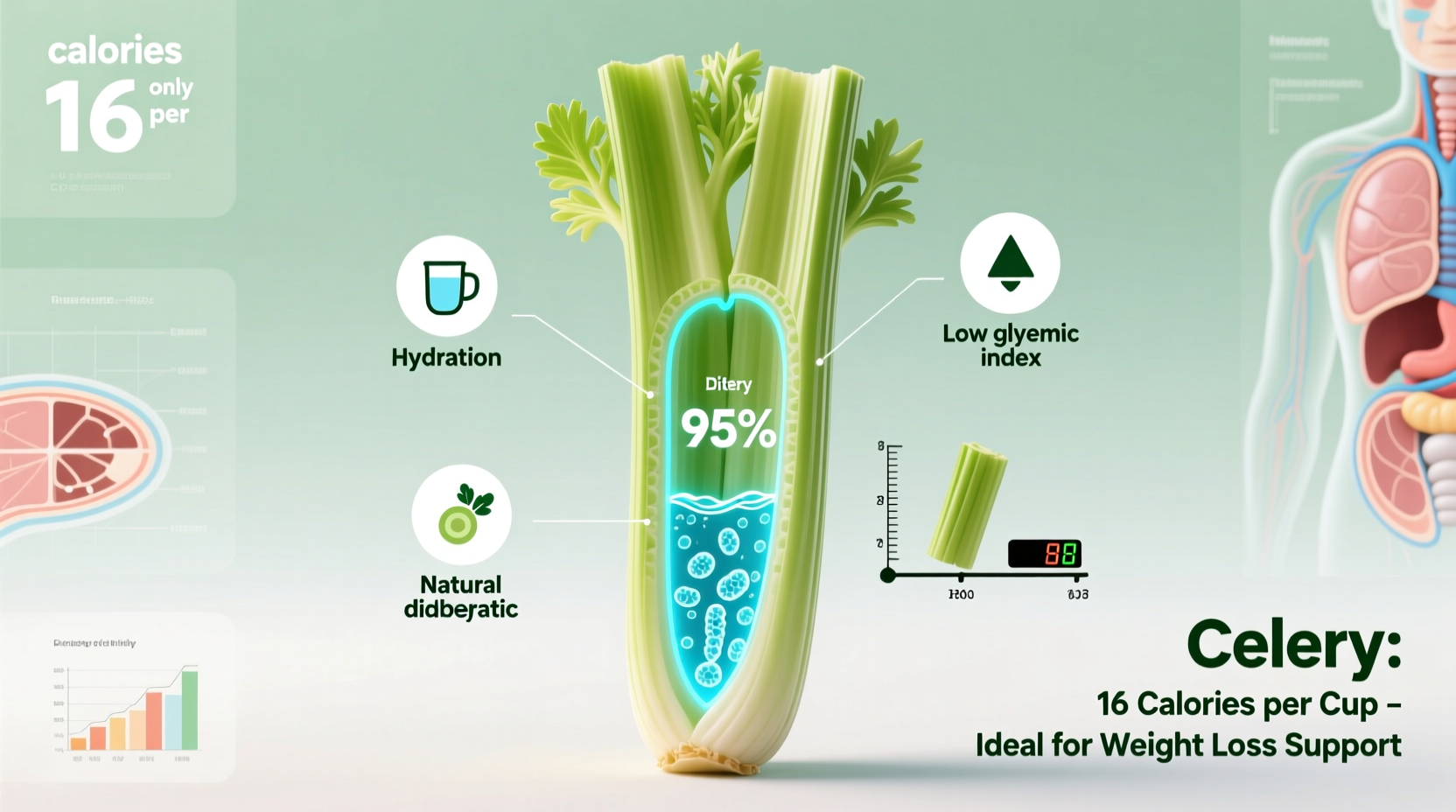
A single medium celery stalk contains just 6-10 calories while providing significant chewing satisfaction. This creates what nutrition scientists call "dietary volume"—filling your plate and stomach without adding substantial calories. According to USDA FoodData Central, one cup of chopped celery (about 100g) contains only 16 calories, making it one of the lowest-calorie vegetables available.
Fiber Content That Promotes Satiety
While celery isn't the highest-fiber vegetable, it still delivers 1.6g of dietary fiber per cup. Research published in Nutrients journal confirms that dietary fiber increases feelings of fullness and reduces subsequent food intake. The insoluble fiber in celery adds bulk to your meals, helping you feel satisfied longer between meals.
Hydration Benefits That Reduce False Hunger
With 95% water content, celery contributes to your daily hydration needs. A study from the National Institutes of Health found that proper hydration can reduce confusion between thirst and hunger signals, preventing unnecessary snacking. The water content in celery also adds physical volume to your stomach, triggering stretch receptors that signal fullness to your brain.

Debunking the 'Negative Calorie' Myth
You've probably heard celery described as a "negative calorie food"—meaning your body supposedly burns more calories digesting it than the food itself contains. Despite its popularity, this claim lacks scientific support.
The thermic effect of food (TEF) represents the energy required to digest, absorb, and metabolize nutrients. For most foods, TEF accounts for 5-15% of the food's calories. Even with celery's extremely low calorie count, research in the Journal of the American Dietetic Association indicates that the energy expended to process celery would be less than 10% of its caloric value—nowhere near enough to create a "negative" balance.
How to Effectively Incorporate Celery Into Your Weight Loss Plan
Understanding celery's realistic benefits helps you use it strategically rather than relying on it as a miracle solution:
Smart Snacking Strategy
Replace high-calorie snacks with celery paired with protein-rich dips like Greek yogurt or hummus. The combination provides sustained fullness through protein, healthy fats, and fiber—addressing multiple satiety pathways simultaneously. A study from CDC's healthy eating guidelines confirms that snacks combining protein and fiber lead to greater satisfaction than carbohydrate-only options.
Meal Volume Booster
Add chopped celery to soups, stews, and salads to increase portion size without significantly increasing calories. This technique, called "volumetrics," was developed by nutrition researchers at Penn State and has been shown to help people consume fewer calories while feeling equally satisfied.
| Vegetable | Calories per Cup | Fiber (g) | Water Content | Satiety Index* |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Celery | 16 | 1.6 | 95% | 72 |
| Cucumber | 16 | 0.5 | 96% | 68 |
| Broccoli | 55 | 2.4 | 91% | 89 |
| Spinach | 7 | 0.7 | 92% | 79 |
*Satiety Index measures how well foods satisfy hunger compared to white bread (set at 100)
Important Limitations to Understand
While celery offers benefits for weight management, it's crucial to recognize its limitations to avoid unrealistic expectations:
Nutritional Gaps Require Complementary Foods
Celery provides minimal protein and healthy fats—essential nutrients for maintaining muscle mass during weight loss. Relying solely on celery could lead to nutrient deficiencies. Pair it with protein sources like lean meats, legumes, or dairy to create balanced meals that support sustainable weight loss.
Context Matters for Different Weight Loss Goals
The effectiveness of celery varies based on your specific situation:
- For moderate weight loss: Celery works well as part of a balanced approach
- For significant weight loss: Requires more comprehensive nutritional planning
- For athletic performance: Needs supplementation with higher-energy foods
- For medical weight management: Should be discussed with healthcare providers
Individual Responses Vary
Research from the USDA Food and Nutrition Information Center shows that individual responses to high-fiber foods vary based on gut microbiome composition. Some people experience significant satiety benefits from celery, while others may need different high-volume foods to achieve similar effects.
Creating Sustainable Results With Celery
The most effective approach combines celery with other evidence-based weight management strategies:
Sample Day Using Celery Strategically
- Breakfast: Oatmeal with berries and a side of celery sticks
- Snack: Celery with 2 tbsp almond butter
- Lunch: Large salad with mixed greens, grilled chicken, and chopped celery
- Snack: Celery and carrot sticks with hummus
- Dinner: Stir-fry with lean protein, broccoli, and celery
Tracking Your Personal Response
Keep a simple food and satiety journal for one week, noting:
- When you eat celery
- How satisfied you feel afterward
- Whether it reduces subsequent snacking
This personalized approach helps determine if celery works effectively for your body and eating patterns.
When Celery Might Not Be Your Best Option
Certain situations require modified approaches:
- Digestive sensitivities: Some people experience bloating from celery's mannitol content
- Low-sodium diets: While naturally low in sodium, celery contains about 30mg per stalk
- Specific medication interactions: Consult your doctor if taking blood thinners (celery contains vitamin K)
Remember that sustainable weight loss typically occurs at a rate of 1-2 pounds per week through a moderate calorie deficit. Celery can support this process by helping you feel satisfied with fewer calories, but it's just one component of a comprehensive approach that includes balanced nutrition, appropriate portion sizes, and regular physical activity.










 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4