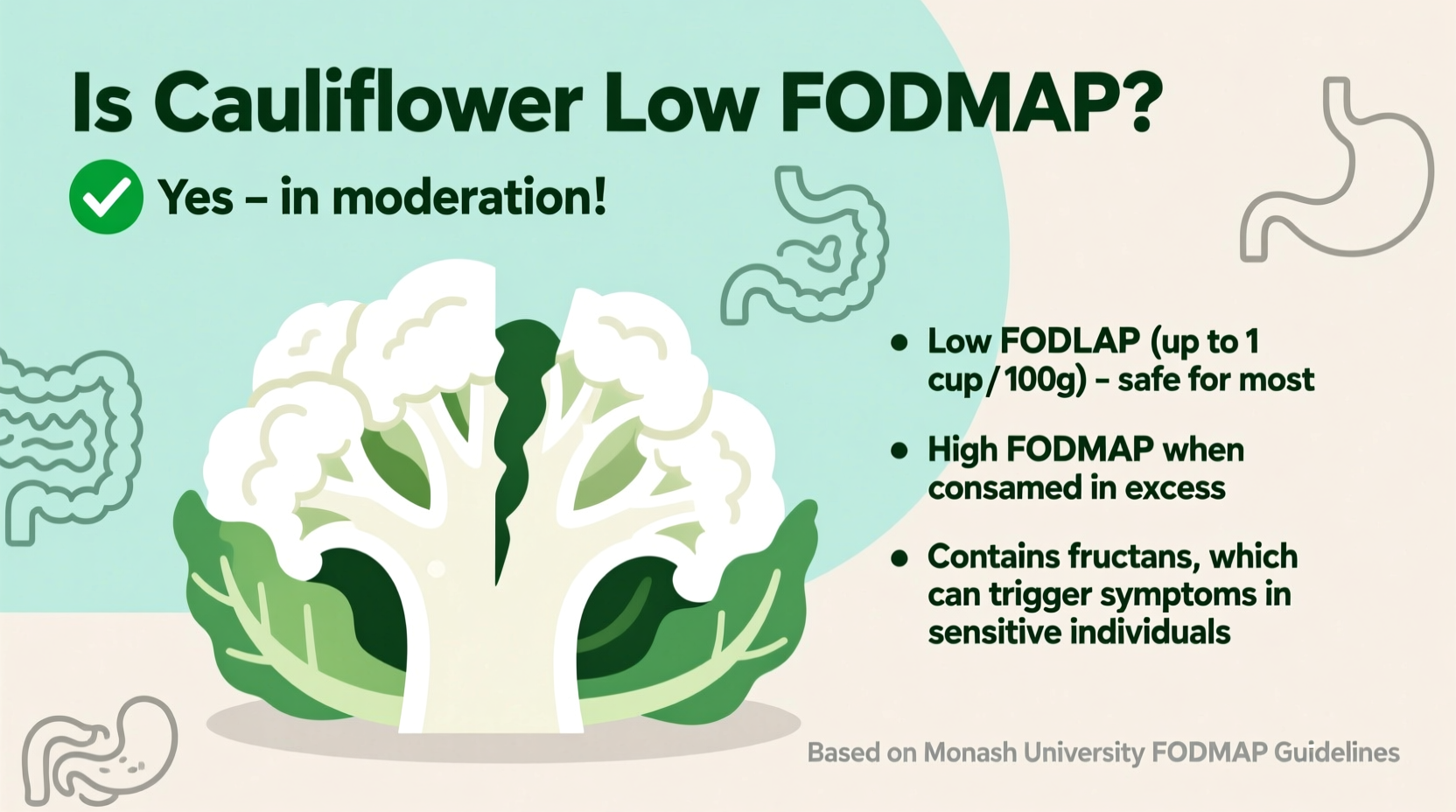
Yes, cauliflower can be low FODMAP—but only in strict portions. According to Monash University's certified testing, a safe low FODMAP serving is limited to 30g (about 1/4 cup chopped). Larger portions become high in mannitol, a FODMAP that triggers digestive issues for many with IBS.
Understanding whether is cauliflower low fodmap matters for anyone managing IBS symptoms through diet. As someone who's helped thousands navigate the low FODMAP journey, I've seen how confusing vegetable classifications can be. Let's cut through the confusion with science-backed clarity.
Why Portion Size Makes All the Difference for Cauliflower
Many assume vegetables are universally "safe" on low FODMAP diets. But cauliflower contains mannitol, a sugar alcohol that's problematic for sensitive digestive systems. The critical factor isn't whether you eat cauliflower—it's how much.
| Portion Size | FODMAP Content | Low FODMAP Status |
|---|---|---|
| 30g (¼ cup chopped) | Low mannitol | ✓ Safe |
| 75g (½ cup chopped) | Moderate mannitol | ⚠️ Caution |
| 100g (¾ cup chopped) | High mannitol | ✗ High FODMAP |
This portion guidance comes directly from Monash University's FODMAP database, the gold standard for low FODMAP research. Their certified lab testing shows that exceeding 30g triggers the "green light" threshold for mannitol.
Practical Strategies for Enjoying Cauliflower Safely
Knowing is cauliflower low fodmap only solves half the problem. Here's how to incorporate it wisely:
Smart Preparation Techniques
- Steam instead of roast: High-heat cooking concentrates mannitol. Gentle steaming preserves texture while minimizing FODMAP density.
- Measure precisely: Use kitchen scales during elimination phase—eye-balling leads to portion errors.
- Pair with FODMAP-fighting foods: Combine with turmeric or ginger, which may help counteract digestive discomfort.
When to Avoid Cauliflower Completely
During the strict elimination phase (typically 2-6 weeks), some practitioners recommend avoiding cauliflower entirely if you're highly sensitive to mannitol. This cauliflower low fodmap diet restriction allows your system to reset before systematic reintroduction.

Low FODMAP Alternatives When Cauliflower Isn't an Option
If you're wondering is cauliflower low fodmap safe for my IBS, sometimes the answer is "not yet." During initial elimination, try these substitutes:
- Turnip (rutabaga): Similar texture with negligible FODMAPs up to 100g
- Zucchini: Versatile up to 150g portions
- Green beans: Safe up to 75g
- Carrots: Unlimited portions (unlike many assume)
Reintroduction Protocol: Testing Your Tolerance
After symptom improvement, systematically test cauliflower tolerance:
- Start with 30g portion after 4 weeks of symptom-free eating
- Wait 72 hours before testing next portion size
- Document reactions in food diary (note: delayed reactions up to 48hrs are common)
- Many discover they tolerate 50-60g—just not standard restaurant portions
Common Misconceptions About Cauliflower and FODMAPs
Let's clarify frequent confusion points:
- Myth: "All cruciferous vegetables are high FODMAP" → Truth: Bok choy and bamboo shoots remain low FODMAP in generous portions
- Myth: "Cauliflower rice is always safe" → Truth: Most store-bought cauliflower rice exceeds 30g per serving
- Myth: "Cooking eliminates FODMAPs" → Truth: Mannitol remains stable through cooking
Your Personalized Low FODMAP Journey
While Monash provides baseline guidelines, individual tolerance varies significantly. The is cauliflower low fodmap question ultimately depends on your unique digestive profile. Work with a registered dietitian specializing in IBS to create your personalized roadmap—not generic internet advice.
Can I eat cauliflower rice on a low FODMAP diet?
Yes, but strictly limited to 30g (about 1/4 cup) of raw cauliflower rice. Most commercial "cauliflower rice" products contain 80-100g per serving, which is high FODMAP. Measure portions carefully using kitchen scales during elimination phase.
Why is cauliflower high FODMAP in larger portions?
Cauliflower contains mannitol, a sugar alcohol that's poorly absorbed by people with IBS. While small amounts (≤30g) stay below the digestive threshold, larger portions overwhelm the small intestine's absorption capacity, causing fermentation, gas, and pain.
Does roasting cauliflower reduce its FODMAP content?
No. Unlike some FODMAPs that leach into cooking water, mannitol remains stable through dry-heat methods like roasting. In fact, roasting concentrates FODMAPs as water evaporates. Steaming preserves more nutrients while maintaining portion-controlled FODMAP levels.
What's a safe low FODMAP substitute for cauliflower mash?
Try turnip (rutabaga) mash—safe up to 100g portions with similar texture. For creamier results, blend with 30g of cauliflower plus low FODMAP thickeners like potato starch. Many find this hybrid approach maintains flavor while staying within FODMAP limits.
How soon after eating high-FODMAP cauliflower do symptoms appear?
Symptoms typically begin 2-4 hours after consumption as mannitol reaches the colon, but can take up to 48 hours to manifest fully. This delayed reaction is why food diaries are essential—they help connect seemingly unrelated meals with later digestive distress.










 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4