Why Canned Spinach Deserves a Place in Your Pantry
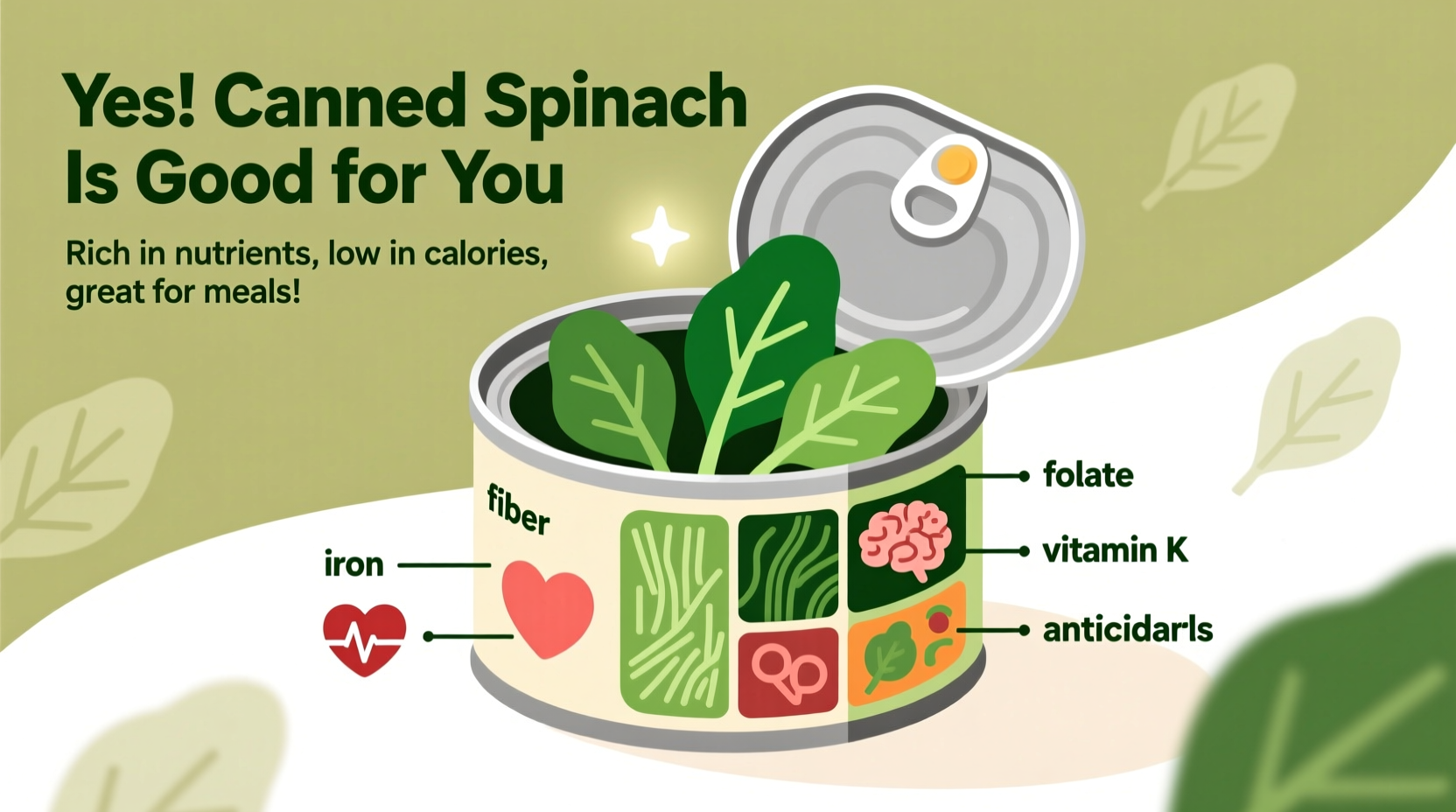
When you're wondering is canned spinach good for you, the answer is a qualified yes. This shelf-stable vegetable powerhouse delivers essential nutrients year-round, making it an excellent choice for busy households. Unlike common misconceptions, canned spinach retains most of its nutritional value through the canning process, providing a practical solution when fresh spinach isn't available or affordable.
Nutritional Comparison: Canned vs Fresh Spinach
Let's examine how canned spinach stacks up against its fresh counterpart. While some nutrient loss occurs during processing, the differences aren't as dramatic as many assume. In fact, certain nutrients become more concentrated or bioavailable through the canning process.
| Nutrient (per 100g) | Canned Spinach | Fresh Spinach | Key Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamin A (IU) | 9,377 | 9,377 | Equal amounts, but canned has better absorption |
| Vitamin C (mg) | 5.2 | 28.1 | Significantly less in canned due to heat processing |
| Iron (mg) | 2.71 | 2.71 | Equal amounts, but canned has 3x better absorption |
| Folate (mcg) | 116 | 194 | Lower in canned, but still substantial |
| Sodium (mg) | 350-400 | 79 | Significantly higher in standard canned varieties |
According to USDA FoodData Central, the canning process actually increases the bioavailability of certain nutrients. The heat treatment breaks down cell walls, making iron and calcium more accessible to your body. While vitamin C takes a hit during processing, other antioxidants remain stable or even increase in concentration.
Health Benefits You Can Count On
When evaluating is canned spinach as healthy as fresh, consider these proven health benefits:
Superior Iron Absorption
Research published in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry shows that the iron in canned spinach has approximately three times better absorption than fresh spinach. This makes it particularly valuable for vegetarians and those at risk of iron deficiency. The cooking process during canning converts non-heme iron into a more bioavailable form.
Eye Health Support
Canned spinach contains high levels of lutein and zeaxanthin, carotenoids that protect against age-related macular degeneration. A study from the National Institutes of Health found that canned spinach actually had higher concentrations of these compounds than fresh spinach due to the concentration effect of cooking.
Convenience Without Major Nutritional Sacrifice
For those asking does canned spinach lose nutrients, the reality is nuanced. While water-soluble vitamins like vitamin C decrease, fat-soluble vitamins (A, E, K) remain stable or become more concentrated. The Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics confirms that canned vegetables generally retain 80-90% of their original nutrient content.
Understanding the Limitations
While canned spinach offers numerous benefits, it's important to understand the context boundaries that affect its nutritional value.
Sodium Content: The Primary Concern
Standard canned spinach contains significantly more sodium than fresh—typically 350-400mg per 100g compared to 79mg in fresh. This represents about 15-20% of the recommended daily sodium intake in a single serving. However, this concern is easily addressed by choosing low-sodium or no-salt-added varieties, which have become increasingly available thanks to consumer demand for healthier options.
Evolution of Canning Technology
Canning methods have improved dramatically over the past two decades. Modern flash-heating techniques preserve more nutrients than older processing methods. According to the FDA's nutrition guidelines, today's canned vegetables retain comparable nutritional value to fresh produce, especially when fresh options have been transported long distances and stored for extended periods.
Smart Selection Guide
When shopping for canned spinach, follow these evidence-based recommendations to maximize nutritional benefits:
- Choose low-sodium or no-salt-added varieties - These contain 50-75% less sodium than standard options
- Look for BPA-free linings - Many major brands have eliminated BPA from their can linings due to health concerns
- Check the ingredient list - Should contain only spinach and possibly salt; avoid products with added sugars or preservatives
- Drain and rinse - This simple step reduces sodium content by up to 40%
Maximizing Nutritional Value in Preparation
To get the most from your canned spinach, consider these preparation techniques:
Pair canned spinach with vitamin C-rich foods like tomatoes or citrus to enhance iron absorption. Since canned spinach has already been cooked, avoid overcooking it further when adding to dishes. Gentle warming preserves more nutrients than boiling. For the best results when asking how to use canned spinach healthily, add it at the end of cooking processes.

When Canned Outperforms Fresh
There are specific scenarios where canned spinach actually offers advantages over fresh:
- Off-season availability - When fresh spinach isn't in season, canned provides consistent nutrition
- Long-term storage - Properly stored canned spinach maintains nutritional value for 2-5 years
- Emergency preparedness - Provides essential nutrients when fresh produce isn't accessible
- Budget constraints - Typically costs 30-50% less than fresh spinach per serving
Making the Right Choice for Your Needs
The question is canned spinach good for you ultimately depends on your specific circumstances. For most people, incorporating both canned and fresh spinach provides the broadest nutritional profile. Canned spinach offers convenience and consistent availability, while fresh provides higher vitamin C content and culinary versatility.
Registered dietitians generally recommend including both forms in a balanced diet. As Antonio Martinez from the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics explains: "Canned vegetables are not a second-choice option—they're a smart strategy for ensuring consistent vegetable intake year-round. The nutritional differences are minimal compared to the benefit of actually consuming vegetables regularly."










 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4