Understanding Safe Garlic Consumption Limits
Garlic transforms ordinary dishes into culinary masterpieces, but understanding how much garlic is too much protects your health while maximizing benefits. This guide delivers science-backed consumption limits verified by medical authorities, helping you enjoy garlic's powerful properties without crossing into dangerous territory.
Garlic Consumption: Quick Reference Guide
Before diving deeper, here's what you need to know immediately about safe daily garlic intake:
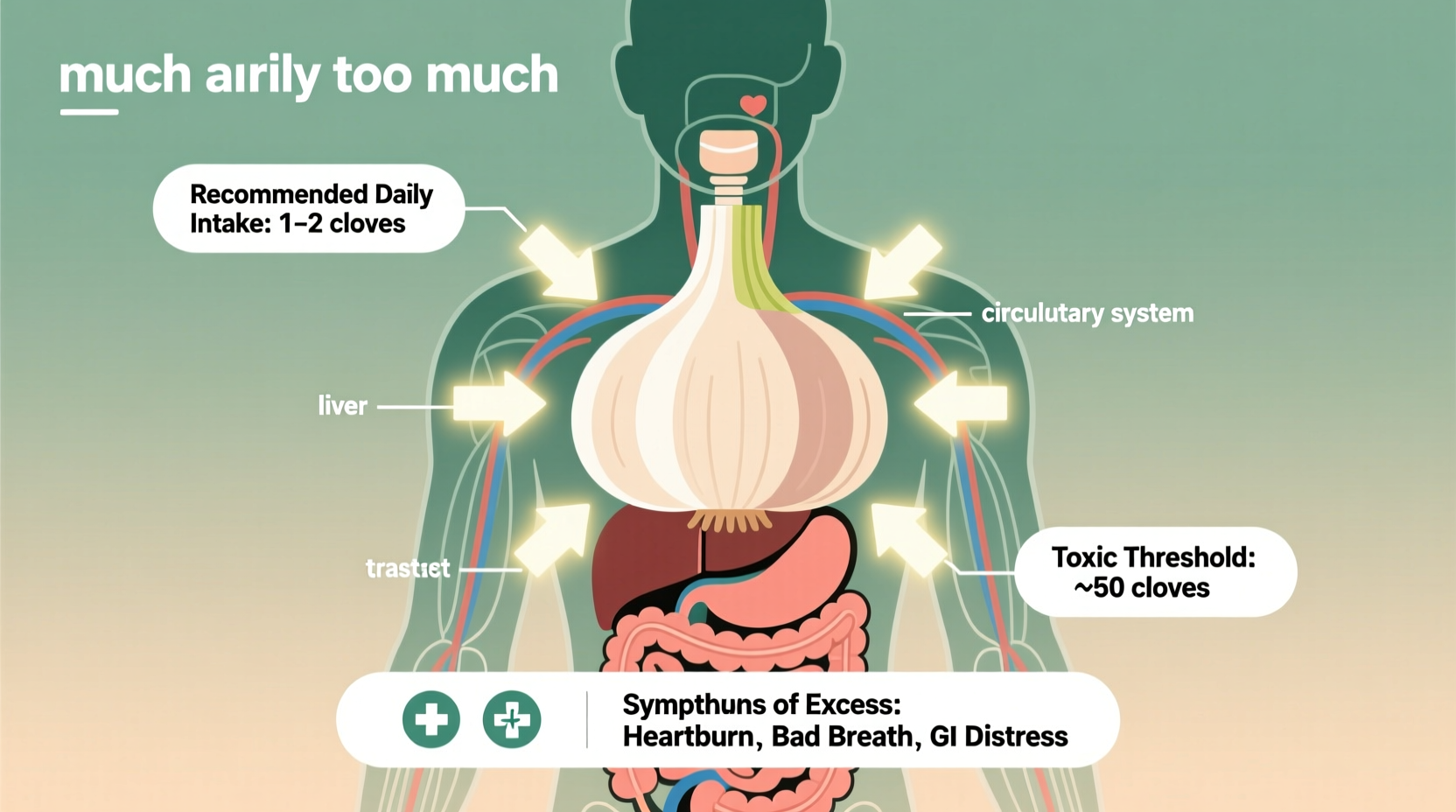
- Adults: 2-3 raw cloves (4-6g) or 600-1,200mg of aged garlic extract daily
- Maximum safe limit: 5 cloves (10g) of raw garlic
- Warning threshold: Persistent heartburn or digestive upset
- Critical risk: Taking garlic supplements with blood thinners
| Consumption Level | Daily Amount | Health Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Optimal Intake | 1-2 raw cloves (2-4g) | Maximum cardiovascular benefits with minimal side effects |
| Moderate Intake | 2-3 raw cloves (4-6g) | Additional immune support, possible mild digestive effects |
| Warning Zone | 3-5 raw cloves (6-10g) | Increased risk of heartburn, gas, and potential medication interactions |
| Danger Zone | 5+ raw cloves (10g+) | Significant bleeding risk, especially before surgery or with blood thinners |
The Science Behind Garlic's Double-Edged Sword
Garlic's active compound allicin delivers impressive health benefits but becomes problematic in excess. According to the National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health, raw garlic contains 5,000-9,000 parts per million of allicin, which breaks down into beneficial sulfur compounds. However, these same compounds irritate the digestive tract when consumed beyond your personal tolerance.
Medical research published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition reveals that garlic's antiplatelet effects become clinically significant at doses exceeding 5 cloves daily. This explains why the FDA specifically warns about garlic's blood-thinning properties at high consumption levels.

Symptoms That Signal You've Crossed the Line
Recognizing garlic overdose symptoms helps you adjust consumption before serious complications develop. These warning signs typically appear within hours of excessive intake:
- Immediate reactions (within 2 hours): Burning sensation in mouth/stomach, heartburn, nausea
- Short-term effects (3-6 hours): Excessive gas, diarrhea, bad breath that persists despite oral hygiene
- Extended exposure (days of high intake): Headaches, dizziness, increased bleeding from minor cuts
- Critical warning signs: Unexplained bruising, prolonged bleeding from small wounds, heart rhythm changes
The Mayo Clinic specifically notes that individuals taking anticoagulants should maintain consistent garlic intake rather than fluctuating between high and low consumption, as this creates unpredictable blood thinning effects.
Situation-Specific Garlic Safety Guidelines
Your safe daily garlic consumption limit changes based on specific circumstances. These evidence-based adjustments keep you protected:
Before Medical Procedures
Stop consuming more than 1 clove daily at least 7-10 days before surgery or dental work requiring bleeding control. The American Society of Anesthesiologists recommends this precaution due to garlic's irreversible platelet inhibition that lasts 7-10 days after consumption.
With Medication Interactions
If taking blood thinners (warfarin, aspirin), HIV medications, or certain birth control pills, limit garlic to 1 clove daily. Research in Pharmacotherapy shows garlic can increase blood levels of these medications by up to 50%, creating dangerous side effects.
Digestive Sensitivity Considerations
Those with IBS or acid reflux should start with 1/2 clove daily, monitoring symptoms for 3 days before increasing. A National Institutes of Health study found 30% of IBS patients experienced symptom exacerbation at just 2 cloves daily.
Maximizing Benefits While Minimizing Risks
Follow these practical strategies to enjoy garlic's benefits without crossing into dangerous garlic consumption levels:
- Crush and wait: Let crushed garlic sit 10 minutes before cooking to activate beneficial compounds while reducing harshness
- Start low: Begin with 1/2 clove daily, increasing gradually over weeks to assess tolerance
- Cook strategically: Add garlic late in cooking to preserve benefits while mellowing flavor intensity
- Track reactions: Keep a food journal noting garlic amounts and any digestive changes
- Choose supplements wisely: If using garlic supplements, select aged garlic extract which has fewer digestive side effects
Remember that how much garlic is too much varies by individual. What causes discomfort for one person might be well-tolerated by another. Pay attention to your body's signals rather than rigid numerical limits.
Special Considerations for Different Groups
Certain populations require extra caution with garlic consumption limits:
- Pregnant women: Limit to 1-2 cloves daily; higher amounts may stimulate uterine contractions
- Children: Under age 12 should consume no more than 1/4-1/2 clove daily
- Elderly: Those on multiple medications should consult doctors about safe amounts
- Diabetics: Garlic may enhance medication effects, requiring blood sugar monitoring
The American Pregnancy Association specifically advises against garlic supplements during pregnancy due to insufficient safety data, while considering culinary amounts generally safe.
Your Practical Garlic Consumption Action Plan
Implement these steps to determine your personal safe garlic intake level:
- Start with 1/2 raw clove daily for 3 days
- Increase by 1/2 clove every 3 days while monitoring symptoms
- Identify your personal threshold where mild digestive effects begin
- Maintain consumption 1/2 clove below this threshold for optimal safety
- Reduce intake by 50% when taking medications or before medical procedures
This personalized approach works better than generic recommendations because individual tolerance varies significantly based on gut microbiome composition and genetic factors affecting allicin metabolism.
Frequently Asked Questions
How much raw garlic is safe to eat daily?
For most adults, 1-2 raw cloves (2-4 grams) daily provides health benefits with minimal side effects. Consuming more than 3 cloves (6 grams) regularly increases risks of digestive upset and potential medication interactions. Those with sensitive digestive systems may need to limit intake to 1 clove daily.
What are the signs of consuming too much garlic?
Common signs include persistent heartburn, excessive gas and bloating, diarrhea, and unusually strong body odor that persists despite hygiene. More serious symptoms include unexplained bruising, prolonged bleeding from minor cuts, and headaches. These typically appear within hours of consuming more than 5 cloves of raw garlic.
Can eating too much garlic cause permanent damage?
While occasional overconsumption typically causes only temporary discomfort, regularly exceeding 5 cloves daily may lead to chronic issues like stomach inflammation or nutrient absorption problems. The most significant risk involves dangerous interactions with blood thinners, which could cause serious bleeding events. No evidence suggests permanent organ damage from culinary garlic amounts, but extremely high supplement doses have shown liver toxicity in rare cases.
How does cooking affect garlic's safety profile?
Cooking significantly reduces garlic's potency and potential side effects. Heat deactivates alliinase, the enzyme that creates allicin, lowering both benefits and risks. You can safely consume approximately twice as much cooked garlic compared to raw without experiencing the same side effects. However, adding garlic late in cooking preserves more beneficial compounds while still reducing harshness.
Should I stop eating garlic if I'm on blood thinners?
You don't need to eliminate garlic completely, but should strictly limit intake to 1 clove daily and maintain consistent consumption. Fluctuating between high and low garlic intake creates unpredictable blood thinning effects. Always consult your doctor before making dietary changes when taking anticoagulant medications, as individual risk factors vary significantly.










 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4