Understanding the exact calorie content of your baked potato helps with meal planning, dietary tracking, and making informed nutrition choices. Whether you're managing weight, following a specific diet plan, or simply curious about your food, knowing these details empowers you to enjoy this versatile vegetable while staying within your nutritional goals.
What Defines a Medium Baked Potato?
When discussing potato sizes, standardization matters. According to the USDA's portion guidelines:
| Size Category | Weight (grams) | Calories |
|---|---|---|
| Small | 138g | 129 |
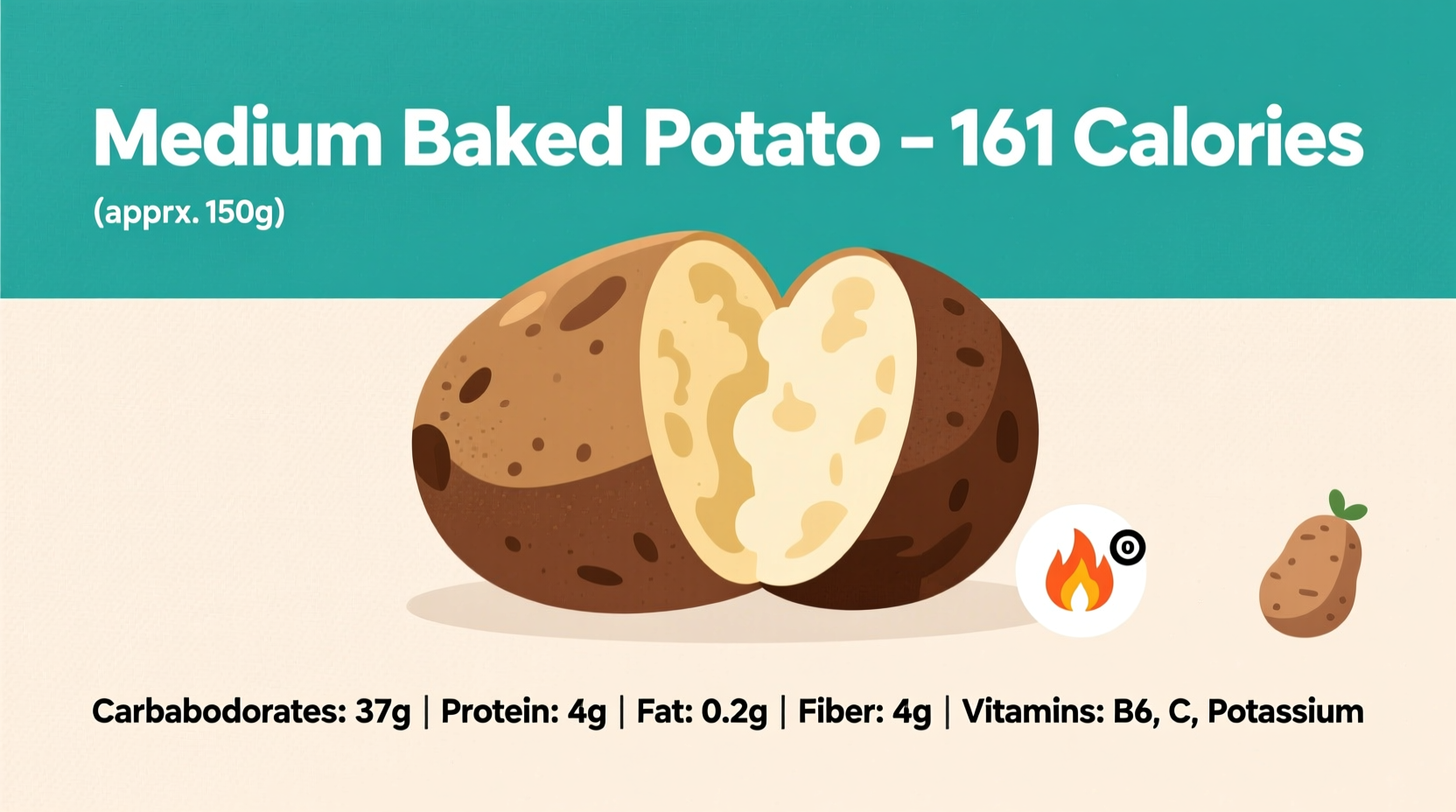
| Medium | 173g | 161 |
| Large | 299g | 278 |
This data comes directly from the USDA FoodData Central, the most authoritative source for nutrition information in the United States. Note that these values represent a plain baked potato with skin, prepared without any added fats or seasonings.
How Preparation Method Affects Calorie Count
The way you prepare your potato significantly impacts its nutritional profile. Here's how different cooking methods change the calorie content for a medium potato:
- Baked with skin: 161 calories (most nutrient retention)
- Boiled: 140 calories (slight nutrient leaching into water)
- Microwaved: 158 calories (similar to baking)
- Fried: 365+ calories (absorbs significant oil)
- Mashed (with milk and butter): 240+ calories
As documented by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, baking preserves more nutrients compared to boiling or frying, making it the healthiest preparation method for maximizing nutritional value while maintaining reasonable calorie counts.

Nutritional Profile Beyond Calories
While calorie count matters, the complete nutritional package determines a food's value. A medium baked potato delivers impressive nutrition:
- Carbohydrates: 37g (12% of daily value)
- Dietary Fiber: 4.3g (15% of daily value)
- Potassium: 926mg (26% of daily value)
- Vitamin C: 17mg (19% of daily value)
- Vitamin B6: 0.6mg (35% of daily value)
- Manganese: 0.5mg (23% of daily value)
According to research published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, potatoes provide more potassium per serving than bananas and are an excellent source of resistant starch when cooled after cooking, which benefits gut health.
Smart Ways to Enjoy Baked Potatoes Without Excess Calories
The real calorie concern with baked potatoes comes from what you add. Consider these healthy topping alternatives:
- Instead of butter: Try Greek yogurt (adds protein with fewer calories)
- Instead of sour cream: Use blended cottage cheese
- Instead of cheese: Sprinkle nutritional yeast for cheesy flavor
- Instead of bacon bits: Add roasted chickpeas for crunch
- For flavor: Herbs, garlic, lemon juice, or hot sauce
Registered dietitians at the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics recommend keeping toppings under 100 calories to maintain the potato's status as a nutrient-dense food rather than a high-calorie indulgence.
Common Questions About Baked Potato Nutrition
Many people wonder about the nutritional differences between potato varieties and preparation methods. Russet potatoes (the classic baking potato) contain slightly more calories than red or Yukon Gold varieties of the same size, but the difference is minimal—typically less than 10 calories per medium potato.
Another frequent question involves the skin: leaving the skin on adds valuable fiber and nutrients while contributing negligible calories. The skin contains about half the potato's total fiber content, making it worth keeping for maximum nutritional benefit.










 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4