When you're experiencing or witnessing a food allergy reaction, knowing exactly how long a food allergy reaction lasts could be critical information. Understanding the timeline helps determine when emergency intervention is needed and what to expect during recovery.
Understanding Food Allergy Reaction Timelines
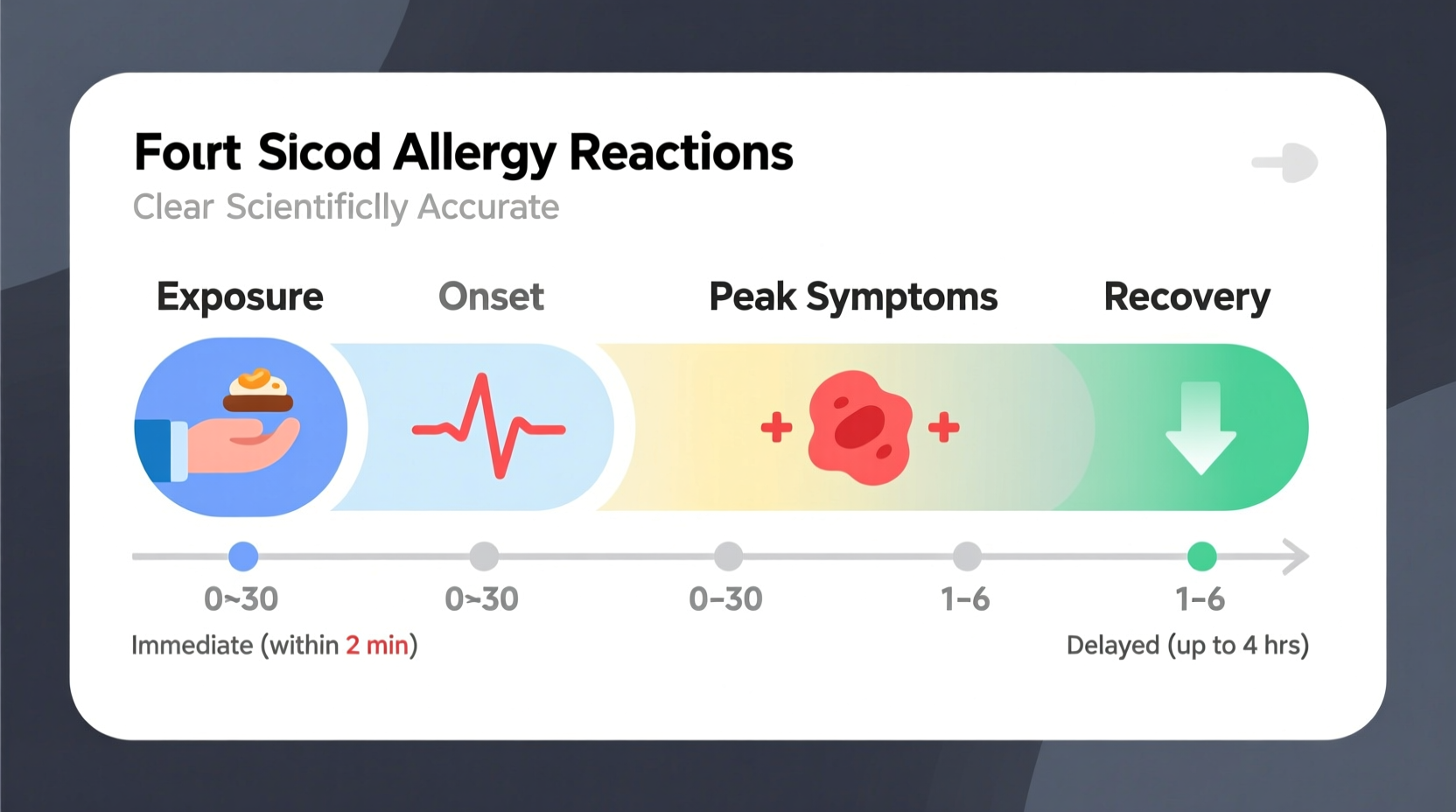
Food allergy reactions don't follow a one-size-fits-all pattern. The duration varies significantly based on multiple factors including the type of allergen, amount consumed, individual sensitivity, and treatment timing. Most reactions begin rapidly—within 5 to 30 minutes of exposure—but some delayed reactions can take up to 2 hours to manifest.
For those wondering how long does a food allergy reaction last after eating, the typical progression follows this pattern:
| Reaction Severity | Onset Time | Typical Duration | Recovery Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mild reactions | 5-30 minutes | 1-2 hours | Symptoms often resolve with antihistamines |
| Moderate reactions | 5-60 minutes | 2-6 hours | May require epinephrine; symptoms gradually improve |
| Severe reactions (anaphylaxis) | Immediate-20 minutes | Several hours | Requires emergency treatment; hospital observation often needed |
| Biphasic reactions | 1-72 hours after initial reaction | Additional 1-12 hours | Second wave requires additional treatment |
When to Seek Emergency Medical Help
Certain symptoms indicate an immediate need for emergency care, regardless of how long a food allergy reaction typically lasts. Call emergency services if you experience:
- Difficulty breathing or wheezing
- Swelling of the throat or tongue
- Significant drop in blood pressure (dizziness, fainting)
- Multiple body systems affected (skin, respiratory, gastrointestinal)
- Symptoms worsening despite epinephrine administration
Even if symptoms seem to improve after using an epinephrine auto-injector, medical evaluation is essential. According to the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology, patients should be monitored for at least 4-6 hours after a severe reaction due to the risk of biphasic reactions.
The Hidden Danger: Biphasic Allergic Reactions
One critical aspect many don't consider when asking how long does a food allergy reaction last is the possibility of biphasic reactions. These secondary reactions occur after the initial symptoms have seemingly resolved.
Research published in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology indicates that approximately 1 in 5 anaphylaxis cases develop biphasic reactions. These secondary reactions typically emerge 8-10 hours after the initial episode but can occur anywhere from 1-72 hours later.
Factors increasing biphasic reaction risk include:
- Severe initial reaction requiring multiple epinephrine doses
- Lung involvement (wheezing, shortness of breath)
- Delayed epinephrine administration
- Adolescent age group
Factors That Influence Reaction Duration
Several variables affect how long food allergy symptoms last, making each reaction unique:
Allergen Type Matters
Different allergens trigger varying reaction patterns. For example:
- Peanut and tree nut reactions often last longer than fruit allergies
- Shellfish reactions frequently involve prolonged gastrointestinal symptoms
- Milk allergy reactions in children may resolve more quickly than adult-onset allergies
Treatment Timing Is Critical
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention emphasizes that prompt epinephrine administration significantly reduces reaction duration and severity. Delaying treatment by even 30 minutes can double the risk of prolonged symptoms.
Managing and Shortening Reaction Duration
While you can't completely control how long a food allergy reaction lasts, proper management can minimize duration:
- Immediate epinephrine use for severe reactions—don't wait to see if symptoms worsen
- Antihistamines for mild symptoms (but never as sole treatment for anaphylaxis)
- Medical observation for at least 4-6 hours after severe reactions
- Avoiding known triggers to prevent additional exposure during recovery
According to clinical guidelines from the American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology, attempting to "ride out" a severe reaction without epinephrine significantly increases both duration and risk of complications.
Recovery Timeline After a Reaction
Complete recovery from a food allergy reaction involves multiple phases:
- Immediate phase (0-6 hours): Active symptoms requiring monitoring and potential additional treatment
- Intermediate phase (6-24 hours): Residual symptoms like fatigue, mild itching, or gastrointestinal discomfort
- Recovery phase (24-72 hours): Gradual return to normal activity; some report continued tiredness
- Long-term considerations: Follow-up with allergist to review the incident and update emergency plan
Most people fully recover within 72 hours, but severe reactions may require longer recovery periods. The duration of food allergy symptoms after treatment typically shortens significantly with proper medical intervention.
Preventing Future Reactions
Understanding how long food allergy reactions last underscores the importance of prevention:
- Work with an allergist to develop a personalized emergency action plan
- Carry epinephrine auto-injectors at all times (check expiration dates regularly)
- Educate family, friends, and coworkers about your specific triggers
- Read food labels meticulously—even products you've safely consumed before
- Communicate allergies clearly when dining out
Regular follow-ups with your allergist can help identify if your reaction patterns are changing, potentially affecting how long your food allergy reactions might last in the future.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can a food allergy reaction last for days?
While most acute symptoms resolve within hours, some residual effects like fatigue or mild gastrointestinal discomfort can persist for 2-3 days after a severe reaction. True active allergic symptoms lasting multiple days without treatment would be unusual and warrant medical evaluation.
How long after exposure do food allergy symptoms start?
Most food allergy reactions begin within 5-30 minutes of exposure. However, some reactions can take up to 2 hours to develop, particularly with certain allergens like red meat (alpha-gal syndrome) which may have delayed reactions occurring 3-6 hours after consumption.
Does drinking water help with food allergy reactions?
Drinking water may help mild oral allergy syndrome symptoms by rinsing allergens from the mouth, but it won't stop or shorten a systemic food allergy reaction. For anything beyond mild oral symptoms, epinephrine (for severe reactions) or antihistamines (for mild reactions) are necessary medical treatments.
Can food allergy reactions get worse each time?
Not necessarily. While some people experience progressively severe reactions, others have consistent or even milder subsequent reactions. You cannot predict the severity of future reactions based on past experiences, which is why carrying epinephrine at all times is crucial for those with diagnosed food allergies.
How long should you monitor after a food allergy reaction?
Medical professionals recommend monitoring for at least 4-6 hours after a moderate to severe reaction due to biphasic reaction risks. For mild reactions treated with antihistamines, monitoring for 2-3 hours is typically sufficient. Always follow your allergist's specific recommendations for your situation.










 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4