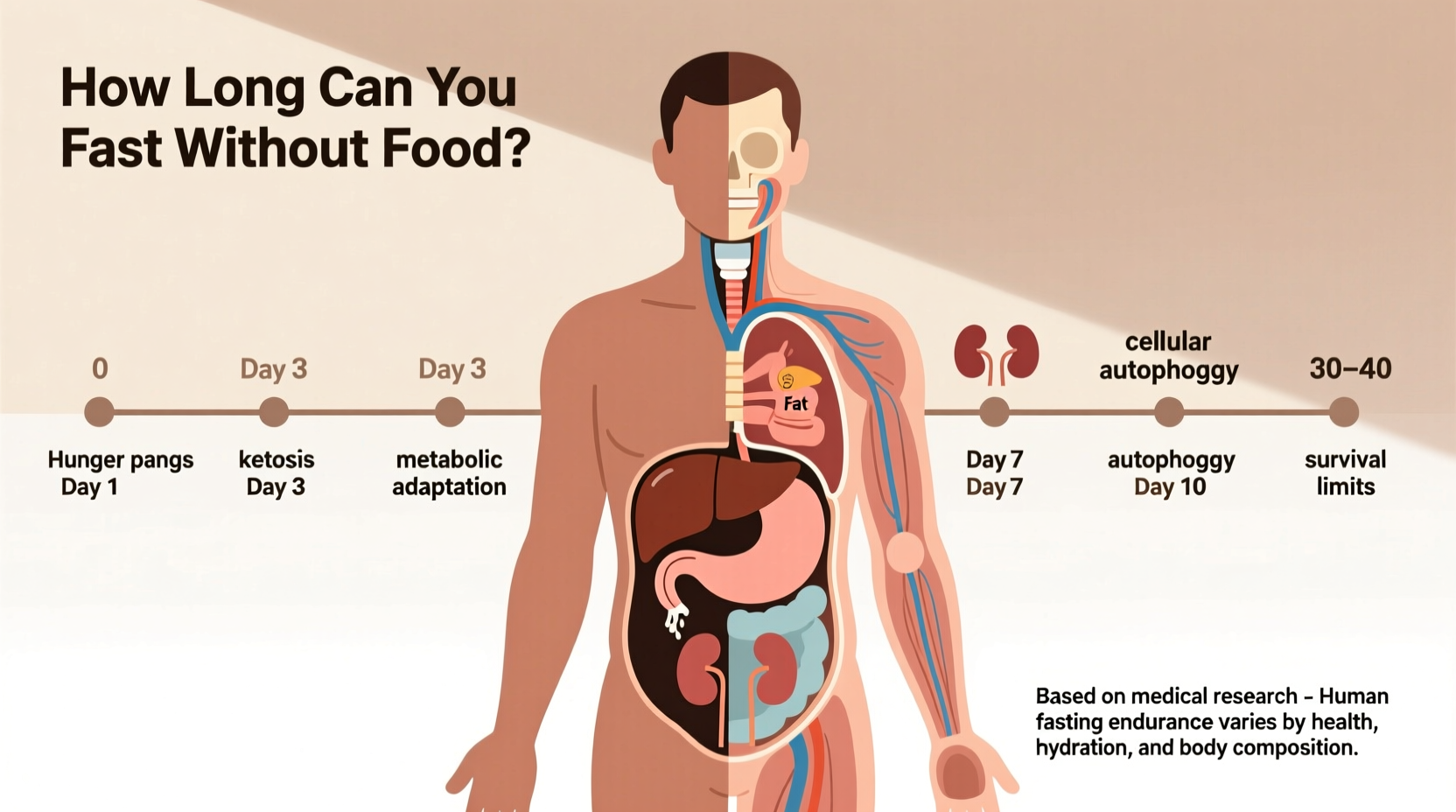
Most healthy adults can safely fast without food for 24-72 hours with proper hydration, but medical supervision is essential beyond 72 hours. Prolonged fasting beyond 7-10 days risks severe complications including organ damage, with survival possible up to 8 weeks under ideal conditions - though this is extremely dangerous and never recommended.
What Your Body Experiences During Fasting: A Science-Backed Timeline
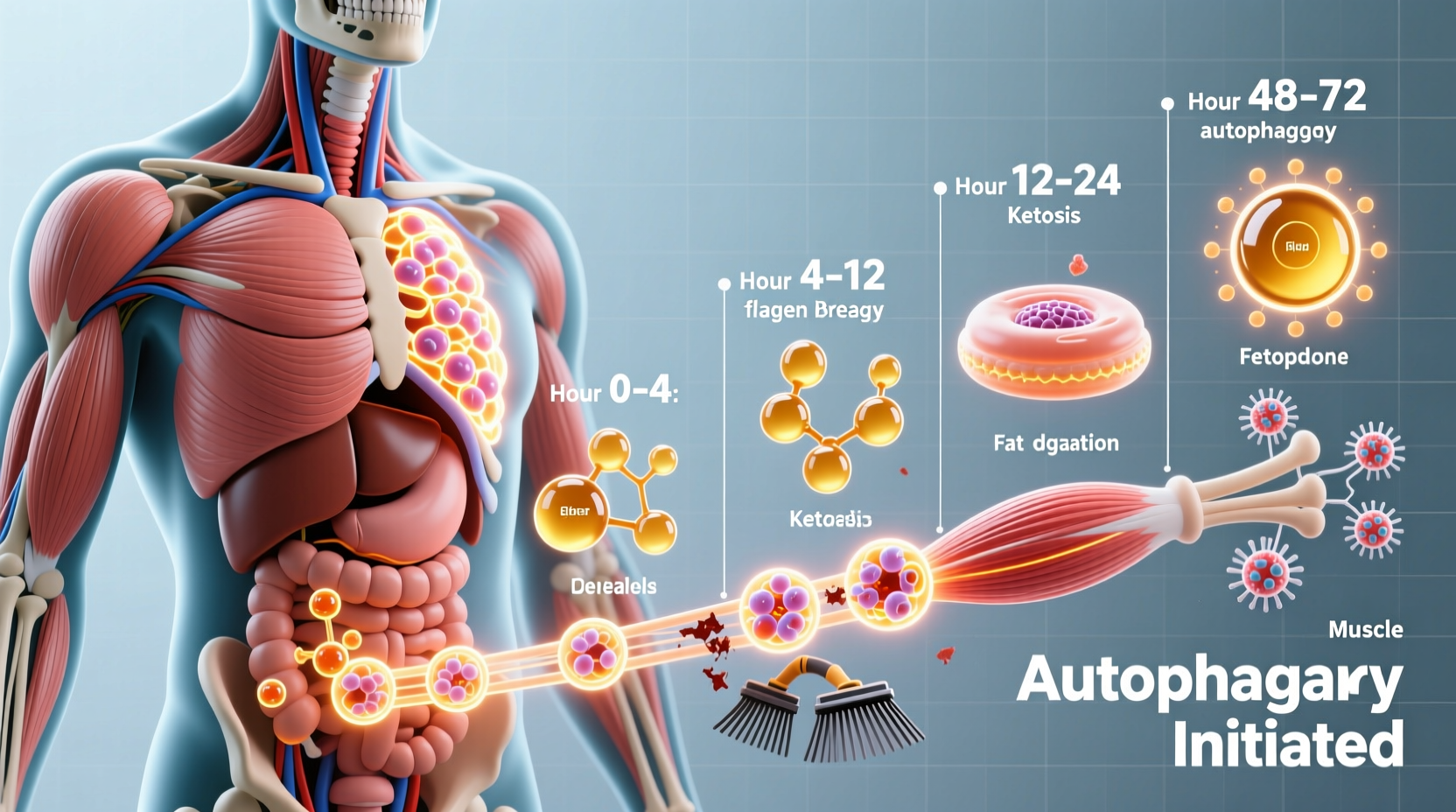
Understanding the physiological stages of fasting helps determine safe limits. Within hours of your last meal, your body initiates critical metabolic shifts. By hour 24, glycogen stores deplete, triggering ketosis where fat becomes the primary energy source. This natural adaptation explains why short-term fasting is generally safe for healthy individuals.
However, the critical danger zone begins around day 3-5. As protein breakdown accelerates to maintain blood glucose, muscle wasting occurs. Electrolyte imbalances become life-threatening without medical monitoring. The National Institutes of Health confirms that prolonged fasting beyond 72 hours requires clinical supervision due to risks of cardiac arrhythmias and refeeding syndrome.
How Long Can You Actually Go? Critical Factors That Change Everything
There's no universal "safe limit" - your individual physiology dramatically alters fasting duration. Consider these context boundaries that determine your personal threshold:
| Factor | Shortens Safe Duration | Extends Safe Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Body Composition | Low body fat percentage | Higher body fat reserves |
| Hydration Status | Dehydration or electrolyte imbalance | Optimal water/electrolyte intake |
| Health Conditions | Diabetes, kidney disease, heart conditions | No chronic health issues |
| Age | Elderly or children | Healthy adults 18-50 |
This contextual variability explains why medical professionals emphasize personalized assessment. The Mayo Clinic explicitly states that fasting beyond 72 hours should only occur under medical supervision, particularly for those with pre-existing conditions.
When Fasting Turns Dangerous: Warning Signs You Must Recognize
Knowing these critical danger signals could save your life. By day 4-5, most people experience:
- Severe dizziness and orthostatic hypotension (blood pressure drops when standing)
- Persistent heart palpitations or irregular heartbeat
- Confusion, disorientation, or inability to concentrate
- Extreme muscle weakness preventing basic movement
These symptoms indicate your body is breaking down vital proteins - including heart muscle. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition documents cases where unsupervised fasting beyond 10 days caused irreversible cardiac damage. Never ignore these red flags: seek immediate medical help if you experience any neurological symptoms or heart irregularities.
Safe Fasting Practices: What Science Actually Recommends
If considering short-term fasting (24-48 hours), follow these evidence-based protocols:
- Hydrate strategically: Consume 2-3L water daily with electrolyte supplements (sodium, potassium, magnesium)
- Limit duration: Never exceed 72 hours without physician clearance
- Break fast properly: Start with bone broth or electrolyte drinks before introducing solid foods
- Monitor symptoms: Track blood pressure and heart rate twice daily using a home monitor
For therapeutic fasting protocols, the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics requires medical supervision for any fast exceeding 24 hours. This isn't cautionary - it's based on documented cases of life-threatening complications in seemingly healthy individuals.
Why the 8-Week Survival Myth Is Misleading
While historical accounts mention survival up to 8 weeks (like hunger strikes), these cases involved:
- Extreme body fat reserves (30%+ body fat)
- Perfect hydration and electrolyte management
- Medical monitoring in controlled environments
These are exceptional scenarios, not safe benchmarks. The CDC emphasizes that prolonged fasting without medical oversight carries significant mortality risks, with complications often emerging unexpectedly after day 7. Your personal "safe limit" is almost certainly shorter than popular myths suggest.
Practical Guidance for Your Fasting Journey
Before attempting any fast:
- Consult your physician if you have diabetes, heart conditions, or take medications
- Start with 12-16 hour overnight fasts before attempting longer durations
- Never fast while pregnant, breastfeeding, or under age 18
- Stop immediately if experiencing chest pain, severe headache, or confusion
Remember: Fasting isn't a weight loss solution but a medical intervention. The American Medical Association states that unsupervised extended fasting provides no proven health benefits that outweigh the risks. Focus on sustainable nutrition patterns instead of extreme measures.










 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4