Why Frozen Spinach Nutrition Surprises Most Consumers
Many shoppers assume fresh produce always beats frozen, but spinach tells a different story. When spinach is flash-frozen within hours of harvest, it preserves nutrients that would otherwise degrade during the 7-10 day journey from farm to supermarket shelf. Research from the US Department of Agriculture confirms frozen spinach maintains higher levels of water-soluble vitamins like folate and vitamin C compared to fresh spinach sold weeks after harvest.
Frozen Spinach Nutritional Profile: What's Really Inside
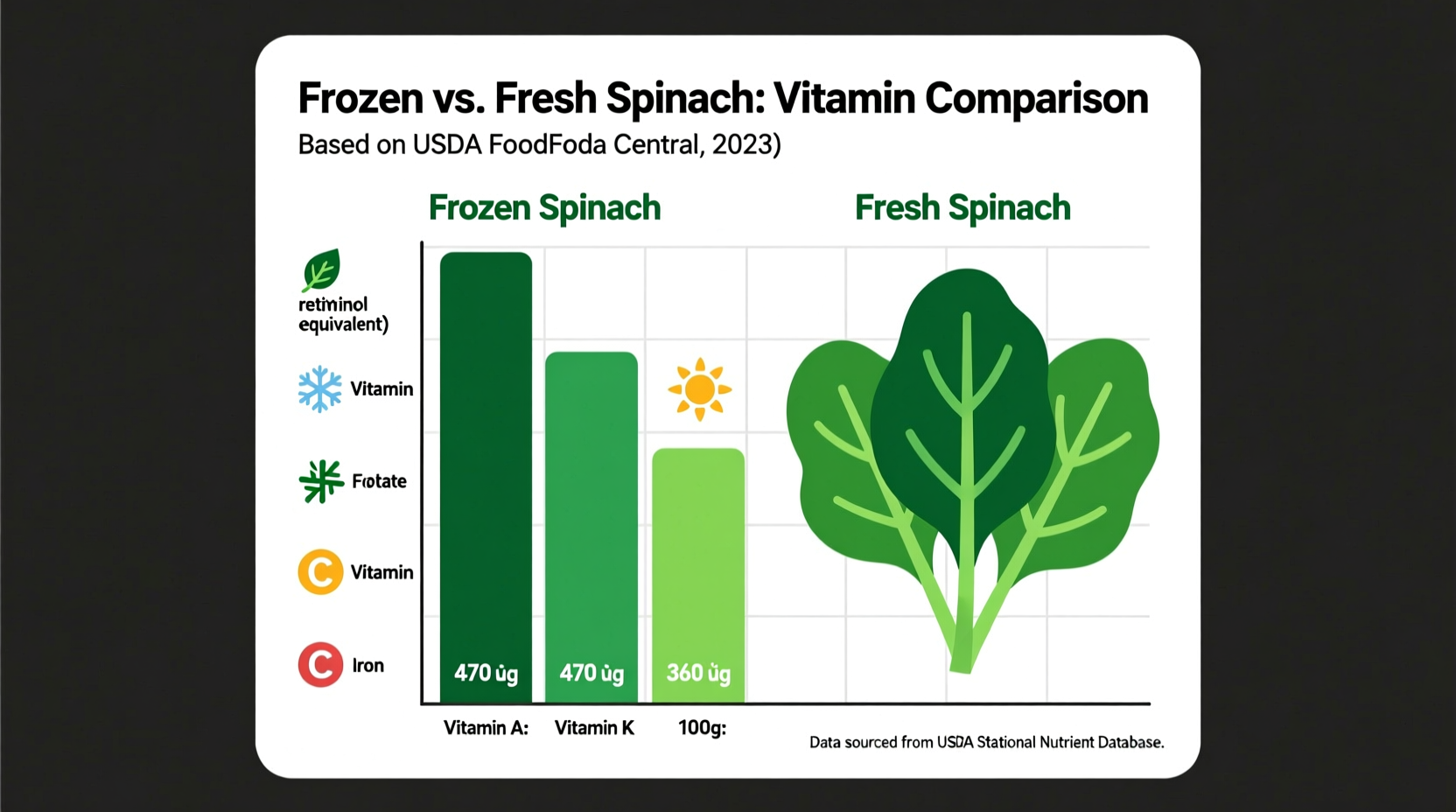
Understanding frozen spinach's complete nutritional value helps you make informed dietary choices. The table below shows nutrient content per 100g serving based on USDA FoodData Central data:
| Nutrient | Frozen Spinach (per 100g) | Fresh Spinach (per 100g) | Daily Value % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calories | 23 | 23 | 1% |
| Protein | 2.9g | 2.9g | 6% |
| Fiber | 3.6g | 2.2g | 13% |
| Vitamin A | 469μg | 469μg | 56% |
| Vitamin K | 483μg | 483μg | 760% |
| Folate | 194μg | 146μg | 65% |
| Vitamin C | 12mg | 28mg | 15% |
| Iron | 2.7mg | 2.7mg | 15% |
The Science Behind Frozen Spinach's Nutrient Preservation
Modern freezing technology has transformed how we preserve vegetable nutrition. Here's what happens to spinach from field to freezer:
- Harvest at peak ripeness - Spinach is picked when nutrient density is highest
- Blanching (1-2 minutes) - Brief hot water treatment stops enzyme activity that degrades nutrients
- Flash freezing (-40°F) - Rapid freezing within 3 hours of harvest locks in vitamins
- Cold chain maintenance - Consistent -18°C storage preserves quality for 8-12 months
According to research published in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, frozen spinach retains 90% of its folate content after 6 months of storage, while fresh spinach loses up to 77% of this vital B-vitamin during typical retail display periods. This nutrient preservation timeline explains why frozen spinach often delivers better nutritional value than "fresh" supermarket spinach.
Maximizing Nutritional Benefits When Cooking Frozen Spinach
You can optimize frozen spinach's nutritional value with these science-backed preparation techniques:
- Don't thaw before cooking - Cooking from frozen preserves water-soluble vitamins that would leach out during thawing
- Add healthy fats - Pair with olive oil or avocado to boost absorption of fat-soluble vitamins A, E, and K
- Moderate cooking time - Sauté for 3-5 minutes rather than boiling to preserve heat-sensitive nutrients
- Pair with vitamin C sources - Combine with tomatoes or citrus to enhance non-heme iron absorption
Frozen vs. Fresh Spinach: When to Choose Which
Both forms have their place in a healthy diet. Consider these factors when deciding:
Frozen Spinach Advantages
- Higher folate and fiber content due to minimal post-harvest degradation
- Available year-round with consistent nutritional profile
- More cost-effective per nutrient density
- Ideal for cooked dishes, smoothies, and baked goods
Fresh Spinach Advantages
- Better texture for raw applications like salads
- Higher vitamin C content when truly fresh (harvested same day)
- No freezer space required
- Preferred for delicate dishes where texture matters
Addressing Common Frozen Spinach Concerns
Many consumers worry about additives in frozen spinach, but USDA regulations require frozen vegetables to contain only the vegetable itself—no preservatives or additives. The FDA mandates that frozen spinach must be 100% spinach with no added ingredients. Sodium content remains naturally low at just 79mg per 100g serving.
Another common misconception is that freezing destroys nutrients. In reality, the blanching process before freezing actually inactivates enzymes that cause nutrient loss, while the freezing process itself preserves what remains. Studies from University of Minnesota Extension show frozen spinach maintains comparable or superior levels of most nutrients compared to fresh spinach after just 3 days of refrigerated storage.
Practical Applications for Health-Conscious Eaters
Incorporate frozen spinach into your diet with these nutrient-maximizing strategies:
- Morning boost - Blend ½ cup frozen spinach into smoothies (adds nutrients without altering flavor)
- Meal prep efficiency - Cook large batches of spinach-based sauces for freezing
- Nutrient preservation - Use frozen spinach in cooked dishes rather than boiling to minimize nutrient loss
- Seasonal flexibility - Maintain consistent vegetable intake year-round regardless of growing seasons










 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4