From Ocean to Kitchen: A Salty Journey Through the Origins of Cooking Salt 🧂
Cooking salt — that humble shaker on your kitchen counter — has quite the adventurous backstory. Whether you’re sprinkling it on fries or curing a holiday ham, salt plays a starring role in kitchens worldwide. But have you ever wondered where does cooking salt come from? Spoiler alert: it's not just mined from beneath our feet or boiled out of the sea for no reason. It’s science, history, and geography rolled into one delicious crystal. Let’s dig (literally) into this salty saga!
Table of Contents
- The Big Picture: What Exactly Is Cooking Salt?
- A Trip Around the World: Where Does Cooking Salt Come From?
- Salt Mining vs. Sea Salt Harvesting – The Showdown
- Types of Salt & Their Origins
- How to Choose the Right Salt for Your Kitchen
- Fun Salt Facts You Can Brag About at Parties
- Conclusion
The Big Picture: What Exactly Is Cooking Salt?
Salt is more than just a seasoning; it’s a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl). While there are many types of salt, “cooking salt” usually refers to any salt used in food preparation — from table salt to fancy artisanal sea salts.
But how did this simple compound become such a culinary cornerstone? The answer lies in its origin story. So grab your snorkel or your hard hat — we're diving deep (and digging wide) to uncover where salt comes from.

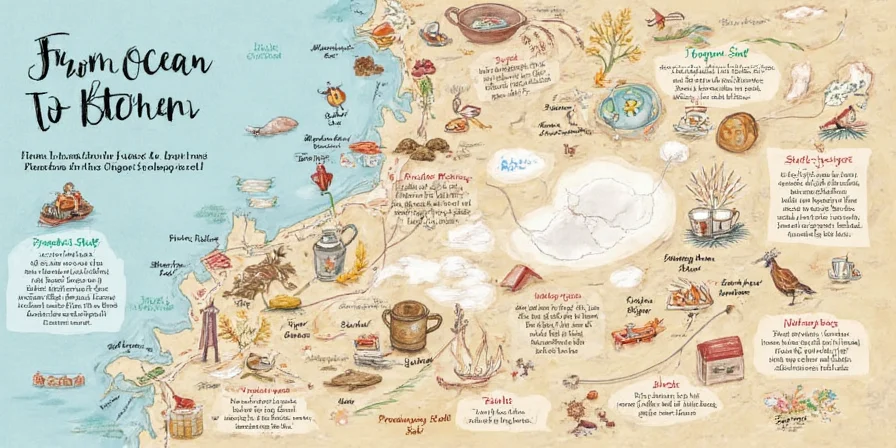
A Trip Around the World: Where Does Cooking Salt Come From?
Salt doesn’t just grow on trees — though if it did, we’d probably still be fighting over who gets to season the steak. There are two primary sources of salt used in cooking:
- Mined salt – extracted from ancient salt deposits buried underground
- Sea salt – harvested by evaporating seawater or saltwater from lakes and ponds
The Mined Marvels
Mined salt comes from ancient salt beds formed millions of years ago when oceans dried up. These deposits are now found deep beneath the Earth's surface. Countries like the United States, Germany, Canada, and China are major producers of rock salt.
The Sea Salt Scene
Sea salt production thrives in warm, dry coastal regions. Places like France (hello, Guérande!), Portugal, Australia, and Japan are famous for their hand-harvested sea salts, often prized for their texture and flavor profiles.

Salt Mining vs. Sea Salt Harvesting – The Showdown
Let’s break down the differences between these two major salt sources with a quick showdown:
| Feature | Salt Mining | Sea Salt Harvesting |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Underground salt deposits | Evaporation of ocean or salt lake water |
| Processing | Heavily processed to remove impurities | Naturally evaporated with minimal processing |
| Texture | Finer, uniform grains | Rougher, flakier, or coarser texture |
| Taste | Mild, neutral flavor | Mineral-rich, complex taste |
| Eco Impact | Higher energy use | More sustainable and eco-friendly |
Types of Salt & Their Origins
Not all salts are created equal! Here’s a breakdown of popular salt varieties and where they come from:
- Table Salt: Mined and refined, often with anti-caking agents. Comes from underground salt mines.
- Kosher Salt: Originally used in Jewish dietary practices. Typically mined but can also be solar-evaporated.
- Sea Salt: Sun-dried and hand-harvested from coastal waters.
- Himalayan Pink Salt: Mined from ancient salt caves in Pakistan, known for its pink hue due to iron oxide.
- Fleur de Sel: Hand-harvested from the surface of salt ponds in France. Known as the “caviar of salts.”
- Flake Salt: Delicate salt crystals formed during evaporation. Often used as a finishing salt.
How to Choose the Right Salt for Your Kitchen
Picking the right salt depends on what you’re cooking and how you want it to taste. Here are some handy tips:
- For everyday cooking: Use table or kosher salt. They dissolve easily and provide consistent salinity.
- For finishing dishes: Opt for flake salt or fleur de sel. Adds a burst of flavor and visual appeal.
- For grilling or roasting: Coarse sea salt or Himalayan pink salt work great for crusts and rubs.
- For baking: Stick with fine-grained salts to ensure even distribution.
Bonus tip: When measuring salt, always consider grain size. One teaspoon of fine salt equals roughly 1.5 teaspoons of coarse salt!
Fun Salt Facts You Can Brag About at Parties
Here’s a sprinkle of trivia to impress your friends next time you pass the salt:
- Salt was once so valuable it was used as currency — hence the word “salary,” derived from the Latin word for salt, salarium.
- The Dead Sea isn’t just a tourist spot; it’s one of the saltiest bodies of water on Earth, with salt concentrations over 30%.
- The largest salt mine in the world is in Goderich, Ontario, Canada. It’s so big you could fit the entire city of Toronto inside it!
- In parts of Ethiopia, people trade salt slabs like gold bars.
- The average American consumes about 3,400 mg of sodium per day — much higher than the recommended 2,300 mg.
Conclusion
So next time you reach for that shaker, remember: you’re holding a piece of ancient seas and underground caverns that have been around longer than most civilizations. Knowing where cooking salt comes from adds a layer of appreciation to every pinch you add to your meals.
Whether it’s mined from the depths of the Earth or harvested under the hot sun, salt is more than just a seasoning — it’s a journey through geology, history, and culinary artistry. Now go forth and season with purpose!

Got questions about salt origins or which salt pairs best with your Sunday roast? Drop us a line in the comments below!











 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4