Understanding ginger root spoilage is essential for both culinary success and food safety. This comprehensive guide provides science-backed information on identifying spoiled ginger, maximizing freshness, and proper storage techniques based on current food preservation research.
How to Identify Spoiled Ginger Root
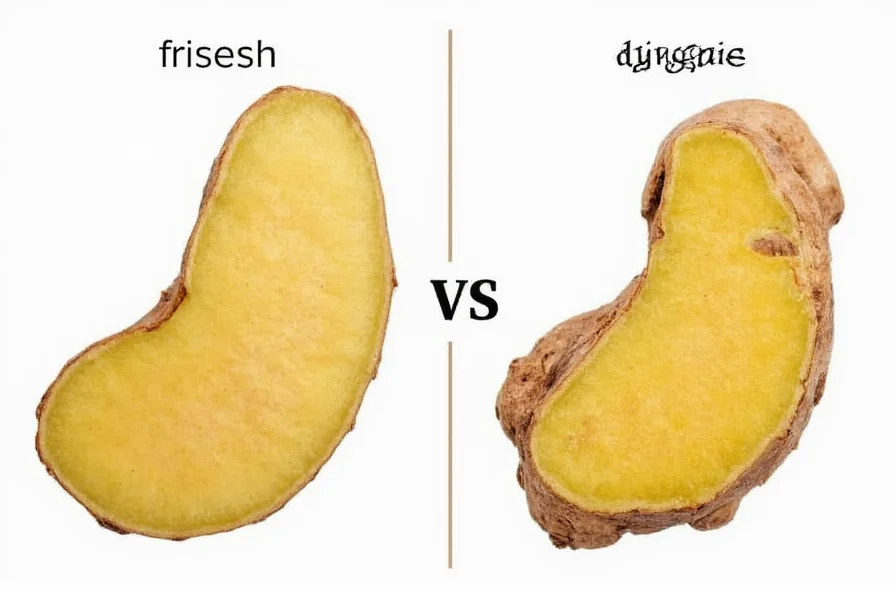
Ginger shows clear visual and sensory indicators when it begins to deteriorate. Recognizing these signs helps prevent consumption of potentially harmful spoiled product while reducing food waste.
Visual Indicators of Bad Ginger
Fresh ginger should have a firm, taut skin with a consistent tan to light brown color. Warning signs include:
- Mold growth (white, green, or black fuzzy patches)
- Darkened or blackened spots spreading across the surface
- Excessive wrinkling beyond normal drying
- Wet, slimy areas on the skin
Tactile and Olfactory Indicators
Texture and smell provide crucial information about ginger's condition:
- Texture: Fresh ginger feels hard and dense. Spoiled ginger becomes soft, mushy, or spongy when pressed.
- Smell: Healthy ginger has a spicy, warm, citrusy aroma. Spoiled ginger develops a sour, fermented, or unpleasant odor.
- Internal examination: Cut ginger should reveal pale yellow flesh. Grayish discoloration or dark spots inside indicate spoilage.
Ginger Root Shelf Life Under Different Storage Conditions
Ginger's longevity varies significantly based on storage methods. Understanding these timelines helps optimize freshness and reduce waste.
| Storage Method | Expected Shelf Life | Quality Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Room Temperature (cool, dry place) | 1-2 weeks | Rapid moisture loss; best for immediate use |
| Refrigerated (whole, in produce drawer) | 3-4 weeks | Maintains flavor and texture best |
| Refrigerated (peeled, in water) | 2-3 weeks | Water changes needed every 2-3 days |
| Refrigerated (in airtight container) | 4-6 weeks | Best method for cut ginger |
| Frozen (whole or sliced) | 4-6 months | Slightly softer texture when thawed |
| Dried (properly dehydrated) | 6-12 months | Requires complete moisture removal |
Proper Ginger Storage Techniques
Implementing correct storage methods dramatically extends ginger's usability while preserving its distinctive flavor compounds and health-promoting properties.
Refrigeration Methods for Maximum Freshness
The refrigerator provides ideal conditions for extending ginger's shelf life:
- Whole ginger in produce drawer: Place unpeeled ginger in the high-humidity crisper drawer. The natural skin acts as a protective barrier against moisture loss.
- Paper towel method: Wrap ginger in a dry paper towel before placing in a plastic bag with small ventilation holes. Replace paper towel if damp.
- Water storage technique: Submerge peeled ginger in water in an airtight container, changing water every 2-3 days. This method maintains crispness but requires more maintenance.
Freezing Ginger for Long-Term Preservation
Freezing preserves ginger's flavor compounds effectively:
- Peel and slice ginger into 1-inch pieces
- Place on parchment-lined baking sheet and freeze until solid (2 hours)
- Transfer to airtight freezer bag, removing excess air
- Label with date for tracking
When properly frozen, ginger can be grated directly from frozen without thawing, making it convenient for cooking and tea preparation. This method of storing fresh ginger root maintains usability while preventing freezer burn.
Food Safety Considerations with Spoiled Ginger
Consuming spoiled ginger poses potential health risks that shouldn't be ignored. While ginger rarely causes serious foodborne illness, mold growth can produce mycotoxins that survive cooking.
When ginger shows minor spoilage in isolated areas, carefully cut away at least 1 inch around the affected area. However, if mold appears throughout the root or the ginger has become soft and mushy, discard the entire piece. This precaution ensures you avoid consuming potentially harmful compounds while maintaining kitchen safety.
Creative Uses for Aging Ginger
As ginger approaches the end of its prime freshness, consider these alternative uses before it fully spoils:
- Make ginger simple syrup for cocktails or beverages
- Create ginger-infused vinegar for salad dressings
- Prepare ginger tea by simmering in water with lemon
- Blend into smoothies where texture matters less
- Make ginger paste for future cooking needs
Common Questions About Ginger Spoilage
Can you eat ginger that has turned slightly gray inside?
Slight graying in ginger may indicate early oxidation rather than spoilage. If the texture remains firm and the smell is normal, it's generally safe to use. However, extensive gray discoloration accompanied by softness or off-odors indicates spoilage and the ginger should be discarded.
How can you tell the difference between normal drying and actual spoilage in ginger?
Normal drying causes ginger to become slightly wrinkled while maintaining firmness. Spoilage involves soft, mushy areas, mold growth, or unpleasant odors. If ginger yields significantly when pressed or shows visible mold, it has spoiled rather than simply dried out.
Is it safe to use ginger that has sprouted?
Sprouted ginger remains safe to eat, though the sprouting process draws nutrients from the root, potentially reducing flavor intensity. Simply cut away the sprouted section and use the remaining firm portion. This differs from potatoes, where sprouts contain harmful compounds.
Can you freeze ginger with the skin on?
Yes, freezing ginger with skin intact is perfectly acceptable. The skin protects the inner flesh during freezing. When ready to use, simply grate the frozen ginger—the skin will separate from the usable flesh. This method of preserving ginger root maintains quality while simplifying preparation.
Does pickling extend ginger's shelf life significantly?
Properly pickled ginger stored in a vinegar-based solution can last 6-12 months refrigerated. The acidic environment prevents bacterial growth. Ensure ginger remains fully submerged in liquid and watch for any signs of mold or off-odors, which indicate spoilage despite pickling.











 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4