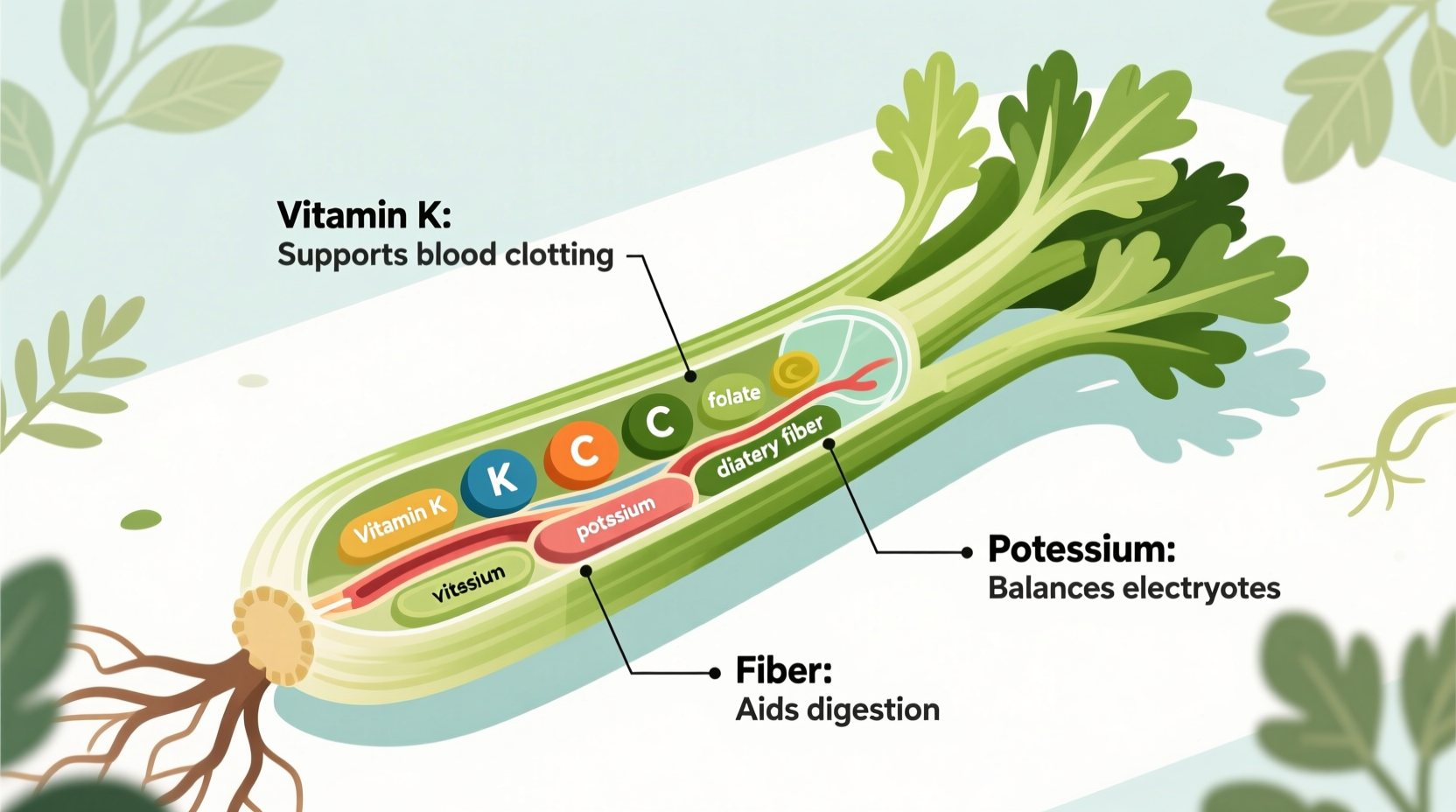
Yes, celery does have nutritional value despite its high water content. While not a nutrient-dense superfood, one cup of chopped celery (101g) provides 134% of your daily vitamin K, 7% of vitamin A, 5% of vitamin C, and 8% of potassium, along with beneficial antioxidants and fiber—making it a valuable low-calorie addition to a balanced diet.
Curious whether that crunchy stalk on your plate is doing anything for your health beyond adding crunch? You're not alone. Many health-conscious eaters wonder does celery have nutritional value or if it's just nature's water stick. Let's cut through the confusion with science-backed facts that reveal exactly what this common vegetable contributes to your nutritional profile.
What's Actually Inside Celery: The Nutritional Breakdown
When evaluating celery nutritional facts per 100g, you'll find it's far from nutritionally empty. According to USDA FoodData Central, a standard cup (101g) of chopped celery delivers:
| Nutrient | Amount | Daily Value % |
|---|---|---|
| Calories | 16 | 1% |
| Fiber | 1.6g | 6% |
| Vitamin K | 32mcg | 134% |
| Vitamin A | 453 IU | 7% |
| Vitamin C | 3.1mg | 5% |
| Potassium | 260mg | 8% |
| Folate | 36mcg | 9% |
This nutritional profile explains why nutritionists consider celery more than just a "negative calorie" food. While it's true that celery is 95% water and extremely low in calories (about 10 calories per stalk), it delivers meaningful amounts of specific micronutrients that many Americans lack in their diets.
Key Health Benefits Backed by Research
Understanding does celery have nutritional value requires looking beyond basic vitamins. Research published in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry identifies over 25 antioxidant compounds in celery, including:
- Apigenin - A flavonoid with demonstrated anti-inflammatory properties
- Luteolin - Shown in laboratory studies to potentially inhibit cancer cell growth
- Phthalides - Compounds that may help lower blood pressure
A 2020 review in Nutrients highlighted celery's potential cardiovascular benefits, noting that regular consumption correlates with modest reductions in blood pressure among prehypertensive individuals. While not a replacement for medication, these findings support celery's role in a heart-healthy diet.

Realistic Expectations: When Celery Shines (and When It Doesn't)
Let's address the elephant in the room: celery won't transform your health if eaten alone. Its nutritional contribution works best within context:
Where celery delivers maximum value:
- As part of a varied vegetable intake for vitamin K (crucial for blood clotting and bone health)
- Providing hydration with electrolytes for athletes or hot weather
- Adding volume and crunch to meals without significant calories
Where celery falls short nutritionally:
- As a primary source of protein, healthy fats, or most vitamins
- When consumed without other nutrient-dense foods
- When only the stalks are eaten (leaves contain significantly more nutrients)
This context matters because many people mistakenly believe is celery actually good for you in isolation. The reality is that celery's nutritional value multiplies when combined with other vegetables and healthy fats—which help absorb its fat-soluble vitamins.
Maximizing Celery's Nutritional Benefits
To get the most from celery's nutritional profile, consider these evidence-based approaches:
- Eat the leaves - Celery leaves contain 3x more vitamin C and calcium than the stalks (per USDA data)
- Add healthy fats - Pair with avocado or olive oil to boost absorption of fat-soluble vitamins
- Don't overcook - Light steaming preserves more nutrients than boiling
- Store properly - Keep in an airtight container with damp paper towels to maintain nutrient levels
Research from the University of California Davis shows that proper storage can maintain celery's vitamin content for up to two weeks—significantly longer than many consumers realize when questioning how healthy is celery really.
Practical Applications for Everyday Eating
Instead of debating is celery a superfood or just water, focus on practical ways to incorporate it effectively:
- Use as a vehicle for nut butters (adding protein and healthy fats)
- Add chopped celery to salads, soups, and stir-fries for texture and nutrients
- Blend leaves into smoothies for a nutrient boost without strong flavor
- Make celery salt by dehydrating and grinding stalks with leaves
Nutrition professionals at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health emphasize that celery's greatest value comes from displacing less nutritious options in your diet—not from any single miraculous property. When considering celery health benefits backed by science, remember it's about consistent, varied vegetable consumption.
Conclusion: The Balanced Truth About Celery's Nutrition
So, does celery have nutritional value? Absolutely—but with important context. While it shouldn't be your sole vegetable source, celery provides specific nutrients often lacking in modern diets, particularly vitamin K and antioxidants. Its low-calorie, high-water profile makes it an excellent tool for increasing vegetable intake without significant calories.
The most accurate answer to does celery have nutritional value lies in understanding its role within a diverse diet. When consumed as part of a varied plant-based eating pattern, celery contributes meaningfully to your overall nutrient intake while adding satisfying crunch and hydration.










 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4