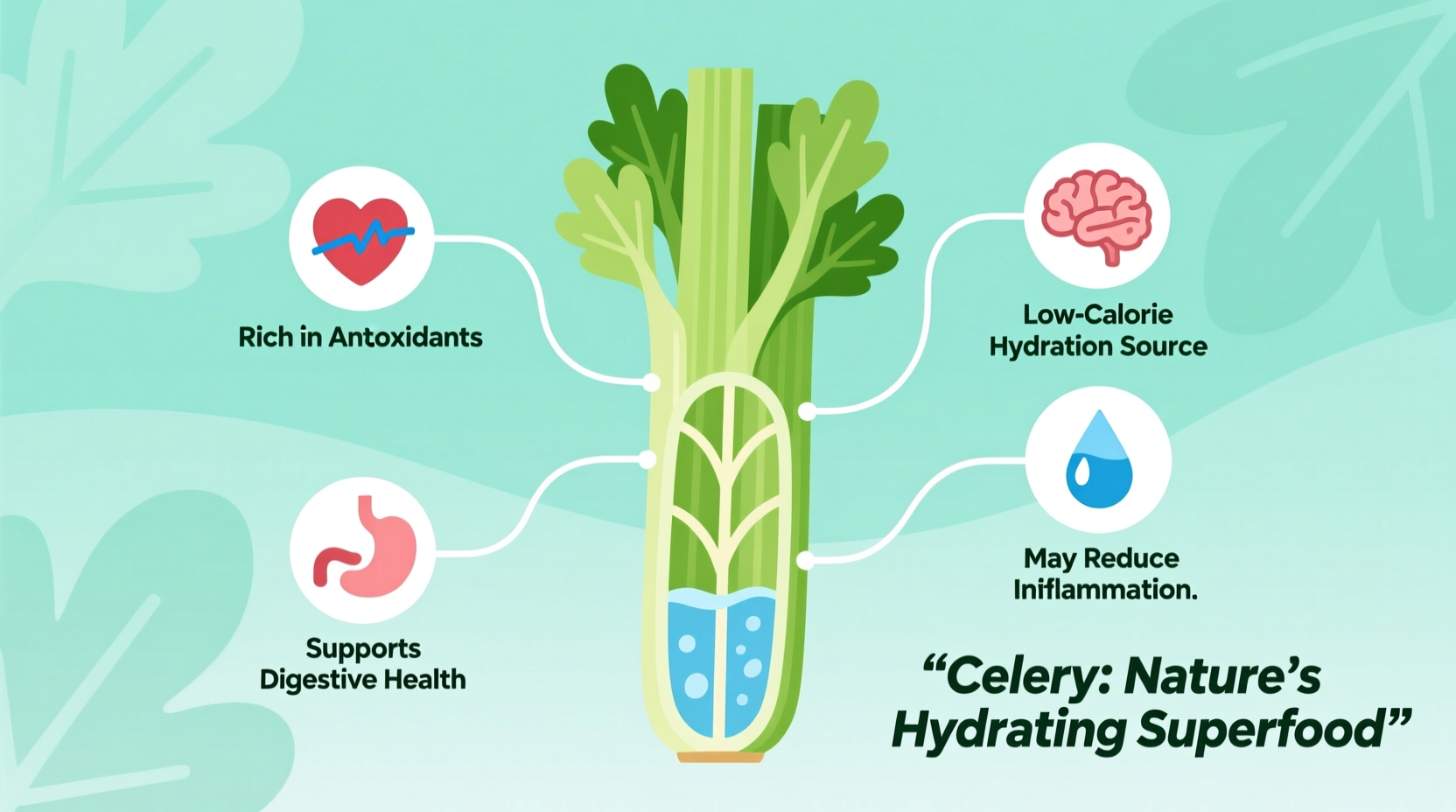
The most significant health advantages of celery include its anti-inflammatory properties, blood pressure regulation potential, and digestive health benefits. Rich in antioxidants like apigenin and luteolin, celery supports cardiovascular health while providing essential vitamins and minerals with minimal calories. Scientific research confirms celery's role in reducing oxidative stress and supporting healthy blood pressure levels when consumed as part of a balanced diet.
Understanding Celery's Nutritional Powerhouse Profile
Often dismissed as a low-calorie snack, celery actually packs a surprising nutritional punch. One cup (101g) of chopped celery delivers:
| Nutrient | Amount per Cup | % Daily Value |
|---|---|---|
| Calories | 16 | 1% |
| Vitamin K | 30 mcg | 25% |
| Vitamin A | 453 IU | 9% |
| Potassium | 260 mg | 7% |
| Fiber | 1.6 g | 6% |
Data sourced from the USDA FoodData Central database confirms celery's impressive nutrient density relative to its calorie content. What makes celery particularly valuable are its phytonutrients—especially apigenin and luteolin—which scientific studies have linked to multiple health benefits.
Science-Backed Health Benefits of Regular Celery Consumption
Cardiovascular Protection Through Natural Compounds
Research published in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry demonstrates that celery's apigenin content helps relax blood vessels, potentially lowering blood pressure. A 2020 clinical review from Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health noted that diets rich in flavonoid-containing vegetables like celery correlate with reduced cardiovascular disease risk.
Unlike pharmaceutical interventions, celery provides these benefits through natural compounds without significant side effects when consumed in normal dietary amounts. The potassium content further supports healthy blood pressure regulation by counteracting sodium effects.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects for Chronic Condition Management
Chronic inflammation underlies many modern health issues. Celery's luteolin content has been studied for its ability to inhibit inflammatory pathways. According to research from the National Institutes of Health, luteolin demonstrates significant anti-inflammatory activity by reducing pro-inflammatory cytokine production.
This makes celery particularly valuable for individuals managing conditions like arthritis or metabolic syndrome. Incorporating celery juice or chopped celery into daily meals provides a natural approach to inflammation management alongside conventional treatments.

Digestive Health and Gut Microbiome Support
Celery's fiber content (1.6g per cup) contributes to digestive regularity while its unique compounds support gut health. The University of Michigan Medicine notes that dietary fiber from vegetables like celery promotes beneficial gut bacteria growth and helps maintain intestinal barrier integrity.
Additionally, celery contains polyacetylenes—compounds with demonstrated antimicrobial properties that may help maintain a healthy gut microbiome balance. This dual action makes celery particularly valuable for digestive wellness.
Antioxidant Protection Against Cellular Damage
With an ORAC (Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity) value of 850 μmol TE/100g, celery ranks among vegetables with significant antioxidant capacity. These antioxidants neutralize free radicals that contribute to cellular damage and chronic disease development.
A Mayo Clinic review on dietary antioxidants explains that consistent consumption of antioxidant-rich foods like celery supports the body's natural defense systems against oxidative stress. The combination of vitamin C, flavonoids, and other phytonutrients creates a synergistic protective effect.
Practical Applications: Maximizing Celery's Health Benefits
Optimal Preparation Methods for Nutrient Retention
To preserve celery's delicate nutrients:
- Store in the refrigerator's crisper drawer with high humidity
- Wash just before use to prevent premature spoilage
- Consume raw when possible to maximize flavonoid content
- If cooking, use minimal water and short cooking times
Dietary Integration Strategies
Incorporate celery into your daily routine with these practical approaches:
- Add chopped celery to salads, soups, and stir-fries
- Blend celery with cucumber and lemon for a hydrating morning drink
- Use celery sticks as a vehicle for healthy dips like hummus or guacamole
- Include celery leaves (often discarded) which contain higher nutrient concentrations
Contextual Considerations: When Celery May Not Be Ideal
While celery offers numerous health advantages, certain considerations apply:
- Medication interactions: Celery's vitamin K content may interfere with blood thinners like warfarin. Consult your physician about consistent vitamin K intake if taking these medications.
- Allergy concerns: Some individuals with pollen allergies may experience oral allergy syndrome when consuming raw celery.
- Dietary balance: Relying solely on celery for health benefits is ineffective. It works best as part of a diverse, plant-rich diet.
The American Dietetic Association emphasizes that no single food provides complete nutrition, highlighting the importance of dietary variety even when incorporating beneficial foods like celery.
Conclusion: Celery's Place in a Health-Conscious Diet
Celery's health advantages extend far beyond its reputation as a low-calorie snack. Scientific evidence supports its role in cardiovascular protection, inflammation reduction, digestive health, and antioxidant defense. By understanding how to properly select, store, and incorporate celery into your diet, you can maximize these evidence-based benefits while enjoying its crisp texture and refreshing flavor.
Remember that celery works best as part of a balanced, diverse diet rather than a standalone solution. Consistent consumption alongside other nutrient-dense vegetables provides the most significant health advantages for long-term wellness.










 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4