Understanding the carbohydrate composition of russet potatoes is essential for meal planning, dietary management, and optimizing your nutritional intake. As one of the most popular potato varieties in North America, russet potatoes serve as a dietary staple for millions, yet many people remain unclear about their exact nutritional profile.
Breaking Down Russet Potato Carbohydrates
When examining carbohydrate content in russet potato per 100g, USDA FoodData Central provides the most reliable figures. A raw russet potato contains:
- Total carbohydrates: 15.9g per 100g
- Dietary fiber: 1.6g per 100g (6% of daily value)
- Sugars: 0.6g per 100g
- Starch: Approximately 13.7g per 100g
The substantial starch content explains why russet potatoes become fluffy when baked—their high starch composition absorbs moisture during cooking. This starch breaks down into simple sugars during digestion, which affects blood glucose levels.
How Cooking Methods Impact Carb Content
Many people wonder if how to reduce carbs in russet potatoes is possible through different preparation methods. While cooking doesn't significantly alter the total carbohydrate content, it does affect the glycemic response:
- Baking: Increases glycemic index to approximately 111 (high)
- Boiling: Results in a moderate glycemic index of about 82
- Cooling after cooking: Creates resistant starch, lowering effective carb impact by 10-15%
According to research published in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, cooling cooked potatoes for 24 hours increases resistant starch content by up to 15%, which functions more like fiber in the digestive system.
| Potato Variety | Total Carbs (per 100g) | Dietary Fiber | Glycemic Index |
|---|---|---|---|
| Russet | 15.9g | 1.6g | 82-111 |
| Sweet Potato | 20.1g | 3.0g | 44-94 |
| Red Potato | 15.3g | 2.2g | 65-89 |
| Yukon Gold | 15.5g | 2.0g | 60-85 |
This russet potato carbs vs sweet potato comparison reveals important nutritional differences. While sweet potatoes contain more total carbohydrates, they generally have a lower glycemic index due to higher fiber content and different starch composition.
Practical Applications for Different Dietary Needs
For those managing carbohydrate intake, understanding how many net carbs in russet potato is crucial. Net carbs are calculated by subtracting fiber from total carbohydrates, as fiber doesn't significantly impact blood sugar.
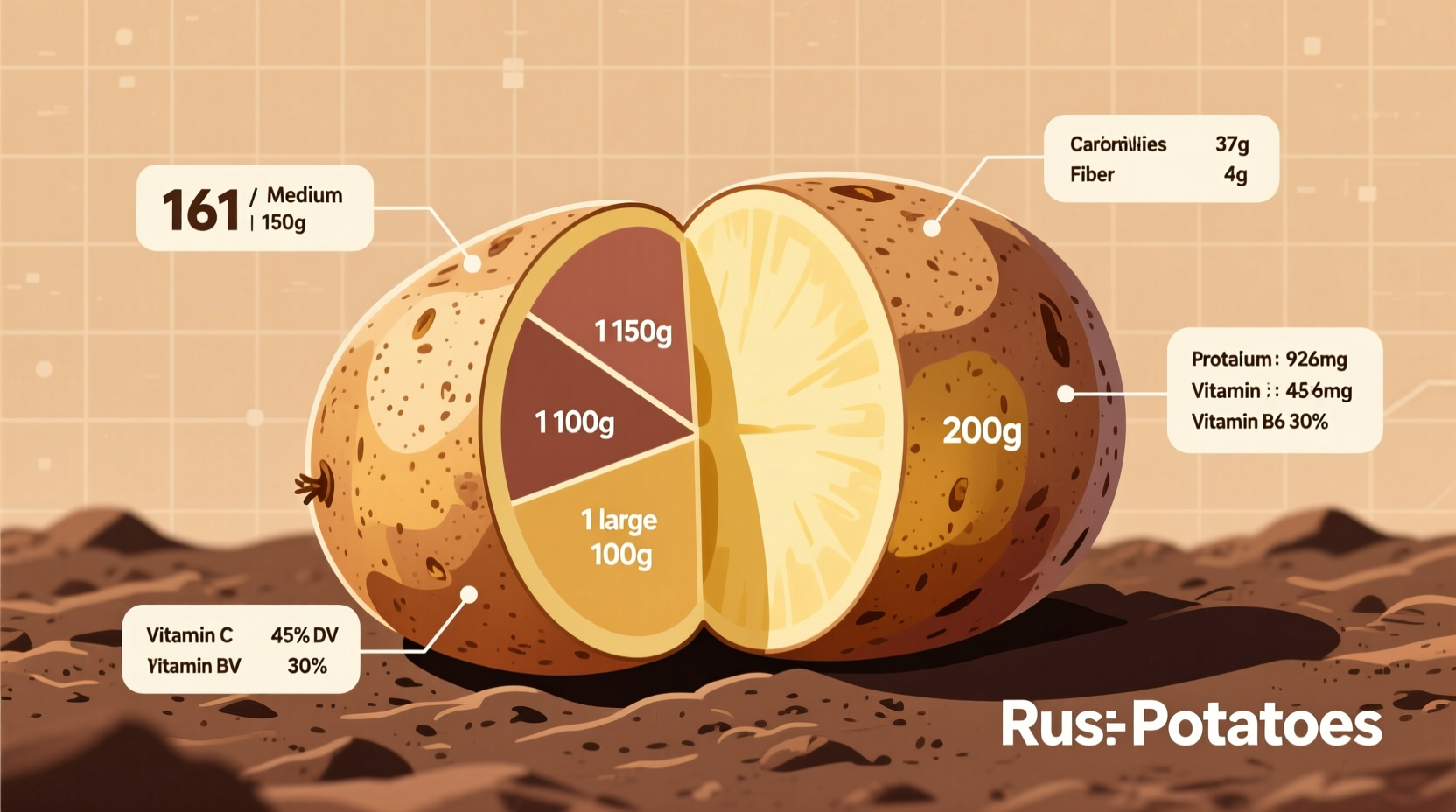
A medium russet potato (5.3" long) provides:
- Total weight: 173g
- Total carbohydrates: 37g
- Dietary fiber: 3.6g
- Net carbohydrates: 33.4g
For context, this represents approximately 11% of a 2,000-calorie diet's recommended daily carbohydrate intake. However, individual needs vary significantly based on activity level, health status, and dietary goals.
Maximizing Nutritional Benefits While Managing Carbs
When considering are russet potatoes high in carbohydrates, the answer is yes—but they also offer valuable nutrients. To optimize their nutritional profile:
- Leave the skin on: The skin contains nearly half the fiber content, reducing net carbs
- Pair with protein and healthy fats: Slows carbohydrate digestion and minimizes blood sugar spikes
- Choose appropriate portion sizes: A reasonable serving is 1/2 to 1 small potato (100-150g)
- Cool before eating: Increases resistant starch content by 10-15% as documented by the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition
Research from the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health indicates that when consumed as part of a balanced meal with adequate fiber, protein, and healthy fats, russet potatoes can fit within most dietary patterns—even for those monitoring carbohydrate intake.
Common Misconceptions About Potato Carbohydrates
Several myths persist about carbs in russet potato skin and overall potato nutrition:
- Myth: All carbohydrates in potatoes are "bad"
- Fact: Potatoes contain complex carbohydrates that provide sustained energy when properly prepared
- Myth: Potatoes have no nutritional value beyond carbohydrates
- Fact: Russet potatoes are excellent sources of potassium, vitamin C, and B vitamins
- Myth: People with diabetes should avoid potatoes completely
- Fact: When portion-controlled and properly prepared, potatoes can be included in diabetes meal plans
The American Diabetes Association confirms that starchy vegetables like russet potatoes can be part of a healthy diabetes eating plan when consumed in appropriate portions and prepared using methods that minimize blood sugar impact.
Putting Russet Potato Carbs in Context
When evaluating the role of russet potatoes in your diet, consider these practical guidelines:
- Active individuals can comfortably include one medium russet potato as part of a balanced meal
- Those managing blood sugar should limit portions to 100g (about 1/2 small potato) and pair with protein
- For weight management, focus on preparation methods—baked or boiled is preferable to fried
- Always include the skin for maximum fiber content and nutrient retention
Remember that glycemic index of baked russet potato varies significantly based on what you eat it with. Adding vinegar, lemon juice, or healthy fats can lower the overall glycemic impact by 20-30% according to studies in the European Journal of Clinical Nutrition.











 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4