Understanding the exact nutritional profile of sweet potatoes helps you make informed dietary choices whether you're managing weight, tracking macros, or simply eating healthier. This comprehensive guide delivers precise calorie information along with practical context you can actually use.
What Defines a "Medium" Sweet Potato?
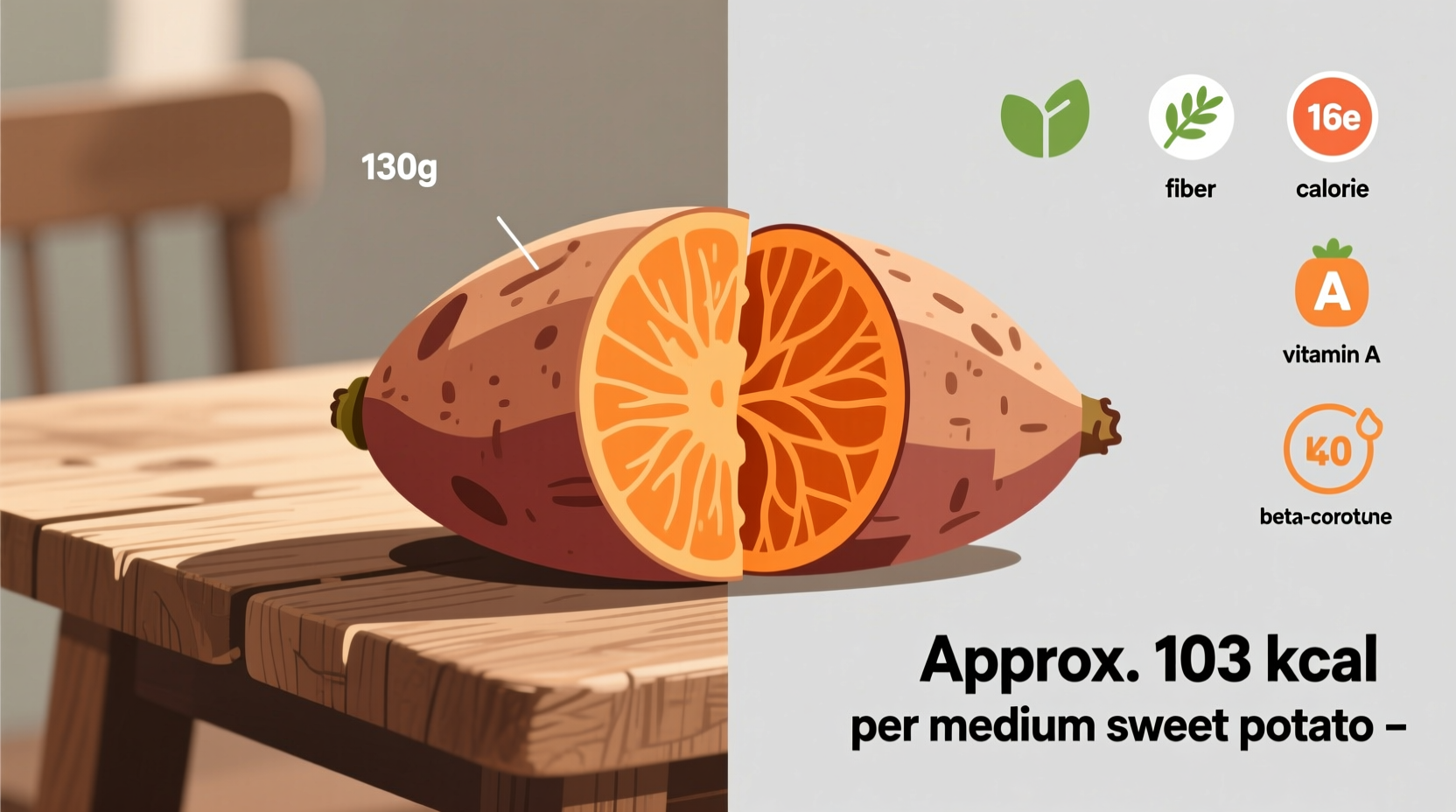
Before we discuss calories, it's crucial to understand what constitutes a "medium" sweet potato. According to the USDA's standardized measurements:
| Sweet Potato Size | Weight (grams) | Approximate Dimensions |
|---|---|---|
| Small | 90g | 4" long, 1.75" diameter |
| Medium | 130g | 5" long, 2" diameter |
| Large | 180g | 6" long, 2.5" diameter |
These standardized measurements come from the USDA's FoodData Central database, which nutrition professionals and researchers rely on for accurate food composition information (fdc.nal.usda.gov).
How Preparation Method Affects Calorie Content
The cooking method significantly impacts the final calorie count of your sweet potato. Here's how different preparation techniques change the nutritional profile:
- Baked with skin: 103 calories per medium potato (130g)
- Boiled: 90 calories per medium potato (130g)
- Steamed: 92 calories per medium potato (130g)
- Air-fried: 105 calories per medium potato (130g)
- Microwaved: 100 calories per medium potato (130g)
When you add toppings, the calorie count increases substantially:
- With 1 tbsp butter: +102 calories
- With 1 tbsp brown sugar: +52 calories
- With 2 tbsp marshmallows: +90 calories
These variations demonstrate important context boundaries for calorie counting—you must consider both the base vegetable and any additions when tracking your intake.
Nutritional Benefits Beyond Calories
While calorie count matters, sweet potatoes offer exceptional nutritional value that makes them worth including in your diet:
- Vitamin A: One medium sweet potato provides 438% of your daily requirement
- Fiber: 2.3g (9% of daily value) supporting digestive health
- Vitamin C: 22% of daily value for immune support
- Potassium: 12% of daily value for blood pressure regulation
- Manganese: 28% of daily value for bone health

Sweet Potato vs. Regular Potato: Nutritional Comparison
Understanding how sweet potatoes compare to regular white potatoes helps you make informed dietary choices:
| Nutrient | Medium Sweet Potato (130g) | Medium White Potato (150g) |
|---|---|---|
| Calories | 103 | 115 |
| Carbohydrates | 27g | 26g |
| Fiber | 2.3g | 2.1g |
| Vitamin A | 438% DV | 0% DV |
| Vitamin C | 22% DV | 28% DV |
| Glycemic Index | 44 (low) | 78 (high) |
This comparison, based on USDA FoodData Central measurements, shows why sweet potatoes often rank higher in nutritional quality despite similar calorie counts. The dramatically higher vitamin A content and lower glycemic index make sweet potatoes a better choice for most dietary plans.
Practical Tips for Incorporating Sweet Potatoes
Here's how to enjoy sweet potatoes while managing your calorie intake:
- Track your portions: Use a kitchen scale until you can accurately estimate medium-sized sweet potatoes
- Choose healthier cooking methods: Baking or boiling preserves nutrients better than frying
- Limit high-calorie toppings: Try Greek yogurt instead of butter, or cinnamon instead of sugar
- Pair with protein: Combine with chicken, fish, or beans to create balanced meals that keep you full longer
- Meal prep smartly: Cook multiple sweet potatoes at once and store in the refrigerator for quick healthy meals
When Sweet Potatoes Fit Your Dietary Goals
Sweet potatoes work well in various eating patterns:
- Weight management: Their high fiber content promotes satiety on relatively few calories
- Diabetes management: Lower glycemic index than white potatoes helps regulate blood sugar
- Vegan/vegetarian diets: Excellent source of complex carbohydrates and nutrients
- Athletic performance: Provides sustained energy release before workouts
Registered dietitians at the Mayo Clinic recommend including sweet potatoes as part of a balanced diet for most adults, noting their exceptional nutrient density relative to calorie content (mayoclinic.org).










 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4