Understanding the exact calorie content of everyday foods is essential for effective meal planning and nutrition management. Many people avoid potatoes due to misconceptions about their caloric value, but when you know precisely what a medium potato contributes to your daily intake, you can make informed dietary choices that support your health goals.
What Exactly Qualifies as a Medium Potato?
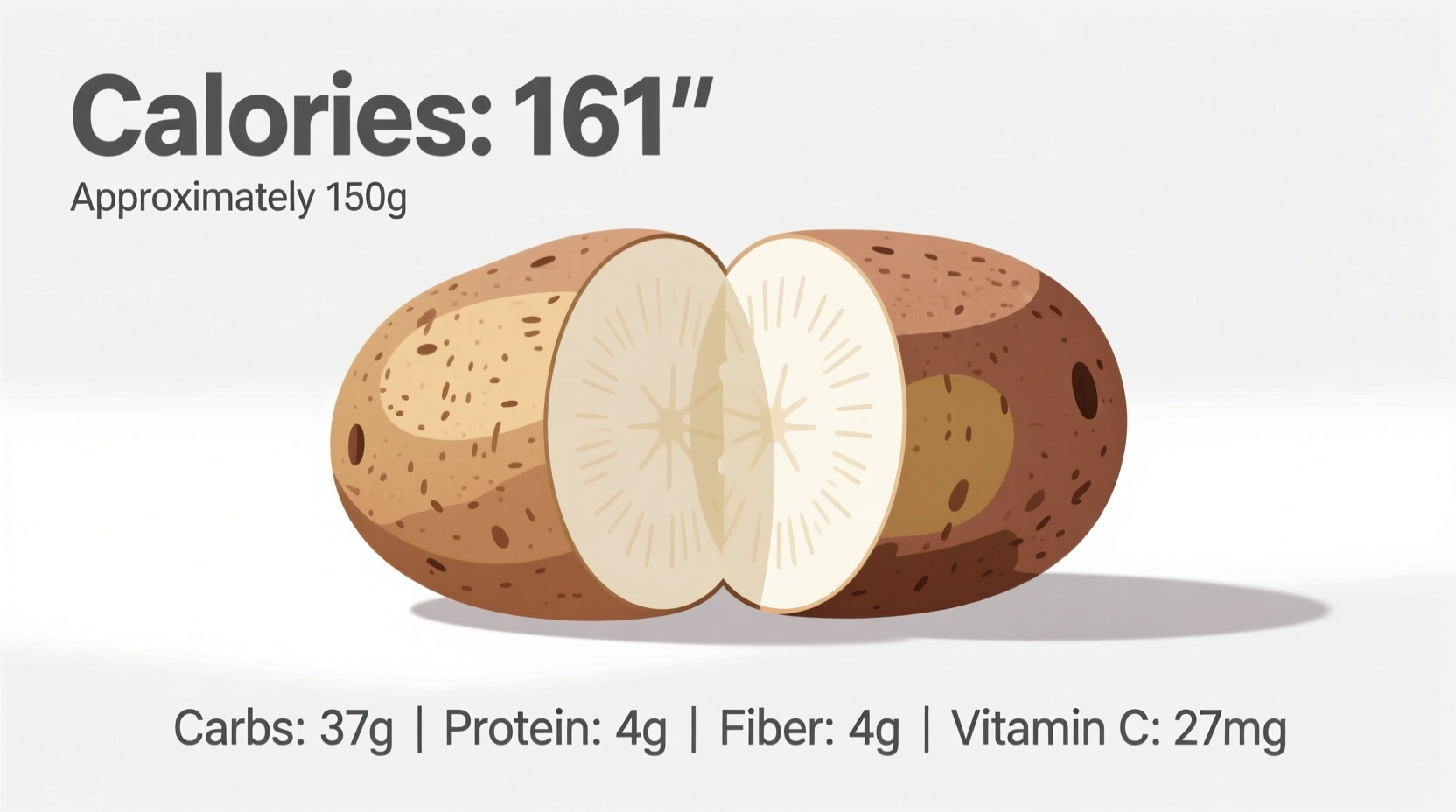
Before examining calorie content, it's crucial to understand what constitutes a "medium" potato. The USDA defines a medium potato as weighing approximately 5.3 ounces (150 grams) with skin. This standard measurement helps ensure consistency when tracking nutritional information.
| Size Classification | Weight (ounces) | Weight (grams) | Approximate Calories |
|---|---|---|---|
| Small | 4.0 | 113 | 85 |
| Medium | 5.3 | 150 | 110 |
| Large | 8.0 | 227 | 168 |
This standardized sizing helps eliminate confusion when following recipes or nutrition plans. Visualize a medium potato as roughly the size of a computer mouse or a small fist for quick identification at the grocery store or in your kitchen.
Nutritional Profile Beyond Calories
While calories provide energy measurement, the complete nutritional picture reveals why potatoes deserve a place in balanced diets. A medium potato with skin delivers:
- Carbohydrates: 26g (9% of daily value)
- Fiber: 2.5g (10% of daily value)
- Protein: 3g
- Vitamin C: 28% of daily value
- Potassium: 26% of daily value
- Vitamin B6: 27% of daily value
The skin contains nearly half of the potato's fiber and a significant portion of its nutrients, making it nutritionally advantageous to keep the skin on when possible. This fact often surprises people who automatically peel potatoes before cooking.

How Cooking Methods Impact Calorie Content
The preparation method significantly affects the final calorie count of your potato. While the base potato remains consistent, added ingredients and cooking techniques can dramatically alter its nutritional profile.
| Cooking Method | Calories (Medium Potato) | Additional Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Baked with skin | 110 | Retains maximum nutrients |
| Boiled with skin | 100 | Slight nutrient loss to water |
| Steamed | 105 | Minimal nutrient loss |
| Fried | 300+ | High in unhealthy fats |
| Air-fried | 130 | With minimal oil |
Historically, potatoes were primarily boiled or baked in their natural state. Modern cooking techniques have introduced higher-calorie preparation methods that significantly alter their nutritional value. The traditional European method of boiling potatoes with their skins on preserves more nutrients compared to peeling before cooking, a practice that has gained renewed attention among health-conscious cooks.
Practical Applications for Daily Nutrition
Understanding how a medium potato fits into your overall dietary needs transforms this humble vegetable from a potential concern to a valuable nutritional asset. For most adults following a 2,000-calorie diet, a medium potato represents approximately 5-6% of daily caloric needs while providing substantial nutrients.
When incorporating potatoes into meals, consider these practical strategies:
- Portion awareness: One medium potato makes an appropriate carbohydrate serving
- Healthy toppings: Replace butter with Greek yogurt or herb-infused olive oil
- Meal balancing: Pair with lean protein and non-starchy vegetables
- Timing matters: Consume earlier in the day for optimal energy utilization
Research from the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition indicates that when prepared without added fats, potatoes have a high satiety index, meaning they help you feel full longer than many other carbohydrate sources. This quality makes them particularly valuable for weight management when consumed in appropriate portions.
Contextual Considerations for Different Dietary Needs
While potatoes offer excellent nutrition, certain health conditions require modified approaches to their consumption. Understanding these context boundaries helps maximize benefits while minimizing potential concerns:
- Diabetes management: Pair potatoes with protein and healthy fats to moderate blood sugar response
- Weight loss: Focus on preparation methods that don't add significant calories
- Athletic performance: Potatoes provide excellent carbohydrate loading before endurance events
- Digestive health: The fiber content supports gut health, especially when skin is consumed
The glycemic index of potatoes varies significantly based on preparation method and what they're served with. Cooling cooked potatoes increases resistant starch content, which has additional digestive benefits. This scientific insight transforms how we view potato preparation for optimal health outcomes.
Common Misconceptions About Potato Calories
Several persistent myths surround potato nutrition that deserve clarification based on current research:
- Myth: Potatoes are high in empty calories
Reality: They provide significant vitamins, minerals, and fiber per calorie - Myth: All potato preparations have similar calorie counts
Reality: Cooking method dramatically affects final nutritional profile - Myth: Potatoes cause weight gain
Reality: When prepared healthily and portion-controlled, they support weight management
Recent studies published in the Journal of Nutrition demonstrate that potatoes consumed as part of a balanced diet don't negatively impact weight management when prepared without excessive added fats. The key lies in preparation method and overall dietary context rather than the potato itself.
Smart Potato Integration for Health-Conscious Eaters
Transform your approach to potatoes with these practical, research-backed strategies:
- Batch cooking: Prepare multiple potatoes at once for easy meal components throughout the week
- Cooling technique: Refrigerate cooked potatoes to increase resistant starch content by up to 50%
- Flavor enhancement: Use herbs, spices, and citrus instead of high-calorie toppings
- Meal timing: Consume potatoes earlier in the day for optimal energy utilization
Professional chefs like those at leading culinary institutions have rediscovered traditional preparation methods that maximize nutritional benefits while creating delicious dishes. By understanding the science behind potato nutrition, home cooks can make informed choices that support their health goals without sacrificing flavor or satisfaction.










 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4