Often misunderstood in modern diets, potatoes are nutritional powerhouses that have sustained civilizations for centuries. This versatile tuber offers science-backed health advantages that extend far beyond basic sustenance. Let's explore the evidence-based benefits that make potatoes a valuable addition to balanced eating patterns.
Nutritional Powerhouse Profile
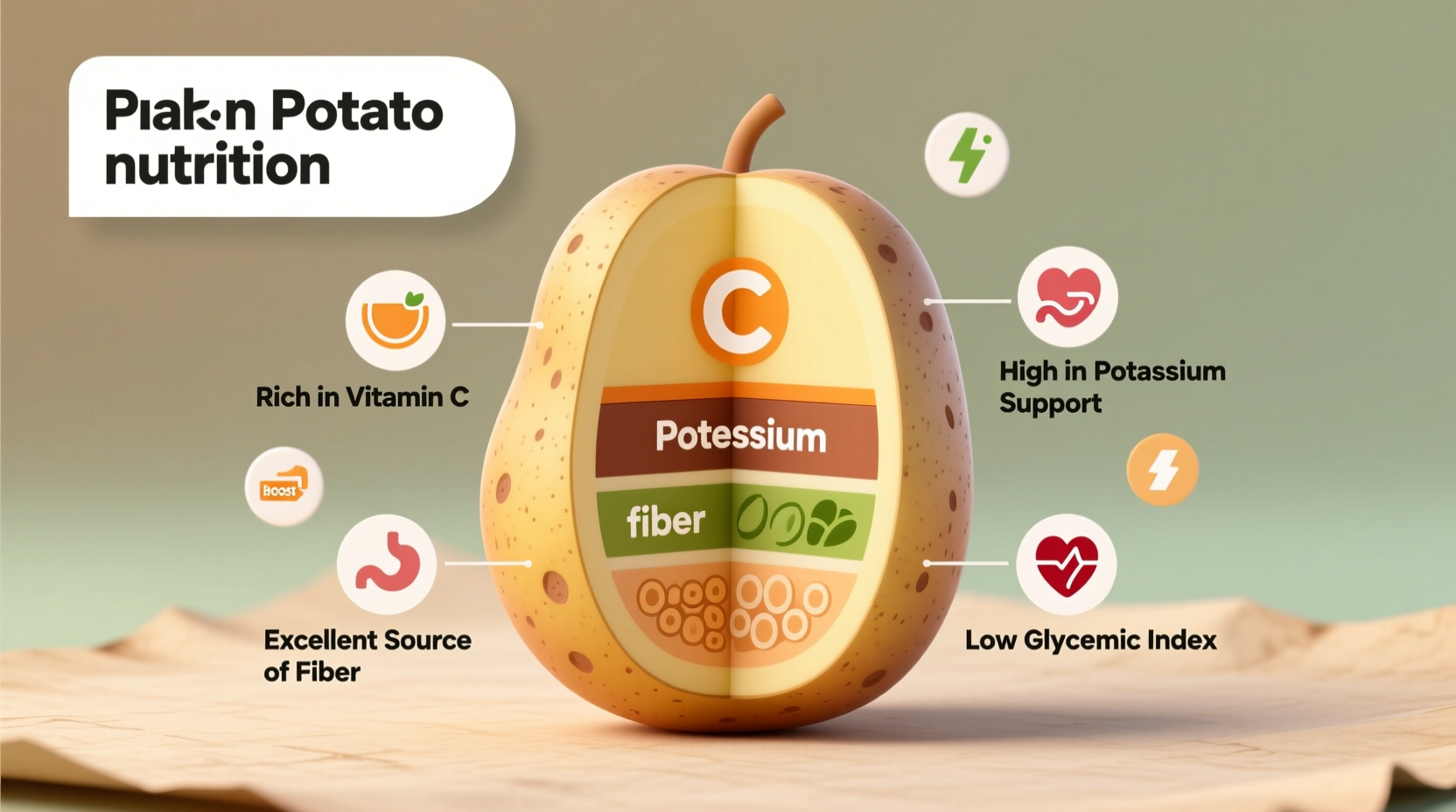
Contrary to popular belief, potatoes rank among the most nutrient-dense staple foods available. A single medium potato (150g) with skin delivers:
| Nutrient | Amount | Daily Value % | Key Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Potassium | 926mg | 26% | Blood pressure regulation |
| Vitamin C | 27mg | 30% | Immune support & collagen synthesis |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.4mg | 22% | Energy metabolism & brain function |
| Dietary Fiber | 3.6g | 14% | Digestive health & satiety |
| Manganese | 0.3mg | 13% | Bone health & metabolism |
Source: USDA FoodData Central (2023)
Science-Backed Health Advantages
Digestive Health Through Resistant Starch
Cooling cooked potatoes increases their resistant starch content by up to 300%, according to research published in the Journal of Nutrition. This specialized fiber feeds beneficial gut bacteria, producing butyrate—a short-chain fatty acid that strengthens the intestinal lining and reduces inflammation. Unlike refined grains, potatoes provide this gut-nourishing compound naturally.
Cardiovascular Support System
With more potassium than bananas (926mg vs 422mg per serving), potatoes help maintain healthy blood pressure levels. The American Heart Association recognizes potassium's role in counteracting sodium's effects. Additionally, the purple varieties contain anthocyanins—antioxidants shown in Circulation journal studies to improve endothelial function and reduce arterial stiffness.
Immune System Enhancement
One medium potato provides 30% of your daily vitamin C needs—more than half a lemon. This essential nutrient stimulates white blood cell production and acts as a powerful antioxidant. During colder months, incorporating potatoes into your diet provides year-round immune support without seasonal limitations.
Energy Metabolism Optimization
The B-vitamin complex in potatoes—particularly B6 and folate—plays crucial roles in converting food into usable energy. These vitamins facilitate over 100 enzymatic reactions involved in metabolism. Athletes and active individuals benefit from potatoes' sustained energy release without the blood sugar spikes associated with refined carbohydrates.
Potato Preparation Methods That Maximize Benefits
How you prepare potatoes significantly impacts their nutritional profile. Research from the University of Maine demonstrates these preparation effects:
- Boiling with skin intact: Preserves 90% of vitamin C compared to 75% when peeled
- Cooling after cooking: Increases resistant starch content by 300% for enhanced gut benefits
- Baking instead of frying: Eliminates unnecessary fats while maintaining nutrient density
- Combining with healthy fats: Olive oil or avocado improves absorption of fat-soluble antioxidants

Contextual Considerations and Limitations
While potatoes offer numerous benefits, certain preparation methods and consumption patterns affect their health impact:
- Potatoes become high glycemic index foods when peeled and processed into mashed form or fries
- Individuals with diabetes should pair potatoes with protein and fiber to moderate blood sugar response
- The nutrient density decreases significantly when potatoes are deep-fried or covered in high-fat toppings
- Green spots on potatoes indicate solanine presence, which should be removed before consumption
Debunking Common Potato Myths
Several misconceptions persist about potatoes that contradict scientific evidence:
Myth: Potatoes lack nutritional value compared to other vegetables
Reality: Potatoes contain more potassium than bananas and more vitamin C than tomatoes by weight, according to USDA comparative analysis.
Myth: All carbohydrates in potatoes convert directly to sugar
Reality: The fiber and resistant starch in potatoes slow glucose absorption, providing sustained energy release when prepared properly.
Myth: Sweet potatoes are always nutritionally superior to white potatoes
Reality: While sweet potatoes contain more vitamin A, white potatoes provide significantly more potassium and comparable vitamin C levels.
Practical Integration Strategies
Incorporate potatoes' benefits into your daily routine with these evidence-based approaches:
- Prepare potato salads with cooled, skin-on potatoes for maximum resistant starch content
- Combine roasted potatoes with cruciferous vegetables for complementary nutrient profiles
- Use mashed potatoes as a base for vegetable-loaded shepherd's pie toppings
- Substitute half the grains in grain bowls with diced roasted potatoes for added potassium
- Create nutrient-dense breakfast hashes with potatoes, leafy greens, and eggs
Remember that variety remains key—different potato varieties offer unique benefits. Purple potatoes provide anthocyanins, yellow varieties contain carotenoids, and white potatoes deliver exceptional potassium levels. Rotating through varieties ensures comprehensive nutrient intake.
Scientific Consensus Timeline
Nutritional understanding of potatoes has evolved significantly:
- 1980s: Potatoes primarily viewed as simple carbohydrate sources
- 1990s: Recognition of potassium content for cardiovascular health
- 2000s: Discovery of resistant starch benefits for gut health
- 2010s: Identification of antioxidant compounds in colored varieties
- 2020s: Integration of potatoes into dietary guidelines as nutrient-dense options
Current research from institutions like the USDA Agricultural Research Service continues to uncover additional health benefits, particularly regarding gut microbiome support and metabolic health.
Conclusion: Potatoes as Nutritional Allies
When prepared thoughtfully and consumed as part of balanced eating patterns, potatoes deliver exceptional nutritional benefits that support multiple aspects of health. Their combination of potassium, vitamin C, resistant starch, and B vitamins makes them valuable dietary components for people of all ages. By understanding proper preparation methods and portion considerations, you can harness potatoes' full nutritional potential while enjoying their versatility and satisfying texture.










 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4